-
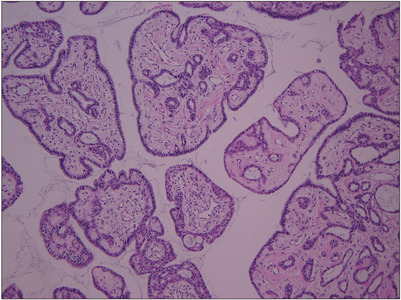
Robotic Excision of a Huge Seminal Vesicle Cyst, Including Intracystic Papillary Adenoma, Saving Fertility
-
Tae Hoon Oh, Ill Young Seo
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):40-43. Published online August 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.40
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- A seminal vesicle cyst is a rare disease, and an intracystic papillary adenoma within the seminal vesicle is extremely rare. The diagnosis and treatment of these diseases are challenging because of the limited data. This paper presents a robotic excision of a huge seminal vesicle cyst, including an intracystic papillary adenoma, preserving fertility in a 40-year-old man.
-
Antimicrobial Therapy and Antimicrobial Stewardship in Urosepsis
-
Tae Hoon Oh
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(1):15-19. Published online April 30, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.1.15
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Since the latest knowledge on the treatment and countermeasures for sepsis is being updated at a rapid pace, becoming familiar with the Surviving Sepsis guidelines is helpful for patient prognosis. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBL) are important factors when selecting early empirical antibiotics for sepsis caused by urinary tract infections. For severe septic shock, prolonged infusion and combination therapy need to be considered.
-
Encrusted Cystitis and Pyeloureteritis in Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Jea Whan Lee, Whi-An Kwon, Seung Chol Park, Tae Hoon Oh, Young Hwan Lee, Joung Sik Rim
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2015;10(1):49-52. Published online April 30, 2015
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Encrusted cystitis and pyeloureteritis are rare chronic infectious conditions characterized by mucosal inflammation and encrustations of the urinary tract. It is caused by fastidious growing urea splitting microorganisms, mainly Corynebacterium. Herein, we report an unusual case of an 80-year-old man with encrusted cystitis and pyeloureteritis who was previously treated with transcatheteral arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdomino-pelvic computerized tomography showed a bilateral hydronephrosis with calcifications of renal pelvis, ureter, and bladder. Cystoscopy showed calcified bladder mucosa with necrosis and bleeding. After transurethral removal of calcified plaques, the patient was treated with antibiotic and oral urine acidification. One-month follow-up cystoscopy showed that inflammation was improved and calcification was significantly reduced.
|