-
Mechanistic Insights Into Persistent Bacterial Cystitis as a Basis for Vaccine Development: A Narrative Review
-
Karen Serrano-Arevalo, Manisha Naskar, Hae Woong Choi
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):60-72. Published online December 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448022011
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
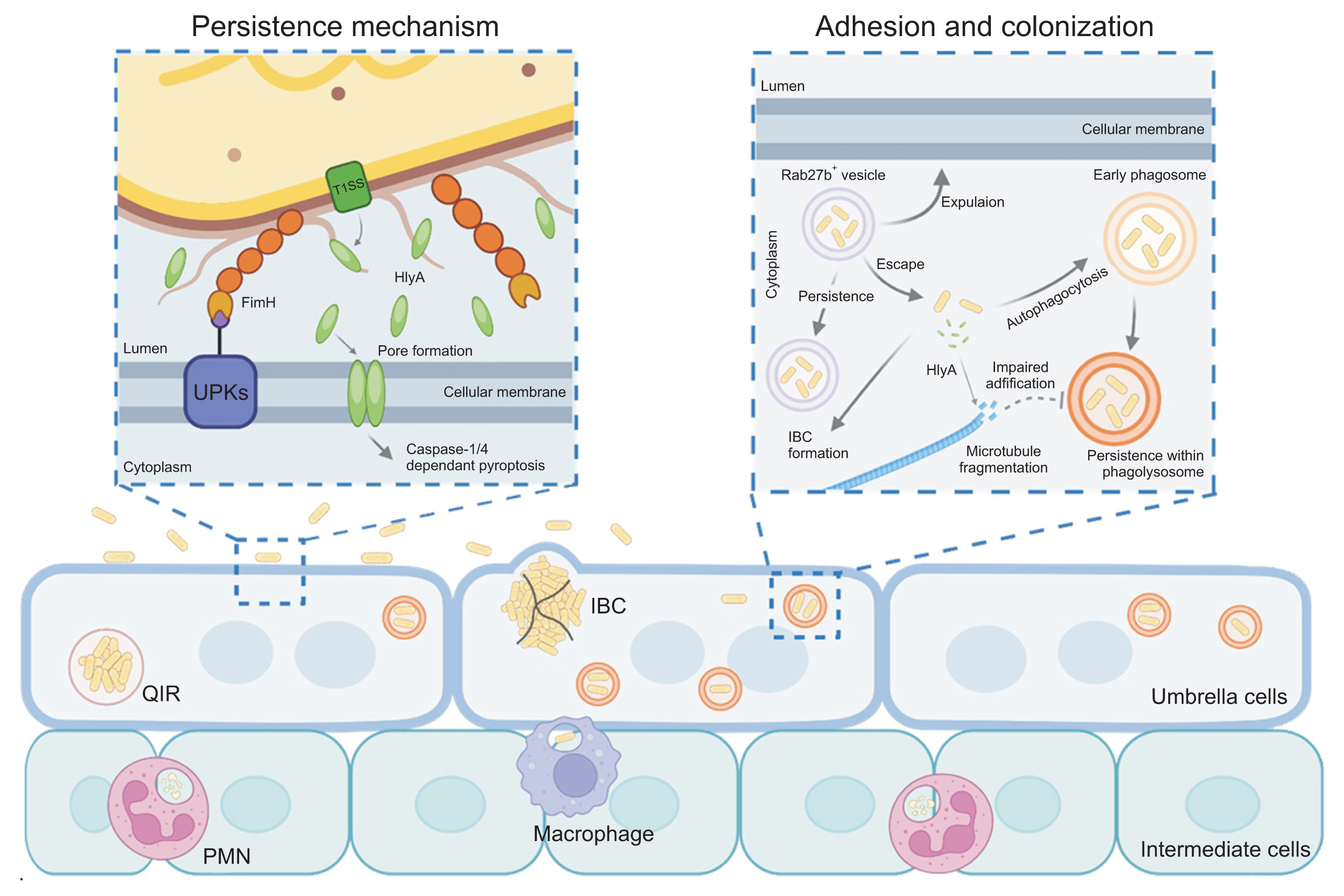
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are primarily caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC), which frequently lead to recurrent infections. These bacteria utilize several strategies to establish infection in the host; in particular, virulence factors such as fimbriae and α-hemolysin facilitate persistent infection, evade host immune responses, and minimize antibiotic exposure. To date, antibiotics have been the primary treatment for UTIs. However, an increasing emphasis has been placed on the need for UTI vaccines, with mucosal vaccine products now available in several countries. Additionally, vaccines targeting intracellular UPEC, utilizing adjuvants, are currently under development. Understanding the pathogenic mechanisms of uropathogens has enabled the development of new treatment approaches, paving the way for next-generation preventive and therapeutic methods that could effectively manage recurrent UTIs in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Mechanisms and clinical implications of bacterial persistence in recurrent urinary tract infections
Changil Choi, Dong Soo Kim, Jin Bong Choi, Taesoo Choi, Jeong Woo Lee
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2026; 67(2): 123. CrossRef - Bacterial biofilm – as a contributor to urinary tract infections
Zuzanna Trześniewska-Ofiara, Mariola Mendrycka, Agnieszka Woźniak-Kosek
Biuletyn Głównej Biblioteki Lekarskiej.2025; 58(384): 83. CrossRef
-
6,755
View
-
58
Download
-
2
Crossref
|