Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Beyond the Number: Interpreting Prostate-Specific Antigen Elevation in the Context of Prostate Inflammation
- Byoungkyu Han, Ki-Hyuck Moon
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):132-143. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550032016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is indispensable but not cancer specific; inflammation, benign prostatic hyperplasia, urinary retention, ejaculation, and instrumentation can all elevate PSA and complicate cancer risk assessment. This review synthesizes current evidence and guidelines to support clinicians in interpreting PSA elevations when inflammation is present or suspected. Acute febrile urinary tract infection and acute bacterial prostatitis may produce very high PSA values, sometimes exceeding 100 ng/mL, and normalization can be slow; therefore, PSA testing during active infection is discouraged. When PSA is only mildly to moderately elevated, standardized repeat testing is essential because a meaningful proportion of results normalize on retesting. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-first pathway improves detection of clinically significant prostate cancer while reducing overdiagnosis and enables biopsy deferral after a negative MRI under structured monitoring. PSA density (PSAD) further refines triage alongside MRI, with practical working thresholds of roughly 0.10–0.20 ng/mL/cm3 calibrated to MRI quality and pretest risk. However, asymptomatic histologic prostatitis (National Institutes of Health category IV) is common and may raise PSA without reliably altering PSAD, which means that PSAD alone cannot confirm that an elevation is attributable solely to inflammation. Validated secondary biomarkers (e.g., Prostate Health Index, 4Kscore, IsoPSA [isoform PSA], Stockholm3, Proclarix, PCA3 [prostate cancer gene 3], SelectMDx [select molecular diagnostics], ExoDx [exosome diagnostics], MPS/MPS2 [MyProstateScore/MyProstateScore 2.0]) are best used selectively when MRI is negative or equivocal and clinical risk remains uncertain. A pragmatic sequence—confirm, image, and refine—helps minimize missed clinically significant cancer while reducing unnecessary antibiotics and biopsies when inflammation is the predominant driver of PSA elevation.
- 685 View
- 14 Download

Original Articles
- Diagnostic Utility of the Sysmex UF-5000 Flow Cytometer in Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: A Retrospective Pilot Study
- Young Kyu Han, Jeong Woo Lee, Hae-Il Park, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):107-113. Published online August 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550022011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader - Purpose
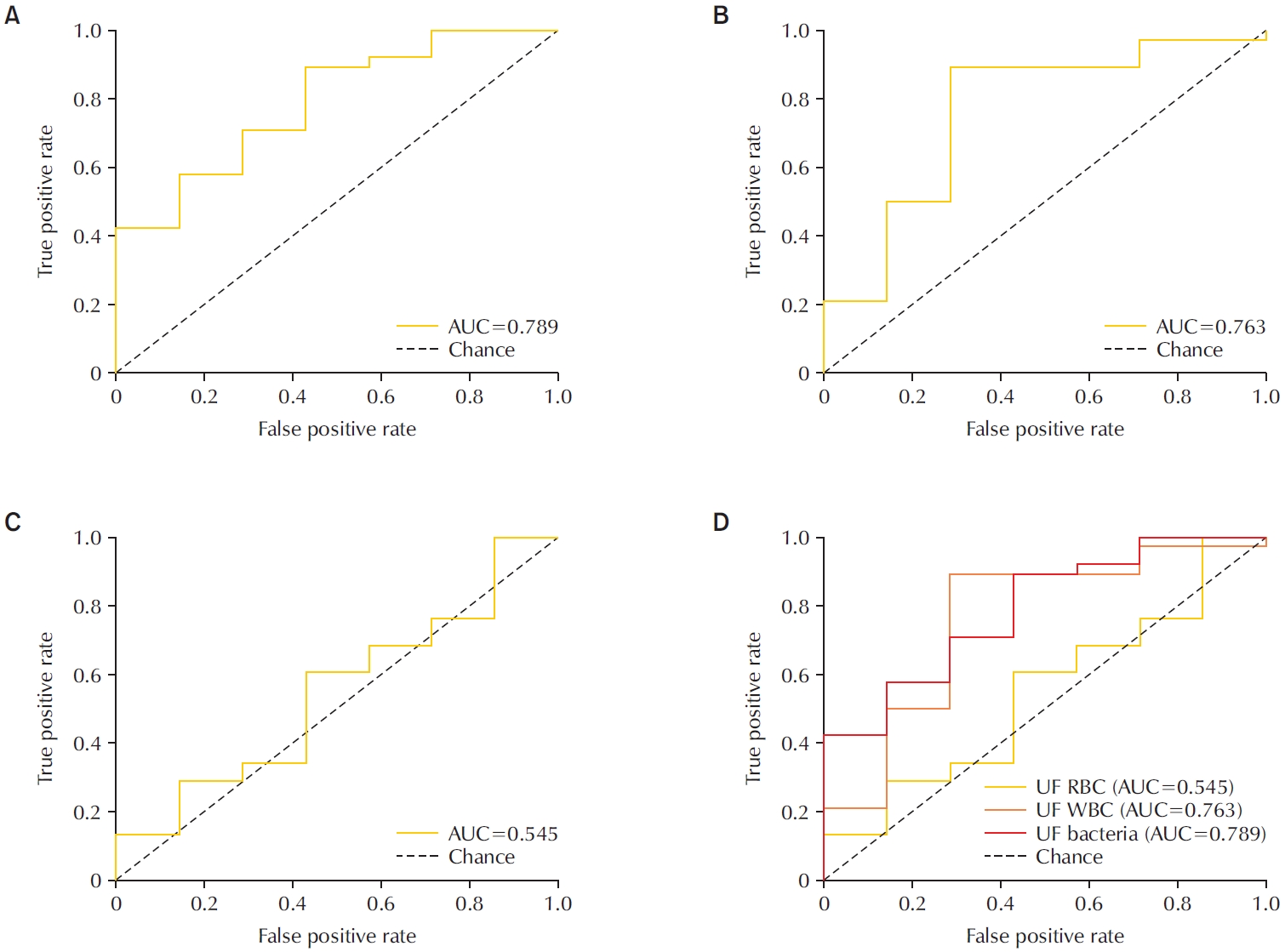
To evaluate the diagnostic performance of the Sysmex UF-5000 flow cytometer in detecting acute bacterial prostatitis (ABP) compared to standard urine culture. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 45 urine samples from patients with a clinical diagnosis of ABP. Each sample was evaluated using the UF-5000 to measure red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), and bacterial counts, and the results were compared with those from standard urine culture and Gram staining. Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated, and sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value were determined. Concordance between Gram classification by the UF-5000 and conventional Gram staining was also evaluated.
Results
Of the 45 patients, 84.4% had positive urine cultures. The bacterial count parameter demonstrated the highest diagnostic performance (area under the curve [AUC]=0.79; sensitivity, 89.5%; PPV, 91.9%), outperforming WBC (AUC=0.76) and RBC (AUC=0.55). The Gram classification flag showed an overall concordance of 85.7% with conventional Gram staining, with a concordance rate of 88% for Gram-negative organisms.
Conclusions
The Sysmex UF-5000 exhibited good concordance with urine culture for patients with ABP, particularly through the bacterial count parameter. Although it does not replace culture, the UF-5000 may serve as a rapid adjunctive tool to support early clinical decision-making in suspected ABP cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef - A Commentary on “Diagnostic Utility of the Sysmex UF-5000 Flow Cytometer in Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: A Retrospective Pilot Study”
Dong-Hoon Lim
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(3): 173. CrossRef
- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 1,462 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Efficacy of Urovaxom for Improving Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Symptoms in Prostate Cancer Patients Who Underwent Radical Prostatectomy: A Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study
- Jun-Koo Kang, Yun-Sok Ha, Sungchan Park, Tae Gyun Kwon, Tae-Hwan Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):42-47. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550014007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) is a multifactorial condition that can significantly diminish quality of life. Although some patients have reported persistent pelvic pain after radical prostatectomy (RP), the prevalence and direct causal relationship between CPPS and RP remain unclear. This multicenter prospective study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of Urovaxom for improving CPPS symptoms. Materials and Methods: A total of 52 prostate cancer patients who underwent RP were enrolled and administered Urovaxom (60 mg/day) for 12 weeks. Changes in National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI), overactive bladder symptom score (OABSS), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), and inflammation markers (white blood cell [WBC], C-reactive protein [CRP]) were analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results
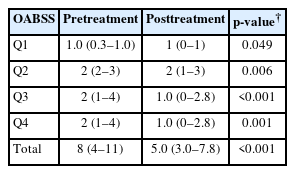
After 12 weeks of treatment, the NIH-CPSI total score significantly decreased from 19 (interquartile range [IQR], 16–23) to 12.5 (IQR, 8.0–16.8) (p<0.001). The OABSS total score decreased from 8 (IQR, 4–11) to 5 (IQR, 3.0–7.8), and the IPSS total score decreased from 13.5 (IQR, 10.0–22.8) to 10.5 (IQR, 5.0–17.0) (p<0.001). WBC levels showed a slight increase (p=0.028), but the clinical relevance of this change is uncertain and warrants further investigation. CRP changes were not statistically significant (p=0.274).
Conclusions
Urovaxom demonstrated significant efficacy in improving CPPS symptoms, particularly pain and reduced quality of life, in patients following RP. These findings suggest Urovaxom as a potential therapeutic option for CPPS after management using RP. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Addressing an Unmet Need in Postprostatectomy Care: Perspectives on Urovaxom
Byeong Jin Kang
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 118. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 5,155 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Reports
- Klebsiella pneumoniae-Induced Emphysematous Prostatic Abscess Accompanied by a Spinal Cord Infarction: Case Report
- Seong Uk Jeh, Min Sung Choi, Chang Seok Kang, Dae Hyun Kim, Jae Hwi Choi, See Min Choi, Sung Chul Kam, Jeong Seok Hwa, Jae Seog Hyun
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):104-108. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448024012
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
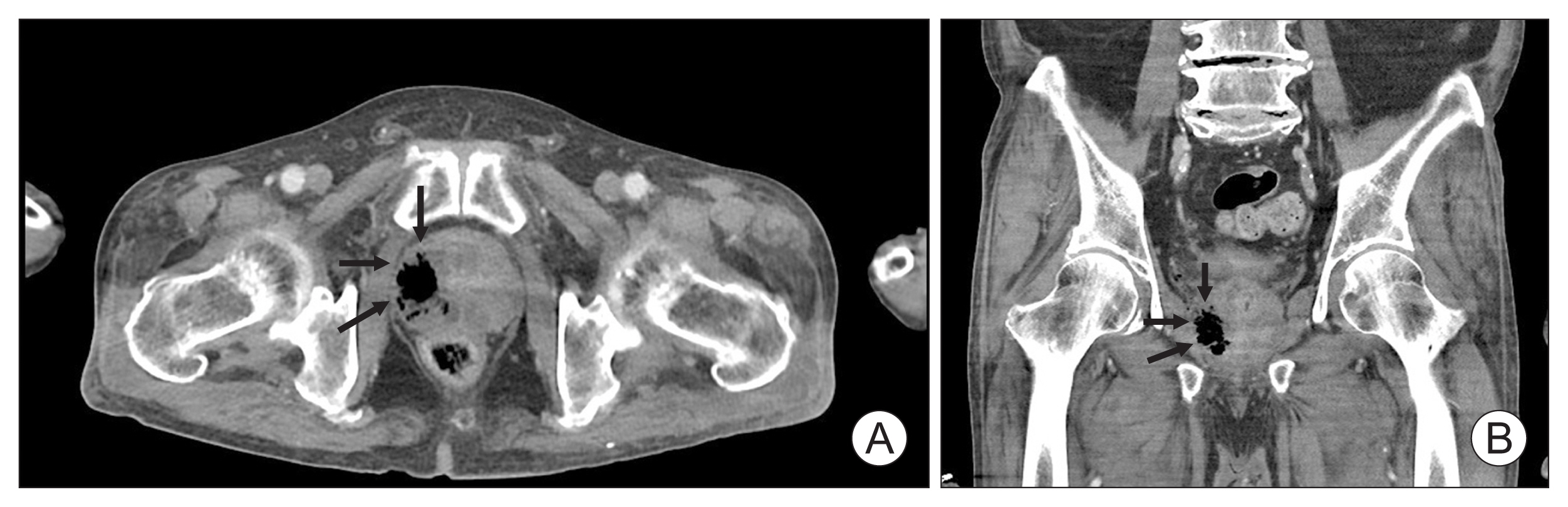
ePub - Various strains can be found in emphysematous prostatic abscesses (EPAs), but the most frequent causative organism is Klebsiella pneumoniae . Hypervirulent K. pneumoniae can disseminate to distant sites by forming a muco-polysaccharide network outside the capsule. Here, we present the first case of K. pneumoniae in an EPA accompanied by a spinal cord infarction. A 65-year-old man was referred to our hospital due to sudden-onset paraplegia after a 5-day history of fever, myalgia, and voiding difficulty. Abdominal computed tomography revealed a collection of air pockets in the prostate, and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging showed high signal intensity in the thoracic spinal cord. The patient was initially treated with antibiotics and surgical drainage. On the third hospital day, therapeutic heparin was added after discussion with a neurologist. The patient had no inflammatory symptoms, experienced some improvement in paraplegia, and was discharged on the 14th hospital day. This study adhered to the case report guidelines.
- 2,231 View
- 23 Download

- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: Case Report
- Kwang Jin Kim, Yoonsuk Lee, Yong Sung Cha, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Hong Chung, Hyun Kim, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):44-47. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) was conducted on two male patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome who were resistant to conventional medical therapies. Both patients underwent 20 sessions of 100% oxygen inhalation (2.0 atmosphere absolute for 90 min/day, five days/week for four weeks) in a hyperbaric chamber. The follow-up period was three months. Although the patients reported a slight improvement in the pain domain of the National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) after HBOT, no changes were noted in the other domains of NIH-CPSI and International Prostate Symptom Score. No adverse events were encountered during or after HBOT.
- 5,283 View
- 35 Download

Original Article
- Pelvic Pain in Men with Mycoplasma Genitalium
- Yumi Seo
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(1):16-23. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: There are debates about Mycoplasma genitalium (M. genitalium) causing prostate infection and inducing pelvic pains. Consequently, M. genitalium-associated pelvic pains were characterized and their manifestation in male pelvic pain syndrome (MPPS) was evaluated through a case-control study.
Materials and Methods: The presence of M. genitalium-associated pelvic pains was examined in 113 M. genitalium-infected men, and the typical presentations of mycoplasma-associated MPPS were characterized through a case-control study involving 80 mycoplasma-infected and 234 case-matched uninfected controls. Finally, changes in symptoms following antimicrobial treatments were compared between 27 cured and 14 persistently infected cases.
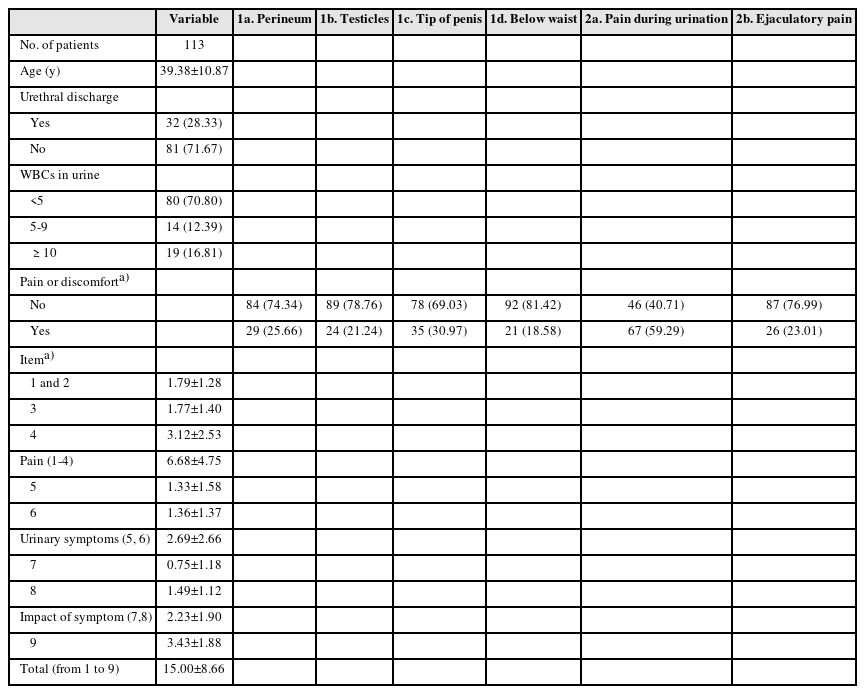
Results: Pain locations from 113 men were followed as items-1a for 25.7%, 1b for 21.2%, 1c for 31%, 1d for 18.6%, 2a for 59.3%, and 2b for 23% from the Korean National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) questionnaire. In addition, the sum scores from the pain domain, voiding domain and total score were 6.68±4.75, 2.69±2.66, and 15.00±8.66, respectively. Successful antibiotic therapy significantly reduced the total score from baseline (15.148±6.798 vs. 5.357±7.025, p=0.001). From the case-control study, mycoplasma-infected men had pains more frequently during urination (1c) and on the tip of the penis (2a) (all p=0.0001) than the controls.
Conclusions: It was found that M. genitalium infection is associated with clinically significant male pelvic pains, which improved with adequate antimicrobial therapies. Urethral irritation symptoms without pyuria may be the typical characteristics of mycoplasma-associated pelvic pains in MPPS.
- 7,235 View
- 33 Download

Case Report
- Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
- Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):114-118. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.114
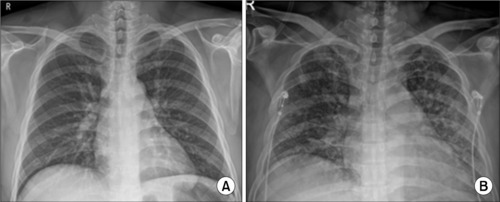
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Acute bacterial prostatitis is an acute urinary tract infection associated with a bladder outlet obstruction or an immunosuppressed state. A 51-year-old man patient visited the hospital with fever, chills, and acute urinary retention that started the day before his visit after consuming a significant amount of alcohol. Conservative treatments, including catheterization for urinary drainage and antibiotics, were performed. On the third day of treatment for acute prostatitis, he complained of dyspnea. The level of oxygen differentiation was reduced significantly, and the tracheal insertion and ventilator were maintained after the radiological examination. The ventilator was discontinued, and the prostate abscess was operated on the eighth day of hospitalization. He was discharged without complications. This paper reports a case of life-threatening pneumonia and a prostate abscess during the treatment of a patient with acute bacterial prostatitis with a review of the relevant literature.
- 3,017 View
- 8 Download

Original Article
- The Feasibility of Radical Prostatectomy for Medication Refractory Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
- Seung Chan Jeong
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(3):76-80. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.3.76
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare the National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) scores of patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) given pharmacological treatment with those who additionally had prostate cancer and underwent surgical treatment.
Materials and Methods: From January 2000 to March 2021, a total of 7,650 patients were diagnosed with chronic prostatitis (N41.1) at our hospital, of which 234 patients were additionally diagnosed with prostate cancer. After excluding patients with severe benign prostatic hyperplasia (>100 g)-related lower urinary tract symptoms or neurological and psychiatric abnormalities, or advanced prostate cancer, 52 patients undergoing pharmacological treatment with a combination of drugs and 20 patients who underwent radical prostatectomy due to additional prostate cancer were included in the analysis. The NIH-CPSI scores of the two groups were compared at the first outpatient visit, 3 months, and 6 months after the first visit. The p-values were calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test, and the Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Results: Patients who underwent radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer showed significant reductions in the voiding and quality of life scores in the NIH-CPSI, but not the pain score at 3 months. After 6 months, there was a significant decrease in the overall NIH-CPSI. On the other hand, in the group on pharmacological therapy, the decrease was statistically significant only in the voiding score at 6 months. However, in the surgery group, 3 patients were found to be suffering from urinary incontinence, and 7 patients from erectile dysfunction.
Conclusions: Radical prostatectomy, therefore, appears to be a promising treatment that can be carefully considered for patients with refractory CP/CPPS who do not receive adequate treatment and thus have a poor quality of life.
- 3,087 View
- 9 Download

Review
- UPOINT System: A Diagnostic/Therapeutic Algorithm for Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
- Phil Hyun Song
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(2):27-32. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.2.27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is a common condition that significantly affects the quality of life. On the other hand, urologists find it challenging to treat this disorder effectively. To date, the Urinary, Psychosocial, Organ-Specific, Infection, Neurological/Systemic, and Tenderness (UPOINT) system is the only classification tool that can improve the treatment outcomes significantly compared to monotherapy. This review focused on the most recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of CP/CPPS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment Modality of Prostatic Abscess according to Size: A Retrospective Study
Gwon Kyeong Lee, Kyoung Ha Jang, Woo Seop Seong, Byeong Jin Kang, Kyung Hwan Kim, Hong Koo Ha
Urogenital Tract Infection.2022; 17(3): 96. CrossRef
- Treatment Modality of Prostatic Abscess according to Size: A Retrospective Study
- 9,726 View
- 65 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


