-
Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
-
Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):114-118. Published online December 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.114
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
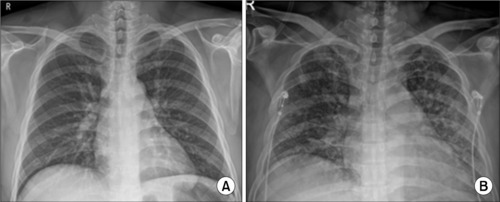
- Acute bacterial prostatitis is an acute urinary tract infection associated with a bladder outlet obstruction or an immunosuppressed state. A 51-year-old man patient visited the hospital with fever, chills, and acute urinary retention that started the day before his visit after consuming a significant amount of alcohol. Conservative treatments, including catheterization for urinary drainage and antibiotics, were performed. On the third day of treatment for acute prostatitis, he complained of dyspnea. The level of oxygen differentiation was reduced significantly, and the tracheal insertion and ventilator were maintained after the radiological examination. The ventilator was discontinued, and the prostate abscess was operated on the eighth day of hospitalization. He was discharged without complications. This paper reports a case of life-threatening pneumonia and a prostate abscess during the treatment of a patient with acute bacterial prostatitis with a review of the relevant literature.
-
Antibiotic Sensitivity of Bacterial Strains from Prostate Abscess Pus Aspirated Using Ultrasound Guidance
-
Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(1):26-30. Published online April 30, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.1.26
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: A prostate abscess is a rare occurrence often caused by immune dysfunction. The diagnostic modality for a prostate abscess is computed tomography or transrectal ultrasound. Transrectal ultrasound-guided aspiration is one such method. If treatment is dependent on the abscess size. This study examined the bacterial strains drained under transrectal ultrasound and their antibiotic sensitivity.
Materials and Methods: The medical records of eight patients diagnosed with a prostatic abscess and treated by transrectal ultrasound-guided aspiration from March 2009 to December 2020 were reviewed retrospectively. The general characteristics, associated diseases, and bacterial strains and their antibiotic sensitivities were identified in blood, urine, and pus cultures.
Results: Eight patients were hospitalized. The average age was 59.5±6.05 years, and the average length of hospitalization was 16.88±5.49 days; 75% had diabetes. No patients had catheterization, spinal injury, or prostate biopsy prior to diagnosis. The mean prostate volume was 47.05±27.3 ml, and the mean prostate abscess size was 2.08±0.83 ml. Under transrectal ultrasonography, the prostate abscess size was 5.43±5.31 ml, and catheters were inserted for treatment in four cases (50%). In the abscess culture test, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus were found in four, three, and one case, respectively. E. coli and K. pneumoniae responded well to amikacin treatment, while seven cases responded well to Piperacillin/Tazobactam treatment.
Conclusions: Prostate abscesses occur mainly in diabetic patients. The most common cultures are E. coli and K. pneumoniae. Intravenous injection of amikacin or Piperacillin/Tazobactam may be helpful as a treatment prior to bacterial identification.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
Urogenital Tract Infection.2023; 18(3): 114. CrossRef - Treatment Modality of Prostatic Abscess according to Size: A Retrospective Study
Gwon Kyeong Lee, Kyoung Ha Jang, Woo Seop Seong, Byeong Jin Kang, Kyung Hwan Kim, Hong Koo Ha
Urogenital Tract Infection.2022; 17(3): 96. CrossRef
-
3,113
View
-
9
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Case of Fournier’s Gangrene in a Patient with Long-Term Indwelling Catheterization due to Urinary Incontinence after Open Radical Prostatectomy
-
Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(1):6-9. Published online April 30, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.1.6
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Fournier’s gangrene is a life-threatening disease that needs to be treated as soon as possible. An 82-year-old male, who exchanged a urethral catheter once a month for urinary incontinence management after open radical prostatectomy, presented with an acute onset of mental change and general weakness. After ten days’ hospitalization, the disease was diagnosed. The scrotal wall was opened, and the infectious tissue was exposed to the air and kept open with an aseptic dressing. After 45 days, his scrotal wound healed and returned to its typical appearance without scarring and wound disruption. He recovered fully from the infection. This paper reports a case of Fournier’s gangrene in a patient with long-term indwelling catheterization due to urinary incontinence after an open radical prostatectomy with a literature review.
-
Characteristics of Uropathogens in Patients with Bladder Stones
-
Sum Kim, Sung Dae Kim, Kyung Kgi Park, Young-Joo Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2013;8(2):109-113. Published online October 31, 2013
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Purpose: Bladder stones is not a rare disease, however, the number of patients with bladder stones has decreased due to improvement of nutrition, hygiene, and optimal antibiotics. Bladder stones are typically found in adults with urinary stasis, such as foreign body, benign prostate hyperplasia, spinal cord injury, and urinary tract infection, and in children with congenital genito-urinary abnormality. The aim of this study was to identify the clinical and microbiological characteristics of patients with bladder stones. Materials and Methods: Patients who had bladder stones between March 2009 and December 2012 were retrospectively reviewed (Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea). We analyzed the presence of spinal cord injury, cancer, previous urinary tract calculi, and urinary tract infection associated with bladder stones and also investigated the largest diameter of bladder stone, and the number of bladder stones, as well as urine and blood culture. Results: A total of 39 patients underwent cystolithotomy or cystolithotripsy. The most common presenting symptoms were voiding disturbance (n=15, 38.5%) and hematuria (n=10, 25.6%). Of these patients, 17 (43.3%) had positive growth of organisms. Of these organisms, Escherichia coli was found in five patients, Enterococcus fecalis in three patients, Pseudomonas aeruginosa in three patients, Klebsiella pneumoniae in two patients, Staphylococcus aureus in two patients, Proteus mirabilis in one patient, and Citrobacter in one patient. Conclusions: We believe that urinary tract infection is a major risk factor in patients with bladder stones. Proper antibiotics would be required in order to reduce the risk of formation of bladder calculi. Further investigation will be needed.
-
The Characteristics of Uropathogen after Percutaneous Nephrostomy in Patients with Palliative Care
-
Hyeon Ju Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Sung Dae Kim, Hyo Jung Song, Seong Hyung Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2012;7(2):142-148. Published online October 31, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Purpose: Obstructive uropathy due to malignant diseases is not only associated with urinary tract infectionbut also renal failure. Palliative decompression using either percutaneous nephrostomy tubes or internal stents improves renal function but is associated with significant morbidity and affecting quality of life. We investigated the characteristics of uropathogens related percutaneous nephrostomy with patients with terminal care.
Materials and Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted of patients who had a nephrostomy tube inserted for malignant ureteric obstruction between January 2007 and July 2012. We analyzed parameters including previous cancer, creatine before nephrostomy procedure, visual analogue scale, creatinine before procedure, and urinary tract infection after nephrostomy tube insertion including urine culture and blood culture.
Results: There were 143 patients with percutaneous nephrostomy in our hospital. Of these patients, 42 had percutaneous nephrostomy for ureteral obstruction with malignancy. Tumors were of urological origin in 50%of patients. Of these patients, 17 had positive urine culture results. Enterococcus faecalis was the most commonbacteria grown.
Conclusions: We considered that UTI was not a rare complication of palliative decompression of malignant Nureteral obstruction, and resistance for antibiotics increases, especially ciprofloxacin. Identification of risk factors for UTI might further improve the safety of percutaneous nephrostomy. (Korean J UTII 2012;7:142-148)
-
Antibiotic Prophylaxis and Risk Factors of Infectious Complication after Endourologic Procedures of the Upper Urinary Tract
-
Sung Dae Kim, Dong Wan Sohn
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2012;7(2):149-157. Published online October 31, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose: We investigated a retrospective analysis of infectious complication and its risk factors after endourologic procedures of the upper urinary tract, focusing on antibiotic prophylaxis (AP).
Materials and Methods: We studied AP in 488 upper urinary tract examinations or treatments.Procedures included ureteral stenting, percutaneous nephrostomy, retrograde pyelography, and diagnostic ureteroscopy. We calculated that the prevalence and kind of AP and the incidence of febrile infectious complications with respect to each procedure and attempted to find the risk factors.
Results: AP was used in 456 (93.3%) cases totally. Antibiotics of quinolone were the most popular medication. There are 17 (3.7%) febrile infectious complication cases after procedure, the most common procedure was percutaneous nephrostomy in 7 cases (6.0%). Bacteriuria, hydronephrosis, whether or not ureteral stent, or nephrostomy, or Foley catheterization was applied prior to examination or treatment, and were independent risk factors for infectious complications (<0.05).
Conclusions: The data suggest that the risks of infectious complications should be evaluated carefully and AP should be recommended according to those risks before the procedures. (Korean J UTII 2012;7:149-157)
-
Bladder Stone causing Acute Renal Failure and Urinary Tract Infection
-
Sung Dae Kim, Young Joo Kim, Jung Sik Huh
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2012;7(2):178-181. Published online October 31, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Bladder stones are not a rare disease, but it is rare for such a calculus to be so large as to cause bilateral hydronephrosis. In a previous report, we described an unusual case of spontaneous bladder rupture due to a giant bladder stone. The patient was a 68-year-old man, who had undergone primary repair of bladder rupture and cystolithotripsy of a giant bladder stone with lithoclast at the age of 63 years old. Then he did loss follow-up to the hospital for 5 years. After 5 years, he came back to the hospital with the same symptoms such as decreased urine volume, suprapubic discomfort. Fortunately, the previous treatment which consisted of litholopaxy and antibiotics was effective again. Worldwide, it is the first reported case of recurrent acute renal failure and urinary tract infection after bladder spontaneous rupture due to a giant bladder stone. (Korean J UTII 2012;7:178-181)
-
Septic Shock Caused by Pancreatic Injury after Radical Nephrectomy
-
Dong-Wan Sohn, Tae Seung Shin, Sung Dae Kim, U-shin Ha, Yong-Hyun Cho
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2009;4(1):93-95. Published online April 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 66-year-old female patient presented with right upper quadrant pain for 3months. Preoperative computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and laboratory tests were not consistent with findings of pheochromocytoma, but rather tumor originating from renal cortex. Pathology revealed pheochromocytoma and pancreatic injury was suspected after the surgery. Septic condition persisted despite of proper antibiotics, drainage, and octreotide therapy. Patient died on 8th day after radical nephrectomy. We report a morbid complication of pancreatic injury leading to septic shock and to death.
-
Spontaneous Bladder Rupture due to Giant Bladder Stone
-
Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2009;4(1):104-107. Published online April 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- "Spontaneous bladder rupture is a very rare condition. It is the term employed for all cases of rupture not associated with trauma, including diseases of the urinary bladder or urinary outflow obstruction. It usually presents as severe abdominal pain. But in some cases, because symptoms are insidious and often atypical among elderly patients, this condition is often undetected. We describe an unusual case of spontaneous bladder rupture due to giant bladder stone."
-
Jaundice and Acute Pyelonephritis due to a Giant Urinoma
-
Sung Dae Kim, Dong Sub Lee, Dong Wan Sohn, Sae Woong Kim, Yong-Hyun Cho
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2008;3(2):244-248. Published online October 31, 2008
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Disruption of the urinary collecting system can produce internalized urine leaks that can be continous urine extravasation and form an encapsulated collection of urine, which is known as a urinoma. Urinoma is also called as pararenal pseudocyst and usually the result of renal injury and may be the result of obstructive uropathy from a ureteral stone or pelvic mass or even a urological procedure. Although urinoma may induce the urinary infection such as acute pyelonephritis, it may not give rise to jaundice due to biliary tract obstruction. We describe an unusual case of jaundice and acute pyelonephritis due to a giant urionoma after high grade renal injury.
-
The Antimicrobial Effect of Antibiotics to Patients with Chronic Prostatitis of Positive Reaction on Chlamydial Antibody
-
Sung Dae Kim, Dong Wan Sohn, Sae Woong Kim, Yong-Hyun Cho
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2008;3(1):81-88. Published online April 30, 2008
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- "Purpose: Chronic bacterial prostatitis is the most common urological disease in adult males, with antibiotic therapy being the gold standard for its treatment. Recent studies suggest that Chlamydia may play a role in chronic prostatitis but was difficult to prove the pathogen to the prostate. We evaluated the effect of three antibiotics (azithromycin, doxycycline, levofloxacin) in patients with chronic prostatitis of positive reaction on Chlamydial antibody. Material and Methods: The study included 54 patients who had symptoms of chronic prostatitis and proven presence of Chlamydia. The presence of Chlamydia was confirmed in expressed prostatic secretion (EPS) immediately after prostatic massage by multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The patients were randomized to receive azithromycin 1.0g (n=16) once, or doxycycline 100mg b.i.d. (n=19) for 21 days or levofloxacin 100mg t.i.d. (n=19) for 21 days. Patients’ sexual partners were treated at the same time. Clinical and bacteriological efficacy (leukocyte count, pathogen eradication rate, NIH-CPSI) was evaluated after the end of therapy. Results: After treatment of antibiotics, the leukocytes counts in the EPS was significantly decreased in all groups (p<0.05), but there was no significant difference in three groups. Also, all of groups was superior to control Chlamydia (azithromycin:doxycycline:levofloxacin=93.75%:78.94%:89.47%) and there was no significant difference of the pathogen eradication rates in three groups. The total NIH-CPSI score was significantly decreased, especially pain domain and quality of life domain (p<0.05), and there was no significant difference in three groups. Conclusions: These data suggest that antibiotics of three groups was effective to the patient with chronic prostatitis of positive reaction on Chlamydia antibody."
-
The Present Status and Counterplans of Nosocomial Infection
-
Sung Dae Kim, Dong Wan Sohn, Sae Woong Kim, Yong-Hyun Cho
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2007;2(2):1-11. Published online May 31, 2007
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- "Although of advances in medical environment we are faced with new pathogen in hospital according to increase of antimicrobial resistance, invasive procedure, population of old men, abuse of immune suppressants. Nosocomial infections are more common phenomena than other infection in clinical practice. Therefore, we should know about the exact definition, diagnostic principles, need of control of nosocomial infection. Especially, We need to understand about it in Korea. So the Korean Society for Nosocomial Infection Control (KOSNIC) organized the Korean Nosocomial Infectious Surveillance System (KONIS) to establish a nationwide database of nosocomial infection rate on the intensive care units of hospitals in Korea. This article focuses on the definition, background, principles of diagnosis, the current status and counterplans of nosocomial infection in Korea. We have full assurance that it should provide a theoretical strategy to enforce the infection control."
-
The Relationship between Sexually Transmitted Diseases and HIV Transmission
-
Sung Dae Kim, Dong Wan Sohn, Seung-Ju Lee, Sae Woong Kim, Yong-Hyun Cho
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2007;2(2):157-166. Published online October 31, 2007
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- More than 42 million people worldwide are now infected with HIV, in spite of sustained prevention activities. Although the spread of HIV has been primarily sexual, epidemiological studies have indicated that the efficiency of the spread of HIV is poor, perhaps as infrequently as 1 in every 1,000 episodes of sexual intercourse. However, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) that cause ulcers or inflammation greatly increase the efficiency of HIV transmission by increasing both the infectiousness of, and the susceptibility to HIV infection. STDs might be particularly important in the early stages of a localized HIV epidemic, when people with risky sexual behaviour are most likely to become infected. In China, eastern Europe and Russia, there has been a remarkable increase in the incidence of STDs in recent years, and this is reflected in the rapid increase in the spread of HIV in these areas. Targeted STDs detection and treatment should have a central role in HIV prevention in these emerging epidemics.
-
Bilateral Vesicoureteral Reflux and Wilms' Tumor Combined with Urinary Tract Infection
-
Byung Il Yoon, Sung Dae Kim, Dong Wan Sohn, Sae Woong Kim, Yong-Hyun Cho
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2007;2(2):221-224. Published online October 31, 2007
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Vesicoureteral reflux is a common condition in children. It may cause and maintain urinary tract infection, evaentually leading to progressive renal damage and end-stage renal disease. Wilms' tumor is the most common primary malignant renal tumor of childhood. There is no literature that vesicoureteral reflux combined with Wilms' tumor. We report rare case of bilateral vesicoureteral reflux combined with left Wilms' tumor.
|