Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Mortality and Risk Factors for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):34-41. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550006003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
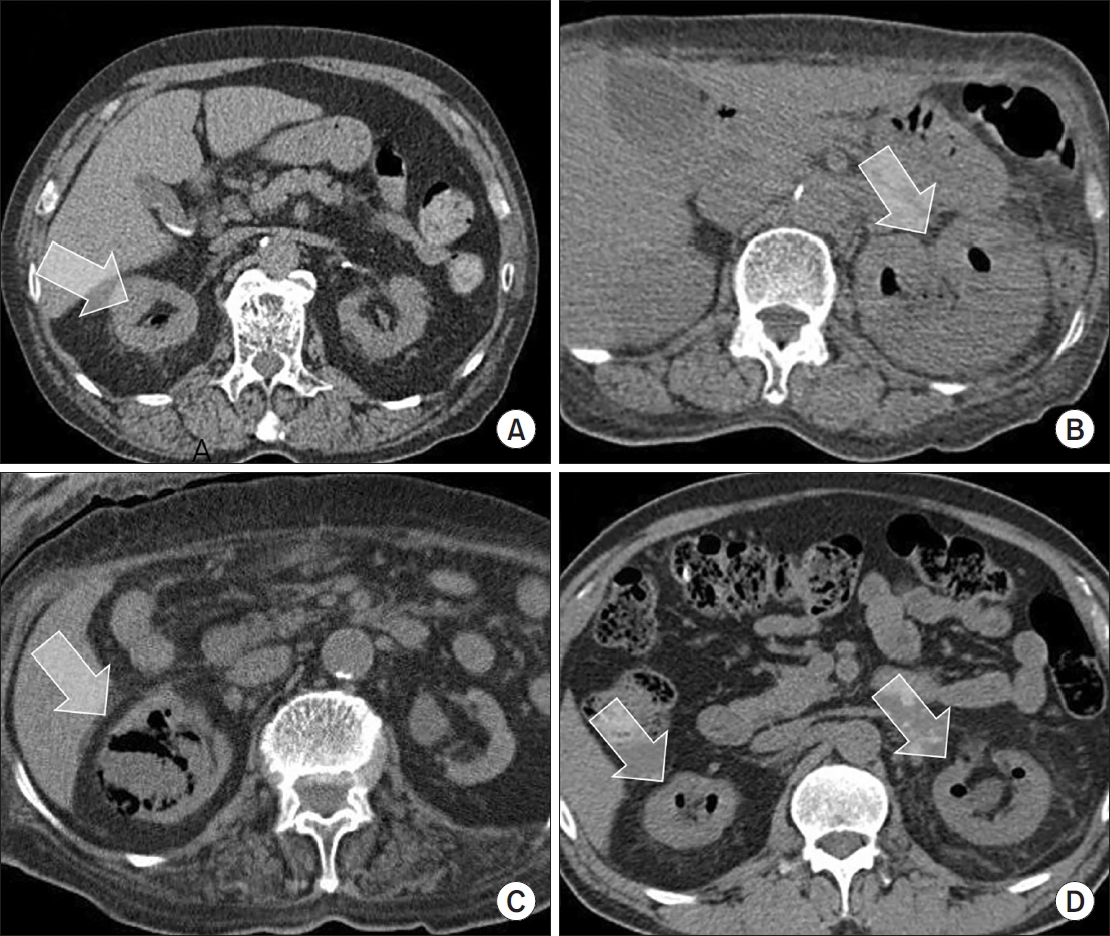
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a life-threatening disease requiring immediate treatment. This multicenter retrospective cohort study aimed to analyze the mortality rate and risk factors associated with EPN. Materials and Methods: Between January 2011 and February 2021, 217 patients diagnosed with EPN via computed tomography who visited 14 teaching hospitals were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical data, including age, sex, comorbidities, Huang and Tseng classification, hydronephrosis, acute kidney injury, blood and urine tests, surgical interventions, percutaneous drainage, and conservative treatments, were compared between the survival and death groups. Risk factors for mortality due to EPN were analyzed using univariate and multivariate methods.
Results
The mean age of survivors and deceased patients was 67.8 and 69.0 years, respectively (p=0.136). The sex distribution (male/female) was 48/146 and 8/15, respectively (p=0.298). Of the 217 patients, 23 died, resulting in a mortality rate of 10.6%. In univariate analysis, the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.004), platelet count (p=0.005), and acute kidney injury (p=0.007) were significantly associated with mortality from EPN. In multivariate analysis, only the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.029) was identified as a risk factor. Mortality rates according to the Huang and Tseng classification were as follows: class I (5.88%), class II (7.50%), class IIIa (14.28%), class IIIb (25.00%), and class IV (23.07%).
Conclusions
EPN is associated with a high mortality rate. Among various clinical factors, the Huang and Tseng classification was the most significant indicator for predicting mortality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 3,368 View
- 60 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: Case Report
- Kwang Jin Kim, Yoonsuk Lee, Yong Sung Cha, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Hong Chung, Hyun Kim, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):44-47. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) was conducted on two male patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome who were resistant to conventional medical therapies. Both patients underwent 20 sessions of 100% oxygen inhalation (2.0 atmosphere absolute for 90 min/day, five days/week for four weeks) in a hyperbaric chamber. The follow-up period was three months. Although the patients reported a slight improvement in the pain domain of the National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) after HBOT, no changes were noted in the other domains of NIH-CPSI and International Prostate Symptom Score. No adverse events were encountered during or after HBOT.
- 5,283 View
- 35 Download

Original Articles
- Trends in Age-Specific Prevalence of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Young Hwan Kim, Se Hwa Hong, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Tae Hyoung Kim, Sae Chul Kim, Sang Baek Koh, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):101-106. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: To elucidate the longitudinal changes in the prevalence of lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) according to age over the past 10 years.
Materials and Methods: The changes in the proportion of prevalence for LUTD, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and urinary incontinence (UI) among South Koreans from 2009 to 2018, were analyzed using the National Health Information Database established by the Korean National Health Insurance Service. All conditions were defined according to the corresponding Korean Standard Classification of Diseases-8 for diagnosis and surgical procedures and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service codes for drugs.
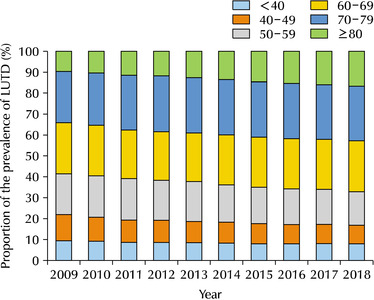
Results: The 60-69, 70-79, and over 80 age groups accounted for more than 60% of the LUTD cases from 2009 to 2018, while significant increases in the crude prevalence of LUTD were observed over a 10-year period in all age groups (p for trend <0.05). In age groups over 60 years, LUTD was more prevalent in men than women, but there was no statistically significant difference in proportion (p>0.05). The changes in the prevalence and prevalence proportion exhibited similar trends in BPH, UI, and LUTD.
Conclusions: LUTD was more prevalent in the elderly aged over 60 years old than in younger adults. Therefore, this study suggests the development of nationwide healthcare policies to manage LUTD in the elderly population of South Korea, which is expected to become the world’s most aged population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing strategies for managing urological disorders in aging populations: a comprehensive review
Hong Liu, Jie Wu
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Nursing strategies for managing urological disorders in aging populations: a comprehensive review
- 4,558 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Characteristics and Treatment Trends for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A 10-Year Multicenter Retrospective Study
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Koo Han Yoo, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(2):49-54. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.2.49
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study examined the characteristics, current treatment trends, and outcomes of patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) in Korea.
Materials andMethods: Two hundred and seventeen patients diagnosed with EPN were evaluated using abdominal computed tomography in 2011-2021 at 15 institutes in Korea. The patients’ demographic and clinical characteristics, treatment modalities, and treatment outcomes were analyzed. The total study period was divided arbitrarily into groups A (2011-2014), B (2015-2017), and C (2018-2021) to analyze the trends in the EPN treatment.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 65.1 years; there were more female patients (74.2%) than male patients. The overall mortality rate was 10.6%. Ninety-five (43.8%), 98 (45.2%), and 24 (11.0%) patients were treated with medical, minimally invasive, and surgical management, respectively; the corresponding mortality rates were 13.7%, 6.1%, and 16.7%. There was no significant change in the proportion of patients treated with medical management over time (group A=46.5%, group B=47.0%, and group C=38.8%). The proportion of patients treated with minimally invasive management gradually increased over time (group A=35.2%; group B=43.9%; group C=55.0%), while those who underwent surgical management decreased gradually over time (group A=18.3%, group B=9.1%, and group C=6.3%). No differences in mortality rates were observed between the groups.
Conclusions: EPN with medical and minimally invasive management had a relatively high treatment success rate, which increased gradually, while surgical management decreased gradually over time in Korea. The mortality rate was relatively lower than that reported in studies published before the 2010s.
- 2,024 View
- 8 Download

Editorials
- Korean Translation of the GRADE Series Published in the BMJ, ‘Use of GRADE Grid to Reach Decisions on Clinical Practice Guidelines When Consensus Is Elusive’ (A Secondary Publication)
- Hyun Jin Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Do Kyung Kim, Ho Won Kang, Ja Yoon Ku, Hong Wook Kim, Jae Hung Jung, Guideline Development Committee in the Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(3):83-89. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.3.83
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - This article is the last of a series providing guidance for the use of the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) system for rating the quality of evidence and grading the strength of recommendations in systematic reviews and clinical practice guidelines. Formulating recommendations with the applicable evidence can be difficult due to the large and diverse nature of guideline committees. This article describes a simple technique called the GRADE grid for clarifying the opinions from guideline panels, dealing with disagreement, and achieving consensus among guideline panels. The grid may be helpful for any guideline groups who want to use GRADE to develop their guidelines and achieve consensus or understand the patterns of uncertainty that surround the interpretation of scientific evidence.
- 1,279 View
- 3 Download

- Korean Translation of the GRADE Series Published in the BMJ, ‘GRADE: Incorporating Considerations of Resources Use into Grading Recommendations’ (A Secondary Publication)
- Hong Wook Kim, Jae Hung Jung, Do Kyung Kim, Ho Won Kang, Ja Yoon Ku, Hyun Jin Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Guideline Development Committee in the Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(2):57-62. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.2.57
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - This article is the fifth translation of a GRADE series published in the BMJ for incorporating the considerations of resources use into grading recommendations. Clinical recommendations inevitably involve judgments about the allocation of resources use (costs). Although costs differ from typical healthcare outcomes, such as mortality, morbidity, and quality of life, costs are another potentially important outcome that differs across and within a jurisdiction. A balance sheet is a useful method for determining if the net benefits are worth the incremental costs. Resource use, not just monetary values, should always be presented in an evidence profile. Formal economic modeling may or may not help judge the certainty of the evidence for resource use.
- 1,216 View
- 1 Download

- Korean Translation of the GRADE Series Published in the BMJ, ‘GRADE: Grading Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations for Diagnostic Tests and Strategies’ (A Secondary Publication)
- Jae Hung Jung, Do Kyung Kim, Ho Won Kang, Ja Yoon Ku, Hyun Jin Jung, Hong Wook Kim, Eu Chang Hwang, Guideline Development Committee in the Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(1):16-25. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - This article is the fourth translation of a GRADE series published in the BMJ, which graded the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations for diagnostic tests or strategies, as a comprehensive and transparent approach for developing recommendations. Randomized trials for diagnostic approaches represent the ideal study design for intervention studies. On the other hand, cross-sectional or cohort studies with a direct comparison of the test results with an appropriate reference standard can provide high-quality evidence. The guideline panel must be reminded that the test accuracy is a surrogate for patient-important outcomes, so such studies often provide a low quality of evidence for recommendations regarding diagnostic tests, even when the studies do not have serious limitations. Diagnostic accuracy studies showing that a diagnostic test or strategy improves important patient outcomes will require the availability of effective treatment, reduction of test-related adverse effects or anxiety, or improvement of the patients’ well-being from prognostic information. Therefore, it is important to assess the directness of the test results regarding the consequences of diagnostic recommendations that are important to patients.
- 1,722 View
- 1 Download

- Korean Translation of the GRADE Series Published in the BMJ, ‘GRADE: Going from Evidence to Recommendations’ (A Secondary Publication)
- Eu Chang Hwang, Do Kyung Kim, Ho Won Kang, Ja Yoon Ku, Hyun Jin Jung, Hong Wook Kim, Jae Hung Jung, Guideline Development Committee in the Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2019;14(3):99-103. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2019.14.3.99
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This article is the third translation of a GRADE series published in the BMJ for developing and presenting recommendations for managing patients. The strength of a recommendation reflects the extent to which we can be confident that desirable effects of an intervention outweigh any undesirable effects. GRADE classifies the strength of recommendations as strong or weak. The strength of recommendation is determined by the balance between desirable and undesirable consequences of alternative management strategies, quality of the evidence, variability in values and preferences, and the appropriate usage of resources.
- 617 View
- 0 Download

- Korean Translation of the GRADE Series Published in the BMJ, ‘GRADE: What Is “Quality of Evidence” and Why Is It Important to Clinicians?’ (A Secondary Publication)
- Ho Won Kang, Jae Hung Jung, Do Kyung Kim, Ja Yoon Ku, Hyun Jin Jung, Hong Wook Kim, Eu Chang Hwang, Guideline Development Committee in the Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2019;14(2):64-70. Published online August 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2019.14.2.64
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This article is second translation of a GRADE series published in the BMJ to create a highly structured, transparent, and informative system for rating quality of evidence for developing recommendations. The process to develop a guideline, we should formulate a clear question with specification of all outcomes of importance to patients. Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) offers four levels of evidence quality: high, moderate, low, and very low for these patient-important outcomes. Randomized trials begin as high quality evidence and observational studies as low quality evidence. Although randomized trials begin as high quality evidence, quality may be downgraded as a result of study limitations (risk of bias), inconsistency (variability in results), indirectness, imprecision (wide confidence intervals), or publication bias. While the quality of evidence derived from observational studies starts at ‘low’ but may be upgraded based on a very large magnitude of effect, a dose-response gradient, and if all plausible biases would reduce an apparent treatment effect.
- 774 View
- 1 Download

- Korean Translation of the GRADE Series Published in the BMJ, ‘GRADE: An Emerging Consensus on Rating Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations’ (A Secondary Publication)
- Do Kyung Kim, Eu Chang Hwang, Ho Won Kang, Ja Yoon Ku, Hyun Jin Jung, Hong Wook Kim, Jae Hung Jung, Guideline Development Committee in the Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2019;14(1):28-32. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2019.14.1.28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clinical practice guidelines are statements that include recommendations intended to optimize patient care based on a systematic review of the evidence assessing the benefits and harm of alternative care options. Guideline developers should use an explicit, judicious, and transparent methodology to make trustworthy guidelines. Although there are a variety of frameworks that can help translate enormous medical knowledge into recommendations, the most widely adopted tool for grading the quality of evidence and making recommendations is GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations). This article is the first translation of a series published in the BMJ with regard to the GRADE Approach for Evidence Based Clinical Practice Guideline Development to provide informative knowledge for moving from evidence to recommendations to Korean guideline developers.
- 537 View
- 0 Download

- Introduction to the GRADE Approach for Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline Development
- Eu Chang Hwang, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2019;14(1):26-27. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2019.14.1.26
- 423 View
- 0 Download

Reviews
- Moving towards Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Jae Hung Jung, Juan V A, Philipp Dahm
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2018;13(3):45-50. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2018.13.3.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The Institute of Medicine in its report “Clinical Practice Guidelines we can trust” defined standards for clinical practice guidelines. However, many guidelines continue to rely on expert opinion and lack a formal framework for moving from evidence to recommendations. These guidelines may or may not be labeled as “consensus statements” and do not meet contemporary standards for guideline documents we would refer to as “evidence-based”. Therefore, the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation working group developed a novel, rigorous and transparent approach to grading certainty (quality) of evidence. In addition, it created a system for “moving from evidence to decisions”, for example for the development of evidence-based guidelines. In this article, we aim to introduce this approach to appraising the certainty of relevant evidence and estimate the benefits and detriments of health care interventions within the larger context of evidence-based medicine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Levels of Evidence, Quality Assessment, and Risk of Bias: Evaluating the Internal Validity of Primary Research
Jan M. Sargeant, Marnie L. Brennan, Annette M. O'Connor
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Serenoa repens for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic enlargement: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Leonel Fabrizio Trivisonno, Nadia Sgarbossa, Gustavo Ariel Alvez, Cecilia Fieiras, Camila Micaela Escobar Liquitay, Jae Hung Jung, Juan Víctor Ariel Franco
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2021; 62(5): 520. CrossRef - Benefits of sucrose octasulfate (TLC-NOSF) dressings in the treatment of chronic wounds: a systematic review
Harikrishna Nair, N Venkateshwaran, Selva Seetharaman S, Wuquan Deng, Apinan Uthaipaisanwong, Emilio Galea
Journal of Wound Care.2021; 30(Sup4): S42. CrossRef - Introduction to the GRADE Approach for Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline Development
Eu Chang Hwang, Jae Hung Jung
Urogenital Tract Infection.2019; 14(1): 26. CrossRef
- Levels of Evidence, Quality Assessment, and Risk of Bias: Evaluating the Internal Validity of Primary Research
- 828 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Clinical Guidelines for Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Acute Uncomplicated Pyelonephritis
- Ki Ho Kim, Jae Heon Kim, Seung-Ju Lee, Hong Chung, Jae Min Chung, Jae Hung Jung, Hyun Sop Choe, Hun Choi, Sun-Ju Lee, The Committee of The Korean Association of Urogenital Track Infection and Inflammation
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(2):55-64. Published online August 31, 2017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To date, there has not been an establishment of guidelines for urinary tract infections, due to limited domestic data in Korea, unlike other North American and European countries. The clinical characteristics, etiology, and antimicrobial susceptibility of urinary tract infections vary from country to country. Moreover, despite the same disease, antibiotic necessary to treat it may vary from country to country. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a guideline that is relevant to a specific country. However, in Korea, domestic data have been limited, and thus, guidelines considering the epidemiological characteristics pertaining specifically to Korea do not exist. Herein, describe a guideline that was developed by the committee of The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation, which covers only the uncomplicated urinary tract infections, as covering all parts in the first production is difficult.
- 1,090 View
- 6 Download

Original Article
- The Antibiotic Susceptibility of Escherichia coli from Community-Acquired Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection: A Focused on Fosfomycin
- Hyun-Sop Choe, Seung-Ju Lee, In Ho Chang, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Hong Chung, Jae Min Chung, Sang Don Lee, Jae Hung Jung, Ki Ho Kim, Seung Ki Min, Yong Gil Na, Hana Yoon, Ho Song Yu, Mi-Kyung Lee, Sun-Ju Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(2):77-81. Published online August 31, 2017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: To assess the antibiotic susceptibility of Escherichia coli from community-acquired uncomplicated urinary tract infection (UTI).
Materials and Methods: Between August and December of 2015, confirmed cases of E. coli as a pathogen of community-acquired uncomplicated UTI were collected and assessed for antibiotic susceptibility in 10 designated hospitals. Additional fosfomycin susceptibility test was performed by a central laboratory using the disk diffusion method.
Results: A total of 347 E. coli isolates were collected from urine samples of community-acquired uncomplicated UTIs patients. The susceptibility rates of antibiotics were as follows: amikacin 100.0% (347), imipenem 100.0% (347), ciprofloxacin 57.1% (198), cefotaxime 74.9% (260), ampicillin 30.0% (104), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole 66.9% (232), and fosfomycin 98.0% (340). All fosfomycin-resistant E. coli isolates were extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing. In 85 cases of ESBL-producing E. coli, the fosfomycin susceptibility rate was 91.8% (78/85).
Conclusions: Fosfomycin may be a useful option for the treatment of community-acquired uncomplicated UTIs. Further studies evaluating the role of fosfomycin in the treatment of UTIs and its clinical efficacy are necessary.
- 392 View
- 0 Download

Reviews
- 2017 Guidelines of The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation: Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis
- Ki Ho Kim, Seung-Ju Lee, Yong-Hyun Cho, Hyun-Sop Choe, Yong Gil Na, Jae Heon Kim, Hong Chung, Jae Min Chung, Jae Hung Jung, Hoon Choi, Sun-Ju Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):3-6. Published online April 30, 2017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acute uncomplicated cystitis is the most common urinary tract infection that mainly occurs in adult females, particularly sexually active young women and postmenopausal women. It is commonly observed in primary health care settings, including urology as well as obstetrics and gynecology; more than half of healthy adult women visit clinics and hospitals at least once in their lifetime due to acute uncomplicated cystitis. The most common bacterium causing this condition is Escherichia coli, followed by Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and etc. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or fluoroquinolones have been used as an empirical antibiotic treatment. However, as fluoroquinolone-resistant organisms or extended spectrum beta-lactamase-producing organisms are becoming more prevalent worldwide, information on regional antibiotic resistance and guidelines on antibiotic use are becoming increasingly more desparate.
- 826 View
- 4 Download

- 2017 Guidelines of The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation: Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection
- Seung-Ju Lee, Hyun-Sop Choe, Yong Gil Na, Ki Ho Kim, Jae Heon Kim, Hong Chung, Jae Min Chung, Jae Hung Jung, Hoon Choi, Sun-Ju Lee, Yong-Hyun Cho
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):7-14. Published online April 30, 2017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recurrent infection after an acute urinary tract infection (UTI) episode is common in adult women. It is onerous to both the patient and the physician to treat frequent recurrent UTI. Every time when UTI recurs, patients experience lower urinary tract symptoms, fatigue, and limitation in everyday life, while the physician has difficulty in counseling patients with a disease entity whose pathophysiology is less known. Currently, prophylactic treatment for recurrent UTI is limited, is ineffective in most cases, and sometimes accompanies unexpected side effects. In this guideline, we aimed to establish feasible and effective recommendations for the treatment of recurrent UTI in healthy adult women.
- 543 View
- 4 Download

Original Article
- Clinical Significance of National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index Pain Score in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Chang Min Lee, Jae Mann Song, Kwang Jin Kim, Tae Wook Kang, Seung Hoon Ryang, Yun Byung Chae, Hyun Chul Chung, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2015;10(2):102-107. Published online October 31, 2015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: Many benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) patients were accompanied by pelvic pain apart from urinary symptoms. Therefore, we evaluate the treatment outcomes of alpha-blockers via a change of international prostate symptom score (IPSS) according to pain score of the National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI).
Materials and Methods: A total of 356 male patients with BPH from March 2011 to May 2014 were analyzed retrospectively. Prostate specific antigen, prostate volume, IPSS, NIH-CPSI, international index of erectile function (IIEF-5), and uroflowmetry were collected. Patients were categorized according to 2 groups based on the presence and severity of pain and baseline characteristics and treatment outcomes were analyzed.
Results: Two hundred twenty-nine patients (64.3%) reported pain/discomfort on NIH-CPSI. Mean IPSS, mean voiding symptoms, mean storage symptoms on IPSS, and mean IIEF-5 showed a significant difference in groups 1A and 1B. Logistic regression analysis showed that NIH-CPSI pain score was a significant predictive factor for severe IPSS (odds ratio, 2.830; 95% confidence interval, 1.307-6.129). After treatment for 3 months, improvement of IPSS, voiding symptoms, storage symptoms, and quality of life was observed in all groups (p=0.001, p<0.001, p=0.026, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001). Group 2B (pain score>5) showed greater improvement of symptoms and statistically significant difference compared with group 2A (pain score ≤5) (p=0.029, p=0.026).
Conclusions: We suggest that the presence and severity of pain score are helpful for therapeutic efficacy in patients with BPH.
- 596 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Penile Mass Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Seung Hoon Ryang, Minseob Eom, Tae Wook Kang, Chang Min Lee, Hyun Chul Chung, Jae Mann Song, Kwang Jin Kim, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2015;10(2):126-129. Published online October 31, 2015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tuberculosis of the penis is rare. The clinical features of penile tuberculosis are usually manifested as ulceration or scars. However, the authors encountered a case of penile tuberculosis that presented as a mass. A painless nodule at the base of the penis was noted in a 63-year-old male patient. Surgical excision was recommended, and pathologic finding revealed granulomatous inflammation in the mass. Acid fast bacilli stain and culture were negative, but a positive result was found in urine polymerase chain reaction for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. He was diagnosed with tuberculosis of the penis and underwent anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy.
- 416 View
- 0 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


