Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Adult Syphilis: A Narrative Review of Clinical Insights and Public Health Implications in Urology
- Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):123-131. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550039017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
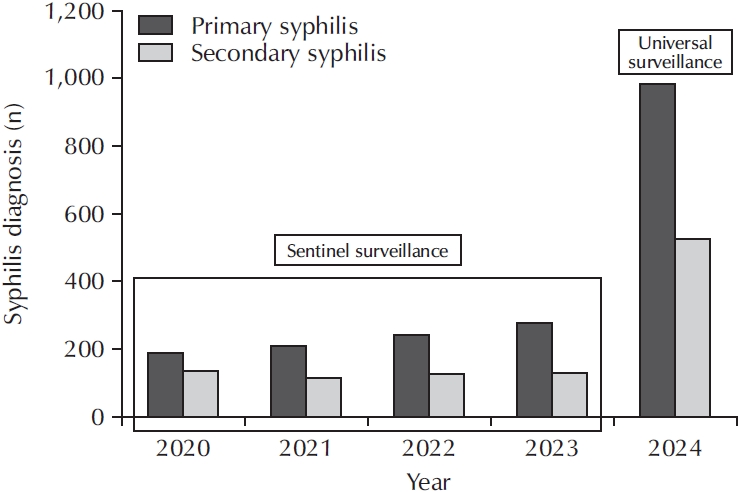
ePub - Syphilis continues to pose a major global public health concern, with more than 7 million cases reported worldwide in 2022, and its incidence continues to rise in numerous regions. In Korea, the shift from sentinel to universal notification in 2024 has revealed a markedly greater disease burden, particularly among men who have sex with men and among younger adults, underscoring changing epidemiological patterns and the urgent need for revised control strategies. In urological practice, syphilis presents with a wide range of often misleading symptoms, including painless genital ulcers, urethritis, and sexual dysfunction, that frequently resemble other genitourinary disorders and complicate diagnostic evaluation. Accurate identification relies on integrating a thorough clinical assessment with serologic testing while remaining alert to diagnostic challenges such as early latent infection, serofast states, and human immunodeficiency virus coinfection. Penicillin G remains the mainstay of therapy, with treatment regimens tailored to the stage of disease and to the presence or absence of central nervous system involvement. Effective partner notification, targeted screening, and consistent follow-up are essential to prevent reinfection and limit further transmission. At a public health level, a multifaceted strategy—strengthened surveillance systems, focused testing in high-risk populations, and embedding syphilis screening within broader sexually transmitted infection care frameworks—is critical to curbing its resurgence. In summary, prompt recognition, adherence to evidence-based management, and coordinated public health measures, together with ongoing advances in diagnostics and prevention, remain fundamental to reducing the continued spread of syphilis and mitigating its impact on both individual and population health.
- 581 View
- 9 Download

Original Articles
- Diagnostic Utility of the Sysmex UF-5000 Flow Cytometer in Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: A Retrospective Pilot Study
- Young Kyu Han, Jeong Woo Lee, Hae-Il Park, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):107-113. Published online August 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550022011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader - Purpose
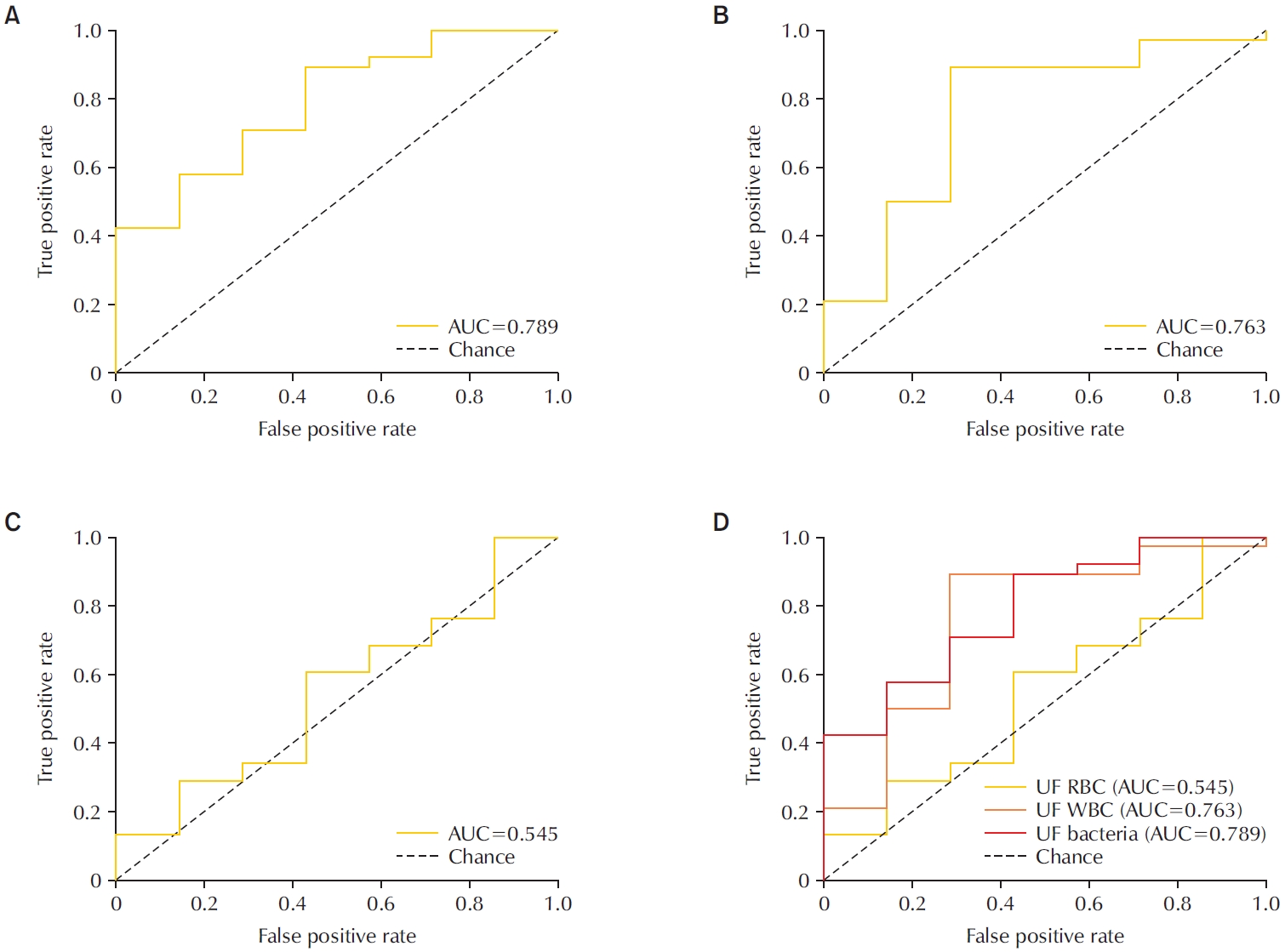
To evaluate the diagnostic performance of the Sysmex UF-5000 flow cytometer in detecting acute bacterial prostatitis (ABP) compared to standard urine culture. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 45 urine samples from patients with a clinical diagnosis of ABP. Each sample was evaluated using the UF-5000 to measure red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), and bacterial counts, and the results were compared with those from standard urine culture and Gram staining. Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated, and sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value were determined. Concordance between Gram classification by the UF-5000 and conventional Gram staining was also evaluated.
Results
Of the 45 patients, 84.4% had positive urine cultures. The bacterial count parameter demonstrated the highest diagnostic performance (area under the curve [AUC]=0.79; sensitivity, 89.5%; PPV, 91.9%), outperforming WBC (AUC=0.76) and RBC (AUC=0.55). The Gram classification flag showed an overall concordance of 85.7% with conventional Gram staining, with a concordance rate of 88% for Gram-negative organisms.
Conclusions
The Sysmex UF-5000 exhibited good concordance with urine culture for patients with ABP, particularly through the bacterial count parameter. Although it does not replace culture, the UF-5000 may serve as a rapid adjunctive tool to support early clinical decision-making in suspected ABP cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef - A Commentary on “Diagnostic Utility of the Sysmex UF-5000 Flow Cytometer in Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: A Retrospective Pilot Study”
Dong-Hoon Lim
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(3): 173. CrossRef
- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 1,459 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Mortality and Risk Factors for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):34-41. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550006003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
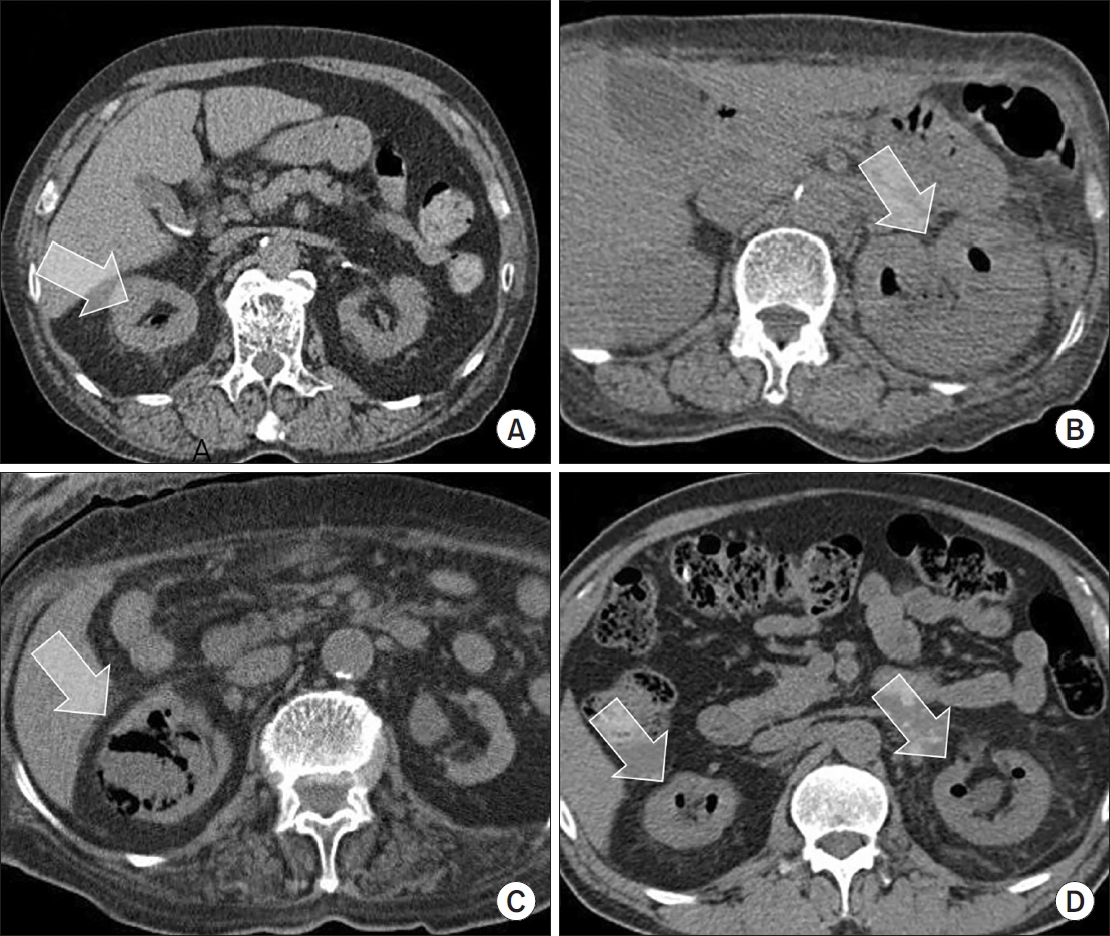
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a life-threatening disease requiring immediate treatment. This multicenter retrospective cohort study aimed to analyze the mortality rate and risk factors associated with EPN. Materials and Methods: Between January 2011 and February 2021, 217 patients diagnosed with EPN via computed tomography who visited 14 teaching hospitals were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical data, including age, sex, comorbidities, Huang and Tseng classification, hydronephrosis, acute kidney injury, blood and urine tests, surgical interventions, percutaneous drainage, and conservative treatments, were compared between the survival and death groups. Risk factors for mortality due to EPN were analyzed using univariate and multivariate methods.
Results
The mean age of survivors and deceased patients was 67.8 and 69.0 years, respectively (p=0.136). The sex distribution (male/female) was 48/146 and 8/15, respectively (p=0.298). Of the 217 patients, 23 died, resulting in a mortality rate of 10.6%. In univariate analysis, the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.004), platelet count (p=0.005), and acute kidney injury (p=0.007) were significantly associated with mortality from EPN. In multivariate analysis, only the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.029) was identified as a risk factor. Mortality rates according to the Huang and Tseng classification were as follows: class I (5.88%), class II (7.50%), class IIIa (14.28%), class IIIb (25.00%), and class IV (23.07%).
Conclusions
EPN is associated with a high mortality rate. Among various clinical factors, the Huang and Tseng classification was the most significant indicator for predicting mortality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 3,368 View
- 60 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- A Narrative Review of Syphilis Notification Systems in Korea: Change to Mandatory Surveillance System
- Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):28-33. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550004002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
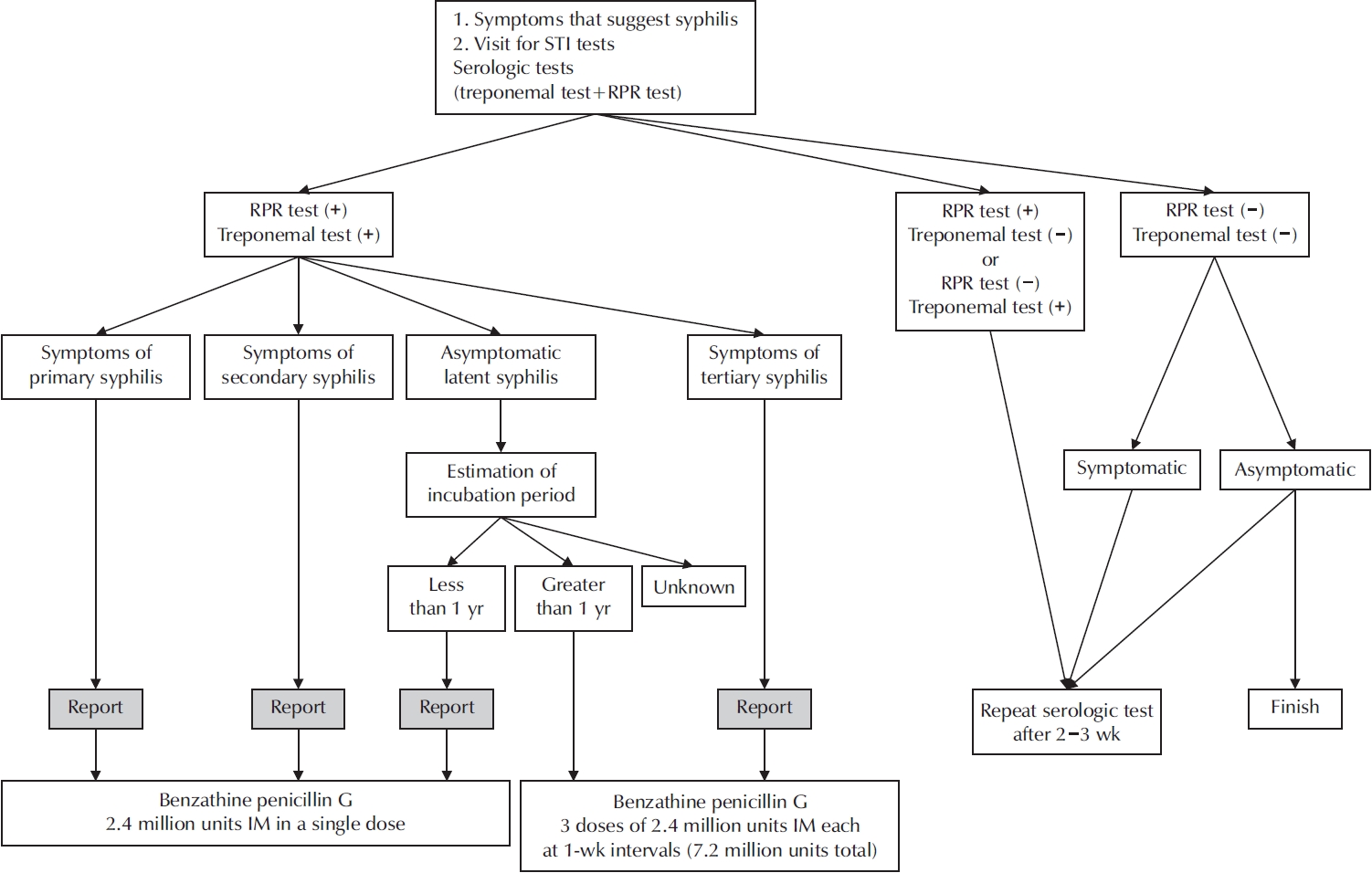
ePub - New cases of syphilis are clearly showing an increasing trend worldwide. However, in a sentinel surveillance system, the collection of information on disease outbreaks is limited, making it difficult to understand the overall outbreak situation and perform detailed analyses of patients' demographic characteristics and disease stages. In accordance with the revision of the Infectious Disease Prevention Act, syphilis was converted from a grade 4 infectious disease subject to sentinel surveillance to a grade 3 infectious disease subject to mandatory surveillance from January 1, 2024, with all medical institutions required to report syphilis diagnosis within 24 hours.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Adult Syphilis: A Narrative Review of Clinical Insights and Public Health Implications in Urology
Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(3): 123. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 5,279 View
- 38 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Trend Analysis of Sexually Transmitted Infection Treatments in Korea
- Soeon Park, Byung Kyu Han, Sangrak Bae, Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):25-30. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.25
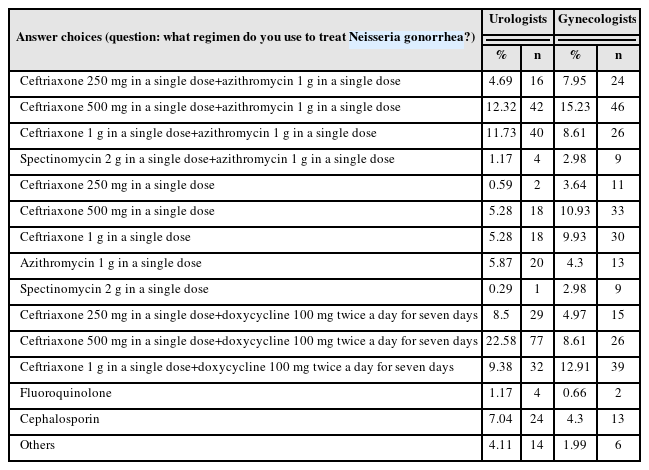
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: The revision of the 2023 Guidelines for the Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) has been released. Hence, it is necessary to analyze the current status of STI treatments in Korea.
Materials and Methods: A questionnaire was distributed to urologists and gynecologists from December 2022 to January 2023 through an online survey program. Three hundred and forty-one urologists and 302 gynecologists responded to the questionnaire.
Results: For Neisseria gonorrhea treatment, ceftriaxone 500 mg and 100 mg of doxycycline twice daily for seven days were most preferred by urologists (22.58%). The treatment most preferred by gynecologists (15.23%) was 500 mg of ceftriaxone and 1 g of azithromycin in a single dose. Both urologists and gynecologists generally treat Chlamydia trachomatis according to the treatment guidelines. For treating Mycoplasma genitalium, 29.03% of urologists preferred administering azithro-mycin at 500 mg once daily, followed by 250 mg for four days. In contrast, 33.11% of gynecologists preferred doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for seven days.
Conclusions: Most urologists and gynecologists followed the treatments recommended in the 2nd edition of the STI treatment guidelines, revised in 2016. As many treatment regimens have changed because of the recent increase in antibiotic-resistant STIs, there is a need to encourage them to follow the new treatment guidelines. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Study of the Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Sexually Transmitted Infections Diagnosed by Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests
Jung Soo Son, Namhee Kim, Hong Sang Oh, Sang Won Park, Dong Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparative Study of the Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Sexually Transmitted Infections Diagnosed by Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests
- 6,766 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Characteristics and Treatment Trends for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A 10-Year Multicenter Retrospective Study
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Koo Han Yoo, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(2):49-54. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.2.49
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study examined the characteristics, current treatment trends, and outcomes of patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) in Korea.
Materials andMethods: Two hundred and seventeen patients diagnosed with EPN were evaluated using abdominal computed tomography in 2011-2021 at 15 institutes in Korea. The patients’ demographic and clinical characteristics, treatment modalities, and treatment outcomes were analyzed. The total study period was divided arbitrarily into groups A (2011-2014), B (2015-2017), and C (2018-2021) to analyze the trends in the EPN treatment.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 65.1 years; there were more female patients (74.2%) than male patients. The overall mortality rate was 10.6%. Ninety-five (43.8%), 98 (45.2%), and 24 (11.0%) patients were treated with medical, minimally invasive, and surgical management, respectively; the corresponding mortality rates were 13.7%, 6.1%, and 16.7%. There was no significant change in the proportion of patients treated with medical management over time (group A=46.5%, group B=47.0%, and group C=38.8%). The proportion of patients treated with minimally invasive management gradually increased over time (group A=35.2%; group B=43.9%; group C=55.0%), while those who underwent surgical management decreased gradually over time (group A=18.3%, group B=9.1%, and group C=6.3%). No differences in mortality rates were observed between the groups.
Conclusions: EPN with medical and minimally invasive management had a relatively high treatment success rate, which increased gradually, while surgical management decreased gradually over time in Korea. The mortality rate was relatively lower than that reported in studies published before the 2010s.
- 2,024 View
- 8 Download

Review
- Healthcare-Associated Urinary Tract Infection: Multi Drug Resistance and Risk Factors
- Jin Bong Choi, Seung-Ju Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2018;13(2):21-25. Published online August 31, 2018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A new category of infections called healthcare-associated (HCA) infections was created due to increased procedures performed in outpatient clinics of hospitals. The risk of HCA infections is on the rise as the use of long-term care facilities (LTCFs) is increasing. HCA-urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most frequently occurring bacterial infections. In clinical and microbiological analyses, HCA-UTI is similar to hospital-acquired-UTI. The prevalence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) organisms in HCA-UTI has increased and is varied according to the type of LTCFs and regions. Finally, prior investigations reported the association between several risk factors and MDR acquisition, which vary considerably according to study design. Therefore, additional research is needed to develop a more accurate methodology.
- 391 View
- 2 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


