Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Fournier Gangrene: A 15-Years Multicenter Retrospective Study in Korea
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Sin Woo Lee, Hyung-Lae Lee, Jeong Woo Lee, Jung Sik Huh, Yeonjoo Kim, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):159-166. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550036018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
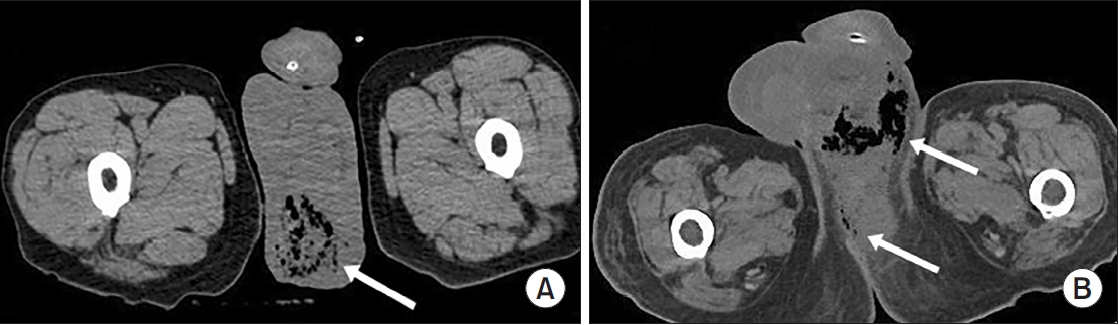
Fournier gangrene (FG) is a rare but life-threatening necrotizing infection requiring prompt recognition and intervention. This multicenter study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics, treatment outcomes including mortality, and risk factors associated with death among patients with FG over the past 15 years in Korea. Materials and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 84 patients diagnosed with FG between 2008 and 2022 across 7 hospitals. Demographics, comorbidities, laboratory findings, and clinical outcomes were analyzed. Mortality-related risk factors were assessed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Results
The mean age was 58.1±15.9 years, and 95.2% of patients were male. Diabetes mellitus (42.9%) and hypertension (36.9%) were the most prevalent comorbidities. Sepsis developed in 38.1% of patients, and the overall mortality rate was 14.3%. In univariate analysis, age ≥70 years, low body mass index, diabetes mellitus, low hemoglobin, low hematocrit, high respiratory rate, and Fournier gangrene severity index (FGSI) ≥9 were significantly associated with mortality. After data correction and multivariate adjustment, diabetes mellitus (odds ratio [OR], 39.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.39–656.32; p=0.010) and respiratory rate (OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.09–1.91; p=0.011) were identified as independent predictors of mortality. FGSI≥9 demonstrated borderline association with mortality (p=0.08), indicating its potential clinical relevance.
Conclusions
In this multicenter Korean cohort, the mortality rate of FG remained substantial at 14.3%. Diabetes mellitus and elevated respiratory rate were independent predictors of mortality, while FGSI≥9 demonstrated a borderline yet clinically meaningful association, suggesting its role as a useful severity indicator in early risk stratification.
- 247 View
- 9 Download

- Diagnostic Utility of the Sysmex UF-5000 Flow Cytometer in Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: A Retrospective Pilot Study
- Young Kyu Han, Jeong Woo Lee, Hae-Il Park, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):107-113. Published online August 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550022011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader - Purpose
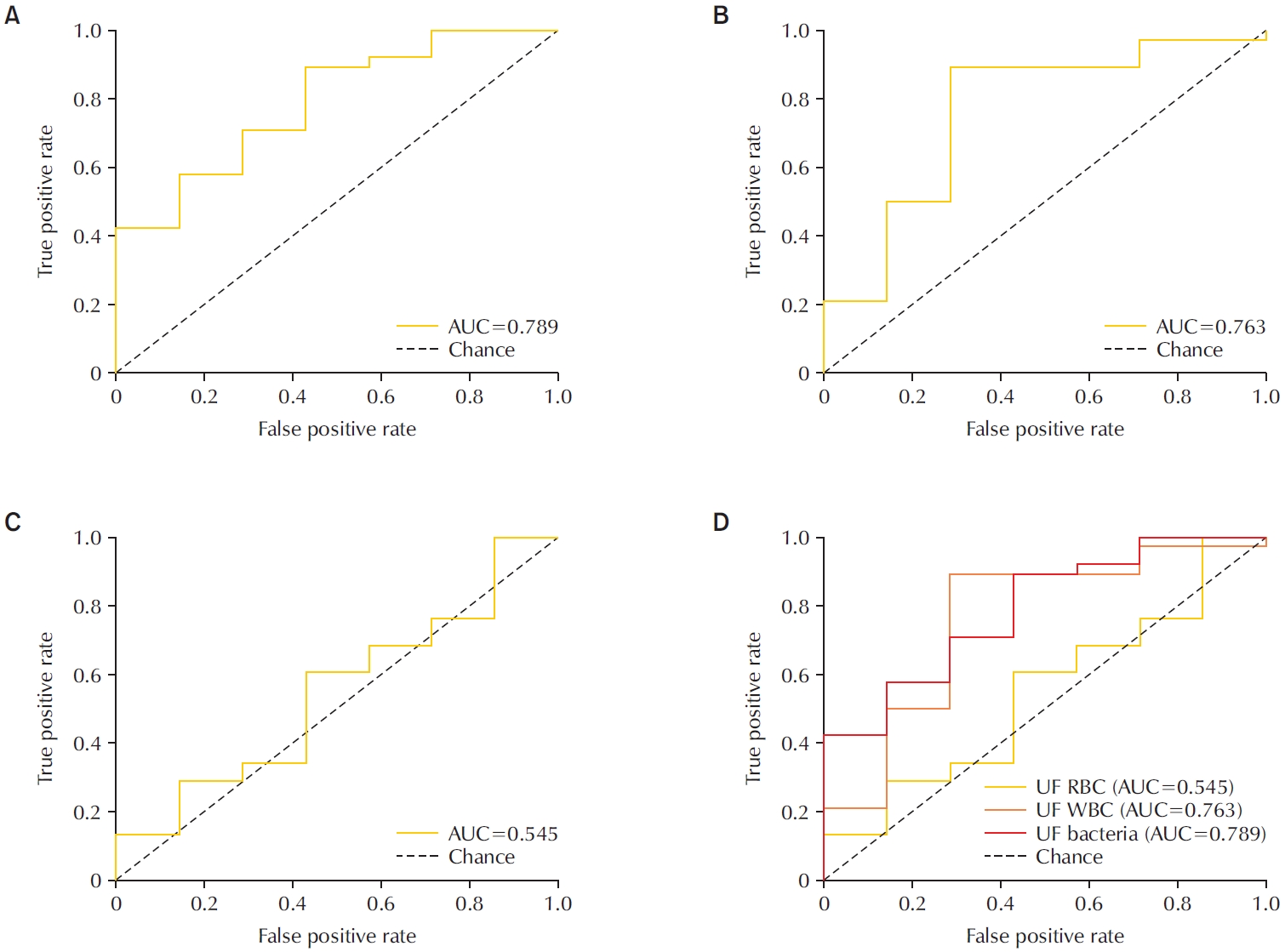
To evaluate the diagnostic performance of the Sysmex UF-5000 flow cytometer in detecting acute bacterial prostatitis (ABP) compared to standard urine culture. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 45 urine samples from patients with a clinical diagnosis of ABP. Each sample was evaluated using the UF-5000 to measure red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), and bacterial counts, and the results were compared with those from standard urine culture and Gram staining. Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated, and sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value were determined. Concordance between Gram classification by the UF-5000 and conventional Gram staining was also evaluated.
Results
Of the 45 patients, 84.4% had positive urine cultures. The bacterial count parameter demonstrated the highest diagnostic performance (area under the curve [AUC]=0.79; sensitivity, 89.5%; PPV, 91.9%), outperforming WBC (AUC=0.76) and RBC (AUC=0.55). The Gram classification flag showed an overall concordance of 85.7% with conventional Gram staining, with a concordance rate of 88% for Gram-negative organisms.
Conclusions
The Sysmex UF-5000 exhibited good concordance with urine culture for patients with ABP, particularly through the bacterial count parameter. Although it does not replace culture, the UF-5000 may serve as a rapid adjunctive tool to support early clinical decision-making in suspected ABP cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef
- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 1,221 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Hemangioma Mistaken for Renal Cell Carcinoma in a Patient With End-Stage Renal Disease: A Case Report
- Hyung-Lae Lee, Dong-Gi Lee, Jeong Woo Lee, Jeonghyouk Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):48-51. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550008004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
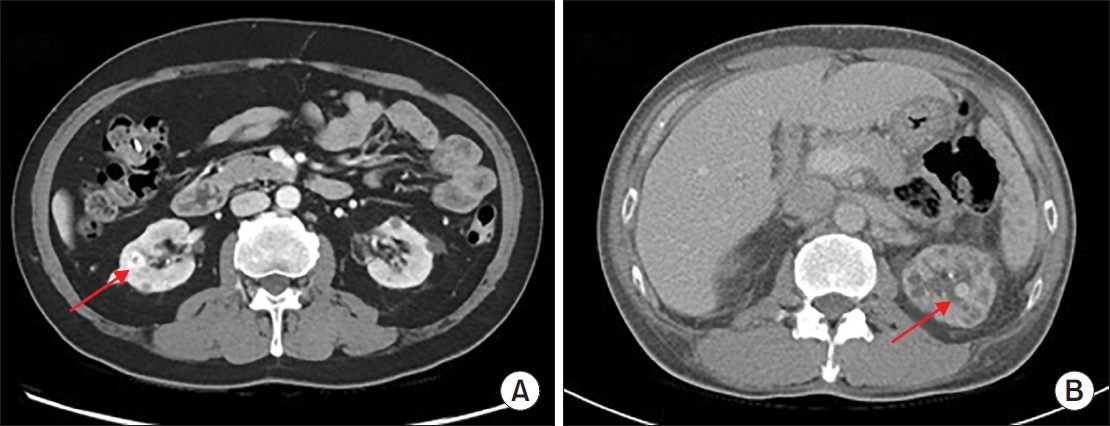
ePub - Hemangiomas are rare, benign vascular neoplasms that are more common in patients with end-stage renal disease. Here, we describe 2 cases of hemangioma misdiagnosed as renal cell carcinoma before renal transplantation. The key finding in our case was the misdiagnosis of hemangiomas as renal cell carcinoma based on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in patients with end-stage renal disease. Because living transplantation was planned for our patients, we performed rapid surgical resection of the heterogeneously enhancing renal masses to avoid delays in transplantation. Our case highlights the importance of rapid surgical resection of enhanced renal masses to confirm diagnosis, thereby avoiding delays in patients scheduled for renal transplantation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 1,810 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Mortality and Risk Factors for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):34-41. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550006003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
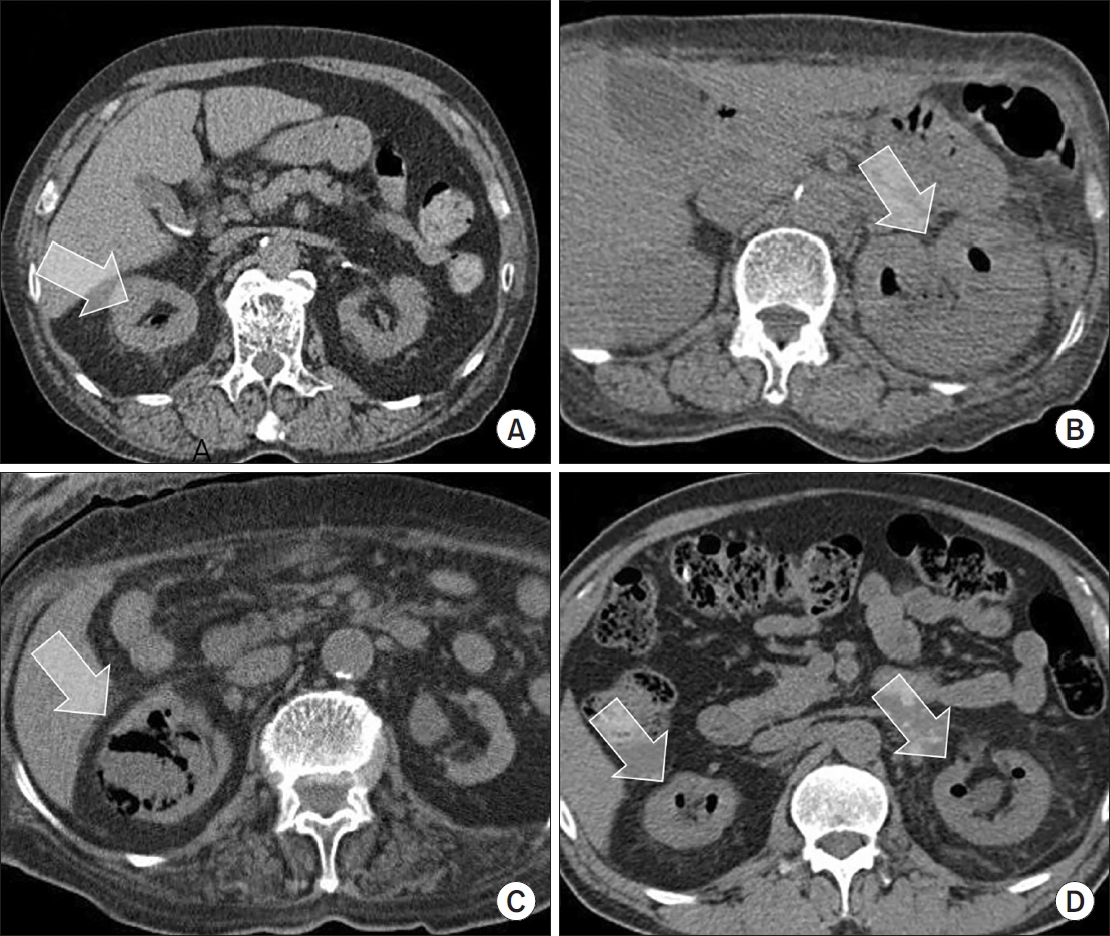
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a life-threatening disease requiring immediate treatment. This multicenter retrospective cohort study aimed to analyze the mortality rate and risk factors associated with EPN. Materials and Methods: Between January 2011 and February 2021, 217 patients diagnosed with EPN via computed tomography who visited 14 teaching hospitals were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical data, including age, sex, comorbidities, Huang and Tseng classification, hydronephrosis, acute kidney injury, blood and urine tests, surgical interventions, percutaneous drainage, and conservative treatments, were compared between the survival and death groups. Risk factors for mortality due to EPN were analyzed using univariate and multivariate methods.
Results
The mean age of survivors and deceased patients was 67.8 and 69.0 years, respectively (p=0.136). The sex distribution (male/female) was 48/146 and 8/15, respectively (p=0.298). Of the 217 patients, 23 died, resulting in a mortality rate of 10.6%. In univariate analysis, the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.004), platelet count (p=0.005), and acute kidney injury (p=0.007) were significantly associated with mortality from EPN. In multivariate analysis, only the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.029) was identified as a risk factor. Mortality rates according to the Huang and Tseng classification were as follows: class I (5.88%), class II (7.50%), class IIIa (14.28%), class IIIb (25.00%), and class IV (23.07%).
Conclusions
EPN is associated with a high mortality rate. Among various clinical factors, the Huang and Tseng classification was the most significant indicator for predicting mortality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 3,114 View
- 59 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Korean Multicenter Study of Infectious Complications after Transurethral Prostate Surgery in Patients with Preoperative Sterile Urine
- Seong Hyeon Yu, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Jae Duck Choi, Koo Han Yoo, Jeong Woo Lee, Dong Hoon Koh, Sangrak Bae, Seung Ok Yang, Joongwon Choi, Seung Ki Min, Hoon Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(3):81-88. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.3.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis and determine the risk factors of infectious complications after transurethral surgery of the prostate.
Materials and Methods: Seven hundred and seventy-two patients who underwent transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HOLEP) were reviewed. Of these, this study enrolled 643 patients without bacteriuria who had not received antibiotics for urinary tract infections for two weeks before surgery. The patients were divided into two groups according to the duration of the antibiotics (Group 1: less than one day, n=396 vs. Group 2: more than one day, n=247).
Results: The overall incidence of postoperative infectious complications in 643 patients was 5.0% (32/643). When postoperative infectious complications were compared according to the duration of the antibiotics (Group 1 vs. Group 2), the infectious complications rates were 5.6% (22/396) vs. 4.0% (10/247), respectively (p=0.393). When postoperative infectious complications were compared according to the duration of antibiotics (Group 1 vs. Group 2) in the TURP and HOLEP groups, the infectious complications rates were 6.3% (12/192) vs. 1.0% (1/103) (p=0.035) and 4.9% (10/203) vs. 6.0% (8/134) (p=0.677), respectively. The duration of Foley catheterization was independently associated with infectious complications (p=0.003).
Conclusions: The results showed that prolonged postoperative catheterization affects postoperative infectious complications associated with transurethral prostate surgery. Although antibiotics administered for less than one day are effective for antibiotic prophylaxis of transurethral prostate surgery, a longer antibiotic therapy is recommended for TURP.
- 3,465 View
- 24 Download

- Pilot Study of Cystochon® (Cranberry Extract, Chondroitin Sulfate, and Hyaluronic Acid Complex) in Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
- Kwang Taek Kim, Jeong Woo Lee, Hyun-Sop Choe
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(2):36-41. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.2.36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study examined whether Cystochon® (cranberry extract, chondroitin sulfate, and hyaluronic acid complex) effectively improves the symptoms and problems of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) patients.
Materials and Methods: From December 2021 to May 2022, the medical records of IC/BPS patients who visited St. Vincent’s Hospital, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, or Gachon University Gil Medical Center were collected. For the treatment of IC/BPS, the patients were given pentosan polysulfate (PPS) for 12 weeks, with Cystochon® then added and maintained for an additional eight weeks. The OʼLeary–Sant symptom and problem index (Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index [ICSI], Interstitial Cystitis Problem Index [ICPI]) was used to measure the treatment response.
Results: After 12 weeks of PPS treatment, ICSI and ICPI improved in all patients. After adding Cystochon® for eight weeks, the ICSI and ICPI indicators improved further. In the ICSI category, significant improvement in symptoms was confirmed in the total ICSI score, particularly in the Q4 (pain-related) questionnaire after adding Cystochon®. In the ICPI category, significant problem improvement was confirmed in the total ICPI score, particularly in the Q1 (frequent urination) and Q4 (pain-related) questionnaires. Although not statistically significant, the remaining indicators generally tended to improve.
Conclusions: The orally administered combination of cranberry extract, chondroitin sulfate, and hyaluronic acid (Cystochon®) may have a clinically positive effect in patients with IC/BPS. Better clinical improvement can be expected when it is added to the PPS treatment, especially in the category of bladder pain. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anti-inflammatory effect of sea buckthorn in an HCl-induced cystitis rat model
Hyun Suk Yoon, Juyeon Yu, Shinhoon Kang, Hana Yoon
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2025; 66(1): 67. CrossRef - Pharmacological Properties of Shionone: Potential Anti-Inflammatory Phytochemical against Different Diseases
Varun Jaiswal, Hae-Jeung Lee
Molecules.2023; 29(1): 189. CrossRef
- Anti-inflammatory effect of sea buckthorn in an HCl-induced cystitis rat model
- 5,622 View
- 15 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Characteristics and Treatment Trends for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A 10-Year Multicenter Retrospective Study
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Koo Han Yoo, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(2):49-54. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.2.49
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study examined the characteristics, current treatment trends, and outcomes of patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) in Korea.
Materials andMethods: Two hundred and seventeen patients diagnosed with EPN were evaluated using abdominal computed tomography in 2011-2021 at 15 institutes in Korea. The patients’ demographic and clinical characteristics, treatment modalities, and treatment outcomes were analyzed. The total study period was divided arbitrarily into groups A (2011-2014), B (2015-2017), and C (2018-2021) to analyze the trends in the EPN treatment.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 65.1 years; there were more female patients (74.2%) than male patients. The overall mortality rate was 10.6%. Ninety-five (43.8%), 98 (45.2%), and 24 (11.0%) patients were treated with medical, minimally invasive, and surgical management, respectively; the corresponding mortality rates were 13.7%, 6.1%, and 16.7%. There was no significant change in the proportion of patients treated with medical management over time (group A=46.5%, group B=47.0%, and group C=38.8%). The proportion of patients treated with minimally invasive management gradually increased over time (group A=35.2%; group B=43.9%; group C=55.0%), while those who underwent surgical management decreased gradually over time (group A=18.3%, group B=9.1%, and group C=6.3%). No differences in mortality rates were observed between the groups.
Conclusions: EPN with medical and minimally invasive management had a relatively high treatment success rate, which increased gradually, while surgical management decreased gradually over time in Korea. The mortality rate was relatively lower than that reported in studies published before the 2010s.
- 1,763 View
- 7 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


