-
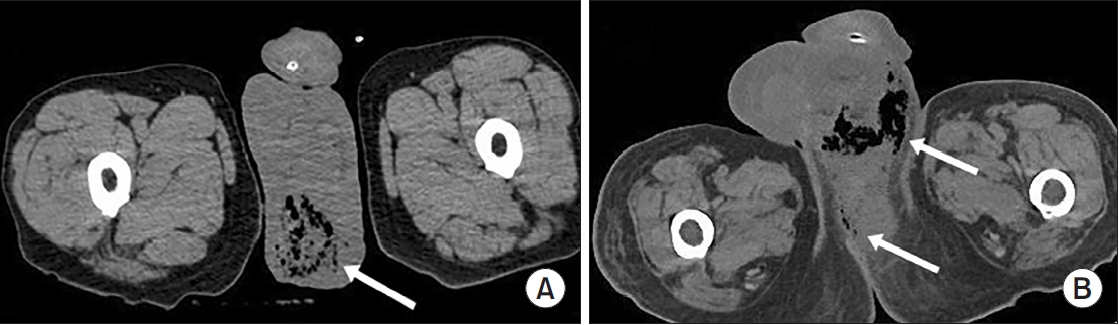
Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Fournier Gangrene: A 15-Years Multicenter Retrospective Study in Korea
-
Seung-Kwon Choi, Sin Woo Lee, Hyung-Lae Lee, Jeong Woo Lee, Jung Sik Huh, Yeonjoo Kim, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):159-166. Published online December 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550036018
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose
Fournier gangrene (FG) is a rare but life-threatening necrotizing infection requiring prompt recognition and intervention. This multicenter study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics, treatment outcomes including mortality, and risk factors associated with death among patients with FG over the past 15 years in Korea.
Materials and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 84 patients diagnosed with FG between 2008 and 2022 across 7 hospitals. Demographics, comorbidities, laboratory findings, and clinical outcomes were analyzed. Mortality-related risk factors were assessed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Results
The mean age was 58.1±15.9 years, and 95.2% of patients were male. Diabetes mellitus (42.9%) and hypertension (36.9%) were the most prevalent comorbidities. Sepsis developed in 38.1% of patients, and the overall mortality rate was 14.3%. In univariate analysis, age ≥70 years, low body mass index, diabetes mellitus, low hemoglobin, low hematocrit, high respiratory rate, and Fournier gangrene severity index (FGSI) ≥9 were significantly associated with mortality. After data correction and multivariate adjustment, diabetes mellitus (odds ratio [OR], 39.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.39–656.32; p=0.010) and respiratory rate (OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.09–1.91; p=0.011) were identified as independent predictors of mortality. FGSI≥9 demonstrated borderline association with mortality (p=0.08), indicating its potential clinical relevance.
Conclusions
In this multicenter Korean cohort, the mortality rate of FG remained substantial at 14.3%. Diabetes mellitus and elevated respiratory rate were independent predictors of mortality, while FGSI≥9 demonstrated a borderline yet clinically meaningful association, suggesting its role as a useful severity indicator in early risk stratification.
-
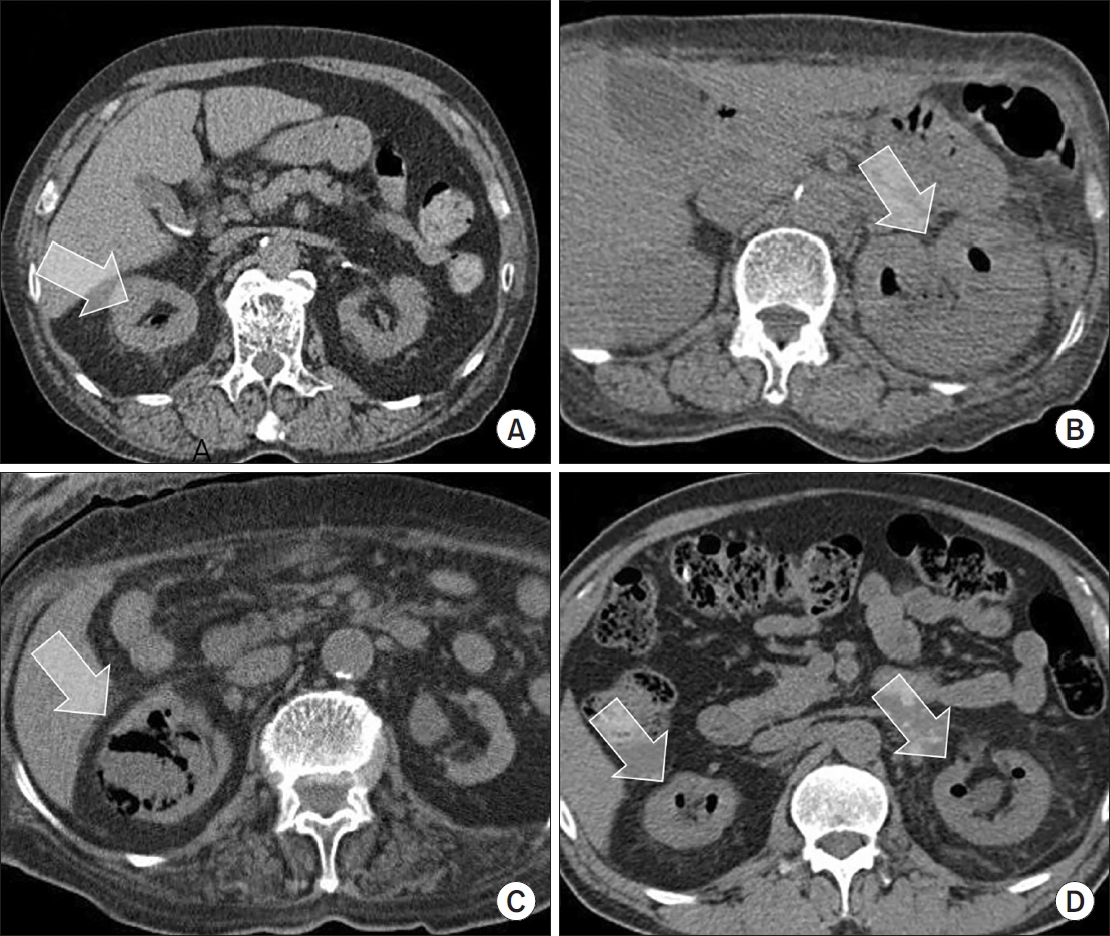
Mortality and Risk Factors for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
-
Seung-Kwon Choi, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):34-41. Published online April 30, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550006003
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a life-threatening disease requiring immediate treatment. This multicenter retrospective cohort study aimed to analyze the mortality rate and risk factors associated with EPN.
Materials and Methods: Between January 2011 and February 2021, 217 patients diagnosed with EPN via computed tomography who visited 14 teaching hospitals were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical data, including age, sex, comorbidities, Huang and Tseng classification, hydronephrosis, acute kidney injury, blood and urine tests, surgical interventions, percutaneous drainage, and conservative treatments, were compared between the survival and death groups. Risk factors for mortality due to EPN were analyzed using univariate and multivariate methods.
Results
The mean age of survivors and deceased patients was 67.8 and 69.0 years, respectively (p=0.136). The sex distribution (male/female) was 48/146 and 8/15, respectively (p=0.298). Of the 217 patients, 23 died, resulting in a mortality rate of 10.6%. In univariate analysis, the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.004), platelet count (p=0.005), and acute kidney injury (p=0.007) were significantly associated with mortality from EPN. In multivariate analysis, only the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.029) was identified as a risk factor. Mortality rates according to the Huang and Tseng classification were as follows: class I (5.88%), class II (7.50%), class IIIa (14.28%), class IIIb (25.00%), and class IV (23.07%).
Conclusions
EPN is associated with a high mortality rate. Among various clinical factors, the Huang and Tseng classification was the most significant indicator for predicting mortality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
-
3,371
View
-
60
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Korean Multicenter Study of Infectious Complications after Transurethral Prostate Surgery in Patients with Preoperative Sterile Urine
-
Seong Hyeon Yu, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Jae Duck Choi, Koo Han Yoo, Jeong Woo Lee, Dong Hoon Koh, Sangrak Bae, Seung Ok Yang, Joongwon Choi, Seung Ki Min, Hoon Choi
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(3):81-88. Published online December 31, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.3.81
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis and determine the risk factors of infectious complications after transurethral surgery of the prostate.
Materials and Methods: Seven hundred and seventy-two patients who underwent transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HOLEP) were reviewed. Of these, this study enrolled 643 patients without bacteriuria who had not received antibiotics for urinary tract infections for two weeks before surgery. The patients were divided into two groups according to the duration of the antibiotics (Group 1: less than one day, n=396 vs. Group 2: more than one day, n=247).
Results: The overall incidence of postoperative infectious complications in 643 patients was 5.0% (32/643). When postoperative infectious complications were compared according to the duration of the antibiotics (Group 1 vs. Group 2), the infectious complications rates were 5.6% (22/396) vs. 4.0% (10/247), respectively (p=0.393). When postoperative infectious complications were compared according to the duration of antibiotics (Group 1 vs. Group 2) in the TURP and HOLEP groups, the infectious complications rates were 6.3% (12/192) vs. 1.0% (1/103) (p=0.035) and 4.9% (10/203) vs. 6.0% (8/134) (p=0.677), respectively. The duration of Foley catheterization was independently associated with infectious complications (p=0.003).
Conclusions: The results showed that prolonged postoperative catheterization affects postoperative infectious complications associated with transurethral prostate surgery. Although antibiotics administered for less than one day are effective for antibiotic prophylaxis of transurethral prostate surgery, a longer antibiotic therapy is recommended for TURP.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of Postoperative Urinary Tract Infection and Sepsis Rates After Adding Cystolitholapaxy to HoLEP:
A Retrospective Analysis
Federico Rovegno, Rajiv Pillai, Zafar Maan, Soumendra Datta, Omar Nasir, Gerald Rix
International Journal of Clinical Urology.2026; 10(1): 1. CrossRef
-
3,723
View
-
24
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Changes of Causative Organism and Antimicrobial Resistance in Urinary Tract Infections After the COVID-19
-
Young Ho Choi, Jong Hyun Tae, Mi-Kyung Lee, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(2):42-49. Published online August 31, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.2.42
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, several studies reported changes in the distribution of microorganisms that cause major legal, respiratory, and gastrointestinal infectious diseases and increases in the antimicrobial resistance rates in Korea. On the other hand, there has been little domestic research on the causative organism of urinary tract infection (UTI). This study investigated the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the distribution of causative organisms and the antimicrobial resistance rate in UTI.
Materials and Methods: This study analyzed 17,201 urine cultures retrospectively from patients who visited Chung-Ang University Hospital from January 2018 to December 2021. Tests were then conducted to determine if there was a significant difference between the data for the eight quarters of the pre-COVID-19 period (January 2018 to December 2019) and the data for the eight quarters post-COVID-19 period (January 2020 to December 2021).
Results: Escherichia coli was the most common causative organism in all periods, but it decreased in the post-COVID-19 period. Enterococcus faecalis increased in the post-COVID-19 period. The ciprofloxacin resistance rate of E. coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae increased, but the ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin resistance rate of E. faecalis decreased.
Conclusions: There was little difference in the causative organism distribution of UTI and antimicrobial resistance rates before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. On the other hand, changes in some causative organisms are identified. Nevertheless, because this study was limited to a single medical institute, data from a broader spectrum of bacterial species collected from multiple institutions will be needed to obtain definitive results.
-
Characteristics and Treatment Trends for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A 10-Year Multicenter Retrospective Study
-
Seung-Kwon Choi, Koo Han Yoo, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(2):49-54. Published online August 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.2.49
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: This study examined the characteristics, current treatment trends, and outcomes of patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) in Korea.
Materials andMethods: Two hundred and seventeen patients diagnosed with EPN were evaluated using abdominal computed tomography in 2011-2021 at 15 institutes in Korea. The patients’ demographic and clinical characteristics, treatment modalities, and treatment outcomes were analyzed. The total study period was divided arbitrarily into groups A (2011-2014), B (2015-2017), and C (2018-2021) to analyze the trends in the EPN treatment.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 65.1 years; there were more female patients (74.2%) than male patients. The overall mortality rate was 10.6%. Ninety-five (43.8%), 98 (45.2%), and 24 (11.0%) patients were treated with medical, minimally invasive, and surgical management, respectively; the corresponding mortality rates were 13.7%, 6.1%, and 16.7%. There was no significant change in the proportion of patients treated with medical management over time (group A=46.5%, group B=47.0%, and group C=38.8%). The proportion of patients treated with minimally invasive management gradually increased over time (group A=35.2%; group B=43.9%; group C=55.0%), while those who underwent surgical management decreased gradually over time (group A=18.3%, group B=9.1%, and group C=6.3%). No differences in mortality rates were observed between the groups.
Conclusions: EPN with medical and minimally invasive management had a relatively high treatment success rate, which increased gradually, while surgical management decreased gradually over time in Korea. The mortality rate was relatively lower than that reported in studies published before the 2010s.
-
Systematic Literature Review of the Urological Field and Considerations in COVID-19
-
Joongwon Choi, Hyun Soo Ryoo, Jae Hyun Ryu, Yun Beom Kim, Seung Ok Yang, Jeong Kee Lee, Tae Young Jung, Jung Hoon Kim, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(1):1-7. Published online April 30, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.1.1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was declared a worldwide pandemic in March 2020 after originating in China. Widespread uncertainty resulting from the pandemic has revolutionized urology practice worldwide, similar to that observed in other fields. The urological manifestations of COVID-19 were investigated by performing a literature search using a combination of keywords related to COVID-19 and urology. To date, COVID-19 has not been associated with any lower urinary tract symptoms, and there is no level 1 evidence that associates it with urinary malignancy and urolithiasis. Viral RNA has been detected in urine (5.74%), but there is no evidence of actual infection via urine. COVID-19 has transformed the standard urological practice into crisis-based care and has changed the medical and surgical priorities dramatically in the field. Most hospitals have established quarantine guidelines for each hospital, and procedures must be performed according to the present circumstances. Furthermore, in the absence of high-level evidence, specific efforts are needed to minimize the risk of COVID-19 infections during care.
-
Efficacy and Tolerability of Solifenacin Fumarate with Overactive Bladder Patients: A Multicenter Observational Study
-
Jae Hun Shim, Se Young Choi, Joon Hee Gook, Yong-June Kim, Woo Heon Cha, Dae Hee Kim, Kyeong Hee Kim, Young Woong Park, Jin Mo Um, Il Sung Lim, Kyung Keun Seo, Kyu Seon Cho, Young Jae Lee, Mi-Kyung Lee, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(1):8-15. Published online April 30, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.1.8
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: Overactive bladder (OAB) is characterized by a series of highly prevalent symptoms among older adults. This study used the Overactive Bladder Symptom Score (OABSS) and Patient Perception of Bladder Condition (PPBC) tools to evaluate the efficacy and stability of solifenacin fumarate in the treatment of OAB.
Materials and Methods: This was a prospective, multicenter, single-arm, 12-week study that enrolled 163 OAB patients. The patients received 5 mg/day of solifenacin fumarate. The changes in the OABSS, symptoms, and PPBC scores were evaluated at 0, 4, and 12 weeks. Subgroup analysis of the OABSS and PPBC scores based on sex, diabetes mellitus (DM) status, and body mass index (BMI) were also evaluated.
Results: At the baseline (week 0), the mean OABSS for all patients was 8.45±2.38 (p=0.199). Subsequently, the mean OABSS declined to 5.41±2.69 (p=0.255) at four weeks and 4.21±2.61 (p=0.240) at 12 weeks. The OABSS subscore and PPBC score decreased significantly during the study (p<0.01). After cases were stratified according to sex, DM status, and BMI, the mean OABSS (mean and subscore) and PPBC score at four and 12 weeks were also improved significantly relative to the baseline scores (both p<0.05). The overall incidence of adverse events was 7.36% (12 cases), and three patients (1.82%) permanently discontinued solifenacin fumarate because of the adverse events.
Conclusions: Solifenacin fumarate is a safe and effective treatment alternative for relieving OAB symptoms, considering the balance between the efficacy, patientsʼ well-being, and tolerability.
-
Comparison of Monomicrobial versus Polymicrobial Candiduria: Time to Awareness of Candiduria
-
Hyunji Kim, Mi-Kyung Lee, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2019;14(1):20-25. Published online April 30, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2019.14.1.20
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose: Candiduria, which is the presence of Candida species in urine, is becoming increasingly common in hospital settings. These normal commensals in humans are often associated with the presence of other microorganisms. In this study, patients presenting with monomicrobial and polymicrobial candiduria were compared.
Materials and Methods: A retrospective study was performed on the demographic, clinical, and laboratory data of 185 patients presenting with candiduria between July 2014 and June 2015 at Chung-Ang University Hospital. The threshold for a positive Candida species urine culture was set to 103 CFU/ml. Data on the following were evaluated: distribution of Candida species; patient age and sex; length of hospital stay; presence of diabetes mellitus (DM), chronic kidney disease (CKD), a urinary catheter, and fever; antibiotic administration; urinalysis; complete blood cells; and C-reactive protein.
Results: Monomicrobial candiduria was more common (128/185, 69.2%) than polymicrobial candiduria (57/185, 30.8%). The most prevalent species was Candida albicans (monomicrobial vs. polymicrobial candiduria, 61.7% vs. 54.4%), followed in order by Candida tropicalis (18.8% vs. 24.6%), and Candida glabrata (14.8% vs. 12.3%), with no significant difference between the two groups. Significant differences in the length of stay, underlying DM or CKD, accompanying symptoms, and urine white blood cells (WBC) and bacterial counts were observed between the two groups (p<0.05).
Conclusions: The length of stay, underlying DM or CKD, accompanying symptoms, and urine WBC and bacterial counts were more associated with polymicrobial candiduria. The early detection and treatment of candiduria will become increasingly important as the Korean population ages.
-
Association between an Interleukin 4 Gene Polymorphism, rs2243268, and Urogenital Tuberculosis
-
Bongsuk Shim, Sang Don Lee, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Seung Il Jung, Won Yeol Cho, Gilho Lee
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2018;13(2):35-39. Published online August 31, 2018
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose: Urogenital tuberculosis (UGT) is rarely reported in developed countries. This study evaluated the genetic susceptibility of Korean patients to UGT.
Materials and Methods: A total of 35 UGT patients who were confirmed pathologically, 44 intrapulmonary tuberculosis (IPT) patients who were confirmed radiologically, and 102 controls over a 6 year period were enrolled in this study. The region of rs2243268 in interleukin-4 (IL-4) gene was amplified from whole blood samples, and the DNA sequences were read using the Sanger method.
Results: Twenty women and 15 men were diagnosed with UGT. The occurrence of the CC, AC, and AA genotypes of rs2243268 were 26 (74.3%), 8 (22.9%), and 1 (2.9%), respectively, in UGT; 28 (63.6%), 15 (34.1%), and 1 (2.3%), respectively, in IPT; and 51 (50.0%), 45 (44.1%), and 6 (5.9%), respectively, in the control groups (p=0.115). The bivariate data of CC and AC/AA were 74.3% and 25.7% in UGT, 63.6% and 36.4% in IPT, and 50.0% and 50.0% in the control groups, respectively (p=0.029). The UGT was significantly different from the control group among the three genotypes (p=0.038, Fisher’s exact test) and bivariate genotypes (p=0.017, Fisher’s exact test). In addition, people carrying the CC genotype had a higher risk of UGT (odds ratios, 2.889; 95% confidence intervals, 1.233-6.770; p=0.015).
Conclusions: A single nucleotide polymorphism in the IL-4 gene, rs2243268, is associated with the development of clinical tuberculosis. The CC type of rs2243268 increases the risk of UGT significantly compared to the CA/AA type.
-
The Antibiotic Susceptibility of Escherichia coli from Community-Acquired Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection: A Focused on Fosfomycin
-
Hyun-Sop Choe, Seung-Ju Lee, In Ho Chang, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Hong Chung, Jae Min Chung, Sang Don Lee, Jae Hung Jung, Ki Ho Kim, Seung Ki Min, Yong Gil Na, Hana Yoon, Ho Song Yu, Mi-Kyung Lee, Sun-Ju Lee
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(2):77-81. Published online August 31, 2017
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose: To assess the antibiotic susceptibility of Escherichia coli from community-acquired uncomplicated urinary tract infection (UTI).
Materials and Methods: Between August and December of 2015, confirmed cases of E. coli as a pathogen of community-acquired uncomplicated UTI were collected and assessed for antibiotic susceptibility in 10 designated hospitals. Additional fosfomycin susceptibility test was performed by a central laboratory using the disk diffusion method.
Results: A total of 347 E. coli isolates were collected from urine samples of community-acquired uncomplicated UTIs patients. The susceptibility rates of antibiotics were as follows: amikacin 100.0% (347), imipenem 100.0% (347), ciprofloxacin 57.1% (198), cefotaxime 74.9% (260), ampicillin 30.0% (104), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole 66.9% (232), and fosfomycin 98.0% (340). All fosfomycin-resistant E. coli isolates were extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing. In 85 cases of ESBL-producing E. coli, the fosfomycin susceptibility rate was 91.8% (78/85).
Conclusions: Fosfomycin may be a useful option for the treatment of community-acquired uncomplicated UTIs. Further studies evaluating the role of fosfomycin in the treatment of UTIs and its clinical efficacy are necessary.
-
Infectious Complications after Prostate Biopsy: A Prospective Multicenter Prostate Biopsy Study
-
Eu Chang Hwang, Ho Song Yu, Seung Il Jung, Dong Deuk Kwon, Sun Ju Lee, Tae-Hyoung Kim, In Ho Chang, Hana Yoon, Bongsuk Shim, Kwang Hyun Kim, Donghyun Lee, Jung-Sik Huh, Dong Hoon Lim, Won Jin Jo, Seung Ki Min, Gilho Lee, Ki Ho Kim, Tae Hwan Kim, Seo Yeon Lee, Seung Ok Yang, Jae Min Chung, Sang Don Lee, Chang Hee Han, Sang Rak Bae, Hyun Sop Choe, Seung-Ju Lee, Hong Chung, Yong Gil Na, Seung Woo Yang, Sung Woon Park, Young Ho Kim, Tae Hyo Kim, Won Yeol Cho, June Hyun Han, Yong-Hyun Cho, U-Syn Ha, Heung Jae Park, The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation (KAUTII)
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2016;11(1):17-24. Published online April 30, 2016
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose: Recent studies have highlighted an increasing trend of infectious complications due to fluoroquinolone-resistant organisms among men undergoing transrectal prostate biopsy. This study evaluated the current incidence of infective complications after trans-rectal prostate biopsy for identification of risk factors in Korean men who received fluoroquinolone prophylaxis.
Materials and Methods: A prospective, multicenter study was conducted in Korea from January to December 2015. Prostate biopsies performed with fluoroquinolone prophylaxis during 3 months in each center were included. A pre-biopsy questionnaire was used for identification of patient characteristics. Clinical variables including underlying disease, antibiotic prophylaxis, enema, povidoneiodine cleansing of the rectum, and infectious complications were evaluated. The primary outcome was the post-biopsy infection rate after fluoroquinolone prophylaxis. Univariable and multivariable analyses were used for identification of risk factors for infectious complications.
Results: The study included 827 patients, of whom 93 patients (11.2%) reported receiving antibiotics in the previous 6 months and 2.5% had a history of prostatitis. The infectious complication rate was 2.2%. Post-biopsy sepsis was reported in 2 patients (0.2%). In multivariable analysis predictors of post-biopsy sepsis included person performing biopsy (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 4.05; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31-12.5; p=0.015) and operation history within 6 months (adjusted OR, 5.65; 95% CI, 1.74-18.2; p=0.004).
Conclusions: The post-prostate biopsy infectious complication rate in this study was 2.2%. Person performing biopsy (non-urologists) and recent operation history were independent risk factors for infectious complications after trans-rectal prostate biopsy.
-
Management of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Positive Gram-Negative Bacterial Urologic Infections
-
Yong Kwan Lim, Mi-Kyung Lee, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2015;10(2):84-91. Published online October 31, 2015
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) are enzymes that confer increased resistance to commonly used antibiotics. The prevalence rates of ESBL producing bacteria are increasing, and the associated increase in morbidity and mortality is becoming a public health concern. ESBL producers are emerging as an important cause of urinary tract infection (UTI) and empirical therapy should therefore be carefully selected for patients with UTI. Fosfomycin or nitrofurantoin would be an appropriate choice for empirical therapy of uncomplicated UTI. Ertapenem or cefepime might be recommended for initial empirical therapy patients suspected of having complicated UTI.
-
Profiles of Yeast Isolated from Urinary Tracts with and without Catheter during 2011-2013
-
Jae Hyung Ryu, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Oh Joo Kweon, Mi-Kyung Lee
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2014;9(2):93-98. Published online October 31, 2014
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
Indwelling urinary catheter is considered the most important risk factor for healthcare-associated urinary tract infection (UTI). The aim of the current study was to compare the prevalence of species distribution and susceptibilities of antifungals against clinical isolates of yeasts from funguria with and without urinary catheter. Materials and Methods: We analyzed 45,839 urine specimens collected from patients between 2011 and 2013. Species identification and antifungal susceptibility test to amphotericin B, fluconazole, voriconazole, and flucytosine were performed using the VITEK 2 system (Biomérieux Inc.). Results: A total of 1,048 (2.29%) urine specimens were yeast culture positive. The most frequent species was Candida albicans (49.0%), followed by C. tropicalis (18.6%), C. glabrata (12.2%), and Trichosporon asahii (7.2%). C. tropicalis was isolated more frequently in catheterized urine than in voided urine (p<0.05). For C. albicans and C. glabrata, frequencies of non-susceptible to fluconazole or voriconazole were higher in catheterized urine than in voided urine. Conclusions: The results of this study suggest the possibility that urinary catheter may influence species distribution of yeast and antifungal susceptibilities. Further investigation is warranted to improve infection control strategies for healthcare- associated UTI.
-
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis for Genitourinary Prosthetics
-
Jung Hoon Kim, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2011;6(1):1-7. Published online April 30, 2011
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Infection is the most troublesome complication in urologic prosthetic surgery. Commonly implanted devices include penile prosthesis, artificial urinary sphincter, and artificial testes. Explantation of the prosthetic device has been standard treatment for infection. This supports the need for prophylactic antibiotic therapy, with the goal of preventing bacterial seeding. Antibiotic regimens should be effective against bacteria, particularly Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcusaureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
-
Species Distribution and Antifungal Susceptibilities of Yeast Isolated from Catheterized Urine Specimen
-
Tae-Hyoung Kim, Jong-Yeon Lee, Jae-Dong Chung, Sang-Hyup Lee, Mi-Kyung Lee
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2011;6(1):73-79. Published online April 30, 2011
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- "Purpose: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of urinary catheter on species distribution and susceptibilities of antifungals against clinical isolates of yeasts from catheter-associated urinary tract infection (CAUTI). Materials and Methods: A total 281 yeast isolates from catheterized urine in a medical and surgical ward were collected. Species identification and antifungal susceptibulity test to amphotericin B, fluconazole, voriconazole and flucytosine were performed by VITEK 2 system (bioM?rieux Inc. Hazelwood, MO, USA). Results: The most frequent species was Candida tropicalis (48.8%), followed by C. albicans (24.6%), C. glabrata (15.7%) and Trichosporon asahii (5.0%). C. tropicalis and T. asahii were more frequently isolated in a surgical ward than medical ward (p<0.05). Decreased susceptibilities to amphotericin B were observed in C. albicans and T. asahii. All isolates except C. glabrata and C. krusei were susceptible to fluconazole and voriconazole. Conclusions: The results of this study suggest the possibility that urinary catheter may lead to influence on species distribution of yeast of CAUTI. There is an need for continuous surveillance of CAUTI by yeast for the control of CAUTI."
|