Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Urogenit Tract Infect > Volume 20(3); 2025 > Article
- Original Article Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Fournier Gangrene: A 15-Years Multicenter Retrospective Study in Korea
-
Seung-Kwon Choi1
 , Sin Woo Lee1
, Sin Woo Lee1 , Hyung-Lae Lee2
, Hyung-Lae Lee2 , Jeong Woo Lee2
, Jeong Woo Lee2 , Jung Sik Huh3
, Jung Sik Huh3 , Yeonjoo Kim4
, Yeonjoo Kim4 , Sangrak Bae5
, Sangrak Bae5 , Tae-Hyoung Kim6
, Tae-Hyoung Kim6
-
Urogenital Tract Infection 2025;20(3):159-166.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550036018
Published online: December 31, 2025
1Department of Urology, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Urology, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
3Department of Urology, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
4Department of Urology, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea
5Department of Urology, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea
6Department of Urology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
-
Corresponding author: Seung-Kwon Choi Department of Urology, Seoul Medical Center, 156 Sinnae-ro, Jungnang- gu, Seoul 02053, Korea Email: urocsk0127@hanmail.net
Copyright © Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 244 Views
- 9 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose Fournier gangrene (FG) is a rare but life-threatening necrotizing infection requiring prompt recognition and intervention. This multicenter study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics, treatment outcomes including mortality, and risk factors associated with death among patients with FG over the past 15 years in Korea.
-
Materials and Methods We retrospectively reviewed 84 patients diagnosed with FG between 2008 and 2022 across 7 hospitals. Demographics, comorbidities, laboratory findings, and clinical outcomes were analyzed. Mortality-related risk factors were assessed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
-
Results The mean age was 58.1±15.9 years, and 95.2% of patients were male. Diabetes mellitus (42.9%) and hypertension (36.9%) were the most prevalent comorbidities. Sepsis developed in 38.1% of patients, and the overall mortality rate was 14.3%. In univariate analysis, age ≥70 years, low body mass index, diabetes mellitus, low hemoglobin, low hematocrit, high respiratory rate, and Fournier gangrene severity index (FGSI) ≥9 were significantly associated with mortality. After data correction and multivariate adjustment, diabetes mellitus (odds ratio [OR], 39.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.39–656.32; p=0.010) and respiratory rate (OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.09–1.91; p=0.011) were identified as independent predictors of mortality. FGSI≥9 demonstrated borderline association with mortality (p=0.08), indicating its potential clinical relevance.
-
Conclusions In this multicenter Korean cohort, the mortality rate of FG remained substantial at 14.3%. Diabetes mellitus and elevated respiratory rate were independent predictors of mortality, while FGSI≥9 demonstrated a borderline yet clinically meaningful association, suggesting its role as a useful severity indicator in early risk stratification.
HIGHLIGHTS
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Fig. 1.
-
Funding/Support
This study received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
-
Research Ethics
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Seoul Medical Center (IRB No. SEOUL 2025-07-005). The requirement for informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
-
Conflict of Interest
SKC and JSH are authors of this article as well as editorial board members of Urogenital Tract Infection. However, they had no involvement in the editorial evaluation or the decision to publish this manuscript. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
-
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: CSK, HLL, THK; Data curation: CSK, HLL, JWL, JSH, YK, SB, THK; Formal analysis: CSK; Methodology: CSK, HLL, THK; Project administration: CSK; Visualization: CSK; Writing - original draft: CSK; Writing - review & editing: CSK.
NOTES
| Variable | Mortality (-) (n=72) | Mortality (+) (n=12) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 56.4±15.4 | 68.3±16.4 | 0.017* |
| Sex | 0.392 | ||
| Male | 69 (95.8) | 11 (91.7) | |
| Female | 3 (4.2) | 1 (8.3) | |
| Underlying disease | |||
| DM | 26 (36.1) | 9 (75.0) | 0.013* |
| HTN | 27 (37.5) | 4 (33.3) | 1.000 |
| CVA | 11 (15.3) | 4 (33.3) | 0.216 |
| CKD | 6 (8.3) | 2 (16.7) | 0.326 |
| ALD | 7 (9.7) | 3 (25.0) | 0.154 |
| Vital sign | |||
| Fever (°C) | 37.0±1.0 | 37.0±1.1 | 0.439 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 93.7±17.7 | 97.2±20.2 | 0.636 |
| Respiration rate (breaths/min) | 20.0±3.1 | 22.6±4.5 | 0.028* |
| Lab finding | |||
| Leukocyte count (/µL) | 17,475.5±8,977.3 | 17,795.0±10,458.9 | 0.954 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.5±4.4 | 10.6±2.7 | 0.022* |
| Hematocrit (%) | 35.6±7.2 | 31.2±6.5 | 0.048* |
| Platelet count (/µL) | 252,002.7±142,153.3 | 255,666.7±230,609.2 | 0.547 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 22.4±23.3 | 14.3±7.1 | 0.259 |
| Serum Cr (mg/dL) | 1.5±1.6 | 1.9±1.3 | 0.125 |
| Serum Na (mmol/L) | 133.1±5.4 | 132.1±6.7 | 0.881 |
| Serum K (mmol/L) | 4.1±0.7 | 4.2±0.8 | 0.831 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.2±0.7 | 2.7±0.6 | 0.063 |
| Variable |
Univariate analysis |
Multivariate analysis |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-value | OR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Age, ≥70 vs. <70 | 4.07 | 1.14–14.55 | 0.031* | 4.32 | 0.61–30.70 | 0.144 |
| Sex, male vs. female | 2.06 | 0.20–21.63 | 0.547 | - | - | - |
| BMI | 0.83 | 0.71–0.99 | 0.035* | 0.76 | 0.55–1.06 | 0.106 |
| DM, positive vs. negative | 5.19 | 1.29–20.91 | 0.020* | 39.61 | 2.39–656.32 | 0.010* |
| HTN, positive vs. negative | 0.81 | 0.22–2.97 | 0.756 | - | - | - |
| CVA, positive vs. negative | 2.73 | 0.70–10.64 | 0.149 | - | - | - |
| CKD, positive vs. negative | 2.17 | 0.38–12.26 | 0.382 | - | - | - |
| ALD, positive vs. negative | 3.05 | 0.67–13.96 | 0.151 | - | - | - |
| Respiration rate | 1.20 | 1.01–1.41 | 0.034* | 1.44 | 1.09–1.91 | 0.011* |
| Hemoglobin | 0.75 | 0.57–0.97 | 0.031* | 0.88 | 0.72–1.07 | 0.195 |
| Hematocrit, <35 vs. ≥35 | 4.64 | 1.15–18.51 | 0.031* | 0.68 | 0.07–6.19 | 0.729 |
| Serum albumin | 0.38 | 0.14–1.06 | 0.064 | - | - | - |
| FGSI, ≥9 vs. <9 | 3.90 | 1.05–14.52 | 0.043* | 7.89 | 0.84–74.20 | 0.071 |
- 1. Eke N. Fournier's gangrene: a review of 1726 cases. Br J Surg 2000;87:718-28.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Shyam DC, Rapsang AG. Fournier's gangrene. Surgeon 2013;11:222-32.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Singh A, Ahmed K, Aydin A, Khan MS, Dasgupta P. Fournier's gangrene. A clinical review. Arch Ital Urol Androl 2016;88:157-64.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Sorensen MD, Krieger JN, Rivara FP, Klein MB, Wessells H. Fournier's gangrene: management and mortality predictors in a population based study. J Urol 2009;182:2742-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Radcliffe RS, Khan MA. Mortality associated with Fournier's gangrene remains unchanged over 25 years. BJU Int 2020;125:610-6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. El-Qushayri AE, Khalaf KM, Dahy A, Mahmoud AR, Benmelouka AY, Ghozy S, et al. Fournier's gangrene mortality: a 17-year systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis 2020;92:218-25.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Hong KS, Yi HJ, Lee RA, Kim KH, Chung SS. Prognostic factors and treatment outcomes for patients with Fournier's gangrene: a retrospective study. Int Wound J 2017;14:1352-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 8. Hong HB, Lee JW, Park CH. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in Fournier's gangrene: a retrospective study of 35 patients. BMC Infect Dis 2024;24:958.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. Jeong HJ, Park SC, Seo IY, Rim JS. Prognostic factors in Fournier gangrene. Int J Urol 2005;12:1041-4.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Hahn HM, Jeong KS, Park DH, Park MC, Lee IJ. Analysis of prognostic factors affecting poor outcomes in 41 cases of Fournier gangrene. Ann Surg Treat Res 2018;95:324-32.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 11. Lin TY, Cheng IH, Ou CH, Tsai YS, Tong YC, Cheng HL, et al. Incorporating simplified Fournier's gangrene severity index with early surgical intervention can maximize survival in high-risk Fournier's gangrene patients. Int J Urol 2019;26:737-43.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Roghmann F, von Bodman C; Löppenberg B, Hinkel A, Palisaar J, Noldus J. Is there a need for the Fournier's gangrene severity index? Comparison of scoring systems for outcome prediction in patients with Fournier's gangrene. BJU Int 2012;110:1359-65.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Corcoran AT, Smaldone MC, Gibbons EP, Walsh TJ, Davies BJ. Validation of the Fournier's gangrene severity index in a large contemporary series. J Urol 2008;180:944-8.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Lin TY, Ou CH, Tzai TS, Tong YC, Chang CC, Cheng HL, et al. Validation and simplification of Fournier's gangrene severity index. Int J Urol 2014;21:696-701.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Shiratori T, Nakamura M, Naito A, Yamamoto M, Okura Y, Yamakawa J, et al. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of Fournier's gangrene in a single tertiary emergency hospital: simplified Fournier's gangrene severity index score is a predictor for death. Glob Health Med 2023;5:362-5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Arora A, Rege S, Surpam S, Gothwal K, Narwade A. Predicting mortality in Fournier gangrene and validating the Fournier gangrene severity index: our experience with 50 patients in a tertiary care center in India. Urol Int 2019;102:311-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Laor E, Palmer LS, Tolia BM, Reid RE, Winter HI. Outcome prediction in patients with Fournier's gangrene. J Urol 1995;154:89-92.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016;315:801-10.PubMedPMC
- 19. Martin-Loeches I, Singer M, Leone M. Sepsis: key insights, future directions, and immediate goals. A review and expert opinion. Intensive Care Med 2024;50:2043-9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Seymour CW, Liu VX, Iwashyna TJ, Brunkhorst FM, Rea TD, Scherag A, et al. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis: for the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016;315:762-74.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, et al. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest 1992;101:1644-55.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

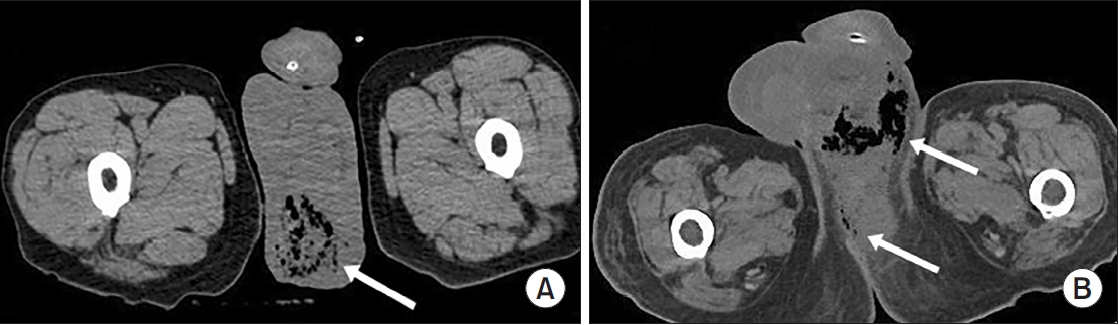
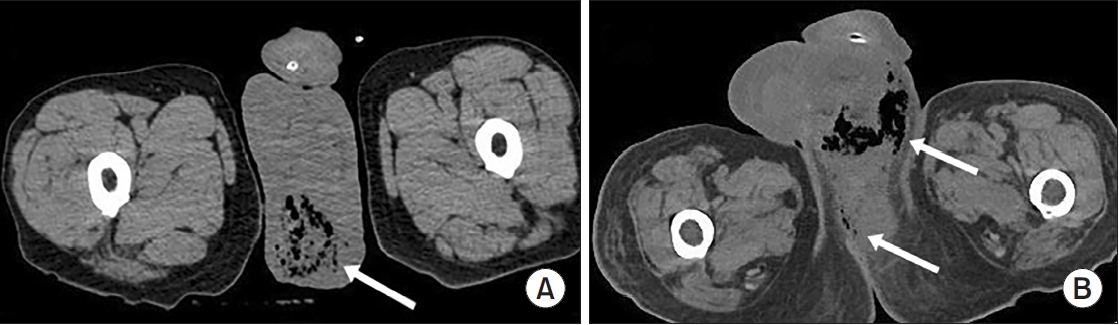
Fig. 1.
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 58.1±15.9 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 80 (95.2) |
| Female | 4 (4.8) |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 23.9±4.9 |
| Underlying disease | |
| DM | 36 (42.9) |
| HTN | 31 (36.9) |
| CVA | 15 (17.9) |
| CKD | 8 (9.5) |
| ALD | 11 (13.1) |
| Management | |
| ICU | 36 (42.9) |
| Sepsis | 32 (38.1) |
| Mortality | 12 (14.3) |
| Variable | Mortality (-) (n=72) | Mortality (+) (n=12) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 56.4±15.4 | 68.3±16.4 | 0.017 |
| Sex | 0.392 | ||
| Male | 69 (95.8) | 11 (91.7) | |
| Female | 3 (4.2) | 1 (8.3) | |
| Underlying disease | |||
| DM | 26 (36.1) | 9 (75.0) | 0.013 |
| HTN | 27 (37.5) | 4 (33.3) | 1.000 |
| CVA | 11 (15.3) | 4 (33.3) | 0.216 |
| CKD | 6 (8.3) | 2 (16.7) | 0.326 |
| ALD | 7 (9.7) | 3 (25.0) | 0.154 |
| Vital sign | |||
| Fever (°C) | 37.0±1.0 | 37.0±1.1 | 0.439 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 93.7±17.7 | 97.2±20.2 | 0.636 |
| Respiration rate (breaths/min) | 20.0±3.1 | 22.6±4.5 | 0.028 |
| Lab finding | |||
| Leukocyte count (/µL) | 17,475.5±8,977.3 | 17,795.0±10,458.9 | 0.954 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.5±4.4 | 10.6±2.7 | 0.022 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 35.6±7.2 | 31.2±6.5 | 0.048 |
| Platelet count (/µL) | 252,002.7±142,153.3 | 255,666.7±230,609.2 | 0.547 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 22.4±23.3 | 14.3±7.1 | 0.259 |
| Serum Cr (mg/dL) | 1.5±1.6 | 1.9±1.3 | 0.125 |
| Serum Na (mmol/L) | 133.1±5.4 | 132.1±6.7 | 0.881 |
| Serum K (mmol/L) | 4.1±0.7 | 4.2±0.8 | 0.831 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.2±0.7 | 2.7±0.6 | 0.063 |
| Variable | Univariate analysis |
Multivariate analysis |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-value | OR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Age, ≥70 vs. <70 | 4.07 | 1.14–14.55 | 0.031 |
4.32 | 0.61–30.70 | 0.144 |
| Sex, male vs. female | 2.06 | 0.20–21.63 | 0.547 | - | - | - |
| BMI | 0.83 | 0.71–0.99 | 0.035 |
0.76 | 0.55–1.06 | 0.106 |
| DM, positive vs. negative | 5.19 | 1.29–20.91 | 0.020 |
39.61 | 2.39–656.32 | 0.010 |
| HTN, positive vs. negative | 0.81 | 0.22–2.97 | 0.756 | - | - | - |
| CVA, positive vs. negative | 2.73 | 0.70–10.64 | 0.149 | - | - | - |
| CKD, positive vs. negative | 2.17 | 0.38–12.26 | 0.382 | - | - | - |
| ALD, positive vs. negative | 3.05 | 0.67–13.96 | 0.151 | - | - | - |
| Respiration rate | 1.20 | 1.01–1.41 | 0.034 |
1.44 | 1.09–1.91 | 0.011 |
| Hemoglobin | 0.75 | 0.57–0.97 | 0.031 |
0.88 | 0.72–1.07 | 0.195 |
| Hematocrit, <35 vs. ≥35 | 4.64 | 1.15–18.51 | 0.031 |
0.68 | 0.07–6.19 | 0.729 |
| Serum albumin | 0.38 | 0.14–1.06 | 0.064 | - | - | - |
| FGSI, ≥9 vs. <9 | 3.90 | 1.05–14.52 | 0.043 |
7.89 | 0.84–74.20 | 0.071 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%). BMI, body mass index, DM, diabetes mellitus, HTN, hypertension, CVA, cerebrovascular accident, CKD, chronic kidney disease, ALD, alcoholic liver disease, ICU, intensive care unit.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%). DM, diabetes mellitus, HTN, hypertension, CVA, cerebrovascular accident, CKD, chronic kidney disease, ALD, alcoholic liver disease, CRP, C-reactive protein. p<0.05, statistically significant differences.
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; BMI, body mass index; DM, diabetes mellitus, HTN, hypertension, CVA, cerebrovascular accident, CKD, chronic kidney disease, ALD, alcoholic liver disease, FGSI, Fourniers gangrene severity index. p<0.05, statistically significant differences.

 KAUTII
KAUTII
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

