Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Urogenit Tract Infect > Volume 20(1); 2025 > Article
- Original Article Mortality and Risk Factors for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
-
Seung-Kwon Choi1
 , Jeong Woo Lee2
, Jeong Woo Lee2 , Seung Il Jung3
, Seung Il Jung3 , Eu Chang Hwang3
, Eu Chang Hwang3 , Joongwon Choi4
, Joongwon Choi4 , Woong Bin Kim5
, Woong Bin Kim5 , Jung Sik Huh6
, Jung Sik Huh6 , Jin Bong Choi7
, Jin Bong Choi7 , Yeonjoo Kim8
, Yeonjoo Kim8 , Jae Min Chung9
, Jae Min Chung9 , Ju-Hyun Shin10
, Ju-Hyun Shin10 , Jae Hung Jung11
, Jae Hung Jung11 , Hong Chung11
, Hong Chung11 , Sangrak Bae12
, Sangrak Bae12 , Tae-Hyoung Kim13
, Tae-Hyoung Kim13
-
Urogenital Tract Infection 2025;20(1):34-41.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550006003
Published online: April 30, 2025
1Department of Urology, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Urology, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
3Department of Urology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea
4Department of Urology, Chung-Ang University Gwangmyeong Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Gwangmyeong, Korea
5Department of Urology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
6Department of Urology, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
7Department of Urology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
8Department of Urology, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea
9Department of Urology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
10Department of Urology, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
11Department of Urology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
12Department of Urology, Uijeongbu St. Mary’ Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea
13Department of Urology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
-
Corresponding author: Seung-Kwon Choi Department of Urology, Seoul Medical Center, 156 Sinnae-ro, Jungnang-gu, Seoul 02053, Korea Email: urocsk0127@hanmail.net
Copyright © Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 3,368 Views
- 60 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a life-threatening disease requiring immediate treatment. This multicenter retrospective cohort study aimed to analyze the mortality rate and risk factors associated with EPN.
-
Materials and Methods Between January 2011 and February 2021, 217 patients diagnosed with EPN via computed tomography who visited 14 teaching hospitals were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical data, including age, sex, comorbidities, Huang and Tseng classification, hydronephrosis, acute kidney injury, blood and urine tests, surgical interventions, percutaneous drainage, and conservative treatments, were compared between the survival and death groups. Risk factors for mortality due to EPN were analyzed using univariate and multivariate methods.
-
Results The mean age of survivors and deceased patients was 67.8 and 69.0 years, respectively (p=0.136). The sex distribution (male/female) was 48/146 and 8/15, respectively (p=0.298). Of the 217 patients, 23 died, resulting in a mortality rate of 10.6%. In univariate analysis, the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.004), platelet count (p=0.005), and acute kidney injury (p=0.007) were significantly associated with mortality from EPN. In multivariate analysis, only the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.029) was identified as a risk factor. Mortality rates according to the Huang and Tseng classification were as follows: class I (5.88%), class II (7.50%), class IIIa (14.28%), class IIIb (25.00%), and class IV (23.07%).
-
Conclusions EPN is associated with a high mortality rate. Among various clinical factors, the Huang and Tseng classification was the most significant indicator for predicting mortality.
HIGHLIGHTS
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS
-
Funding/Support
This study received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
-
Research Ethics
This retrospective cohort study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul Medical Center (SEOUL 2021-05-006-002).
-
Conflict of Interest
SKC, a member of the Editorial Board of Urogenital Tract Infection, is the corresponding author of this article. However, he played no role whatsoever in the editorial evaluation of this article or the decision to publish it. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
-
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: SKC; Data curation: SB, JBC, YK, JMC, JHS, JHJ, HC, THK; Formal analysis: ECH, SKC; Methodology: SKC; Project administration: SKC; Visualization: SKC; Writing - original draft: SKC; Writing - review & editing: JWL, SIJ, ECH, JC, WBK, JSH.
NOTES

| Variable | Mortality (-) (n=194) | Mortality (+) (n=23) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 67.8±12.9 | 69.0±11.6 | 0.136 |
| Sex | 0.298 | ||
| Male | 48 (24.7) | 8 (4.1) | |
| Female | 146 (75.3) | 15 (7.7) | |
| Underlying disease | |||
| DM | 159 (82) | 19 (9.8) | 0.601 |
| HTN | 96 (49.5) | 9 (4.6) | 0.237 |
| CVA | 22 (11.3) | 4 (2.1) | 0.289 |
| CKD | 60 (30.9) | 6 (3.1) | 0.416 |
| Huang & Tseng classification | 0.004* | ||
| I | 64 (33) | 4 (2.1) | |
| II | 74 (38.1) | 6 (3.1) | |
| IIIa | 30 (15.5) | 5 (2.6) | |
| IIIb | 15 (7.7) | 5 (2.6) | |
| IV | 10 (5.2) | 3 (1.5) | |
| Lab finding | |||
| Leukocyte count (/µL) | 18,144±20,391 | 22,195±12,704 | 0.353 |
| Platelet count (/µL) | 212,809±138,751 | 125,434±141,784 | 0.005* |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 20.22±29.33 | 22.41±10.48 | 0.723 |
| Serum Cr (mg/dL) | 2.9±2.78 | 3.2±2.45 | 0.531 |
| HbA1c | 9.84±2.595 | 9.97±3.204 | 0.864 |
| Acute kidney injury | 102 (52.6) | 19 (9.8) | 0.007* |
| Hydronephrosis | 63 (32.5) | 3 (1.5) | 0.059 |
| Treatment | 0.138 | ||
| Nephrectomy | 20 (10.3) | 4 (2.1) | |
| PCN or PCD | 92 (47.4) | 6 (3.1) | |
| Conservative treatment | 82 (42.3) | 13 (6.7) |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CRP, C-reactive protein; Cr, creatinine; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; PCN, percutaneous nephrostomy; PCD, percutaneous catheter drainage.
*p<0.05, statistically significant differences.
| Risk factor | OR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Huang & Tseng classification | 1.481 (1.010–2.109) | 0.029 |
| Thrombocytopenia, <200 K/mL | 2.126 (0.707–6.389) | 0.179 |
| Acute kidney injury | 3.143 (0.976–10.118) | 0.055 |
| Huang & Tseng classification | Mortality (–/+) | Mortality rate |
|---|---|---|
| I | 64/4 | 5.88% |
| II | 74/6 | 7.50% |
| IIIa | 30/5 | 14.28% |
| IIIb | 15/5 | 25.00% |
| IV | 10/3 | 23.07% |
- 1. Huang JJ, Tseng CC. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: clinicoradiological classification, management, prognosis, and pathogenesis. Arch Intern Med 2000;160:797-805.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Tang HJ, Li CM, Yen MY, Chen YS, Wann SR, Lin HH, et al. Clinical characteristics of emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2001;34:125-30.PubMed
- 3. Chuang YW, Chen CH, Cheng CH, Hung SW, Yu TM, Wu MJ, et al. Severe emphysematous pyelonephritis in a renal allograft: successful treatment with percutaneous drainage and antibiotics. Clin Nephrol 2007;68:42-6.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Preker AS, Cotlear D, Kwon S, Atun R, Avila C. Universal health care in middle-income countries: lessons from four countries. J Glob Health 2021;11:16004.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Ahangar A, Ahmadi AM, Mozayani AH, Dizaji SF. The role of risk-sharing mechanisms in finance health care and towards universal health coverage in low-and middle-income countries of World Health Organization Regions. J Prev Med Public Health 2018;51:59-61.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Chu KM, Naidu P, Hendriks HJ, Nash J, Coetzee FJ, Esteves M, et al. Surgical care at rural district hospitals in low- and middle-income countries: an essential component of universal health coverage. Rural Remote Health 2020;20:5920.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Ngo XT, Nguyen TT, Dobbs RW, Thai MS, Vu DH, Dinh LQV, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of mortality in emphysematous pyelonephritis patients: a meta-analysis. World J Surg 2022;46:2377-88.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Kone K, Mallikarjun NT, Rams M. Mortality in emphysematous pyelonephritis: can we reduce it further by using a protocol-based treatment? The results of a prospective study. Urol Ann 2022;14:73-80.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Aboumarzouk OM, Hughes O, Narahari K, Coulthard R, Kynaston H, Chlosta P, et al. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: time for a management plan with an evidence-based approach. Arab J Urol 2014;12:106-15.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Nana GR, Brodie A, Akhter W, Karim O, Motiwala H. Nephroureterectomy for emphysematous pyelonephritis: an aggressive approach is sometimes necessary. A case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep 2015;10:179-82.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Seymour CW, Liu VX, Iwashyna TJ, Brunkhorst FM, Rea TD, Scherag A, et al. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis: for the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016;315:762-74.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016;315:801-10.PubMedPMC
- 13. Shankar-Hari M, Phillips GS, Levy ML, Seymour CW, Liu VX, Deutschman CS, et al. Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: for the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016;315:775-87.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Trujillo-Santamaria H, Robles-Torres JI, Teoh JY, Tanidir Y, Campos-Salcedo JG, Bravo-Castro EI, et al. A novel mortality risk score for emphysematous pyelonephritis: a multicenter study of the Global Research in the Emphysematous Pyelonephritis group. Curr Urol 2024;18:55-60.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Aggarwal D, Mandal S, Parmar K, Manoharan V, Singh S, Yadav AK, et al. Predictors of mortality and nephrectomy in emphysematous pyelonephritis: a tertiary care centre study. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2023;105:323-30.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Bedoui MA, Saadi A, Zaghbib S, Mokadem S, Boussaffa H, Hermi A, et al. Risk factors for sepsis and mortality in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis : a series of 68 cases (case series). Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2024;86:240-4.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Desai R, Batura D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of risk factors and treatment choices in emphysematous pyelonephritis. Int Urol Nephrol 2022;54:717-36.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Park K, Park J, Kwon YD, Kang Y, Noh JW. Public satisfaction with the healthcare system performance in South Korea: universal healthcare system. Health Policy 2016;120:621-9.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Song YJ. The South Korean health care system. JMAJ 2009;52:206-9.
- 20. Moon TJ. Light and shadows of the Korean healthcare system. J Korean Med Sci 2012;27 Suppl(Suppl):S3-6.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
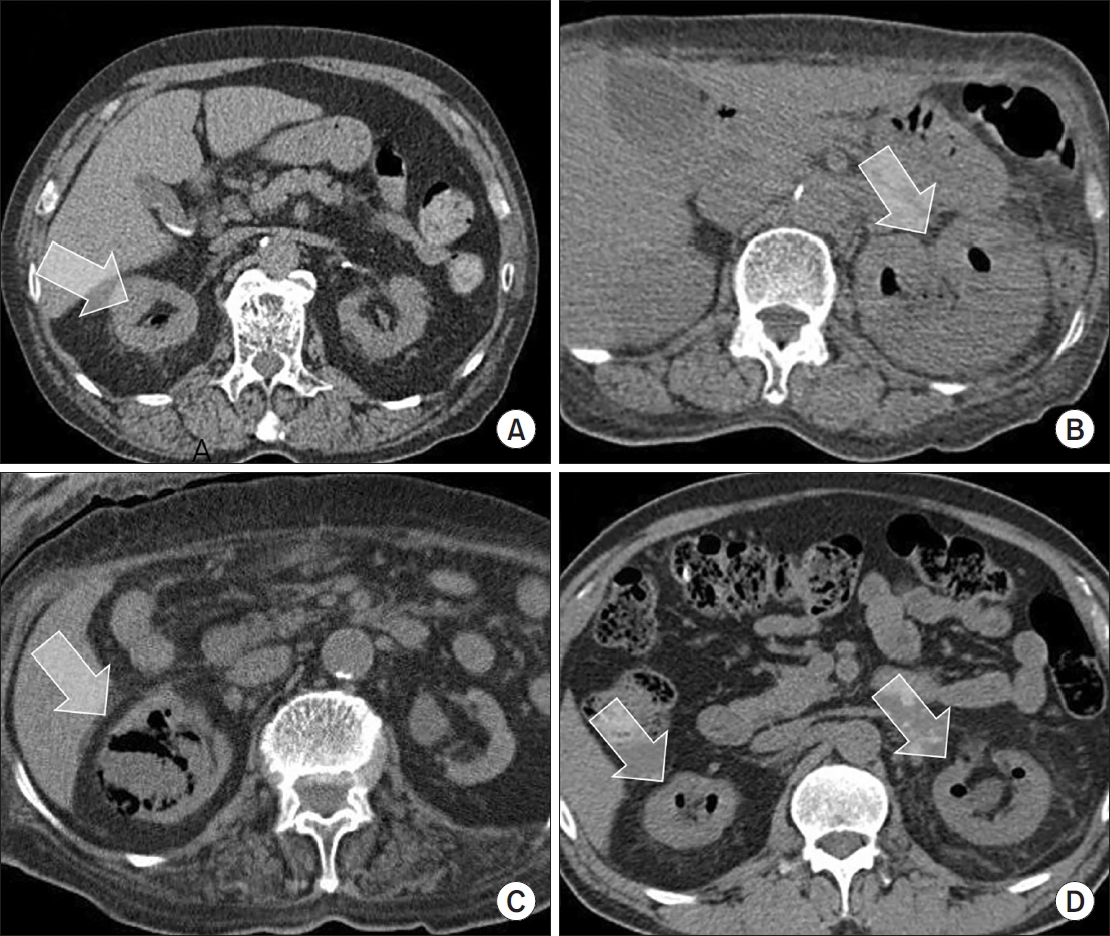
Fig. 1
| Variable | Mortality (-) (n=194) | Mortality (+) (n=23) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 67.8±12.9 | 69.0±11.6 | 0.136 |
| Sex | 0.298 | ||
| Male | 48 (24.7) | 8 (4.1) | |
| Female | 146 (75.3) | 15 (7.7) | |
| Underlying disease | |||
| DM | 159 (82) | 19 (9.8) | 0.601 |
| HTN | 96 (49.5) | 9 (4.6) | 0.237 |
| CVA | 22 (11.3) | 4 (2.1) | 0.289 |
| CKD | 60 (30.9) | 6 (3.1) | 0.416 |
| Huang & Tseng classification | 0.004 |
||
| I | 64 (33) | 4 (2.1) | |
| II | 74 (38.1) | 6 (3.1) | |
| IIIa | 30 (15.5) | 5 (2.6) | |
| IIIb | 15 (7.7) | 5 (2.6) | |
| IV | 10 (5.2) | 3 (1.5) | |
| Lab finding | |||
| Leukocyte count (/µL) | 18,144±20,391 | 22,195±12,704 | 0.353 |
| Platelet count (/µL) | 212,809±138,751 | 125,434±141,784 | 0.005 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 20.22±29.33 | 22.41±10.48 | 0.723 |
| Serum Cr (mg/dL) | 2.9±2.78 | 3.2±2.45 | 0.531 |
| HbA1c | 9.84±2.595 | 9.97±3.204 | 0.864 |
| Acute kidney injury | 102 (52.6) | 19 (9.8) | 0.007 |
| Hydronephrosis | 63 (32.5) | 3 (1.5) | 0.059 |
| Treatment | 0.138 | ||
| Nephrectomy | 20 (10.3) | 4 (2.1) | |
| PCN or PCD | 92 (47.4) | 6 (3.1) | |
| Conservative treatment | 82 (42.3) | 13 (6.7) |
| Risk factor | OR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Huang & Tseng classification | 1.481 (1.010–2.109) | 0.029 |
| Thrombocytopenia, <200 K/mL | 2.126 (0.707–6.389) | 0.179 |
| Acute kidney injury | 3.143 (0.976–10.118) | 0.055 |
| Huang & Tseng classification | Mortality (–/+) | Mortality rate |
|---|---|---|
| I | 64/4 | 5.88% |
| II | 74/6 | 7.50% |
| IIIa | 30/5 | 14.28% |
| IIIb | 15/5 | 25.00% |
| IV | 10/3 | 23.07% |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%). DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CRP, C-reactive protein; Cr, creatinine; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; PCN, percutaneous nephrostomy; PCD, percutaneous catheter drainage. p<0.05, statistically significant differences.
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.

 KAUTII
KAUTII
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

