-
Mortality and Risk Factors for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
-
Seung-Kwon Choi, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):34-41. Published online April 30, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550006003
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose
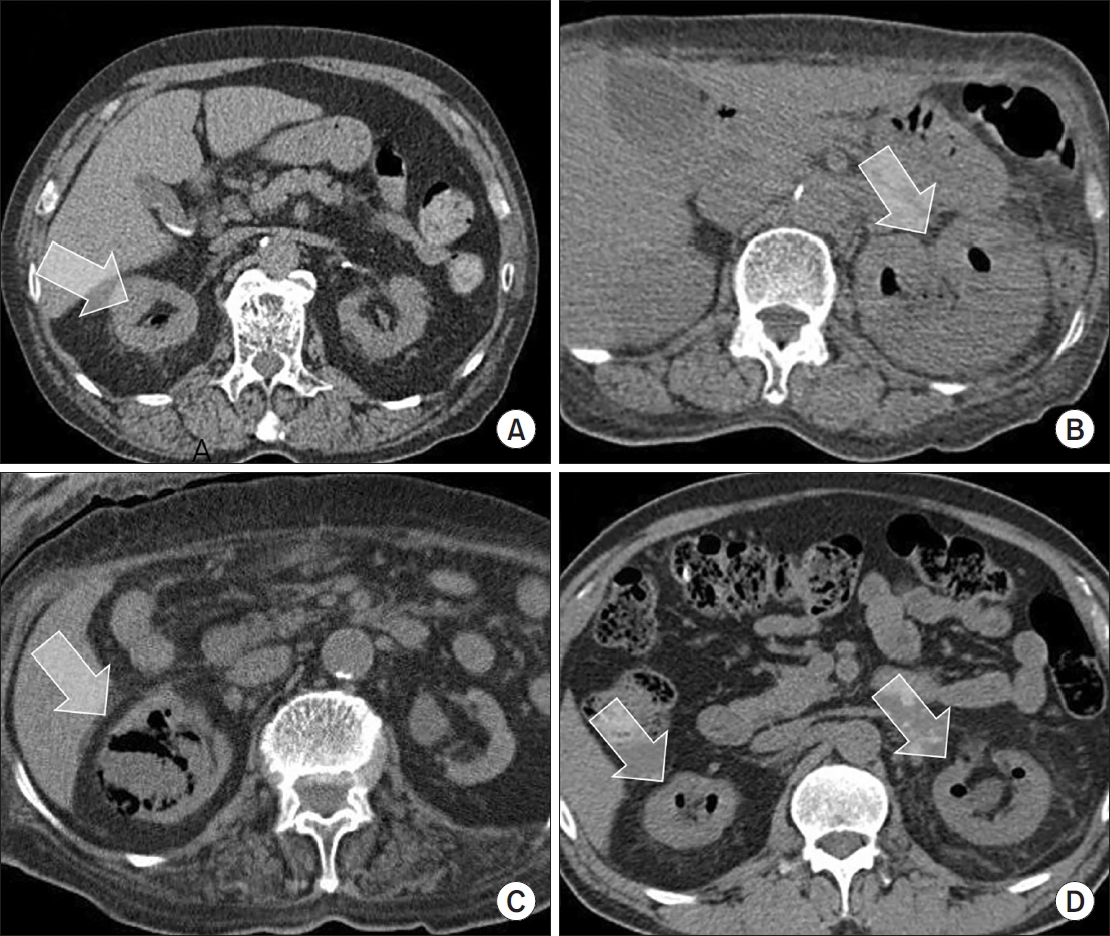
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a life-threatening disease requiring immediate treatment. This multicenter retrospective cohort study aimed to analyze the mortality rate and risk factors associated with EPN.
Materials and Methods: Between January 2011 and February 2021, 217 patients diagnosed with EPN via computed tomography who visited 14 teaching hospitals were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical data, including age, sex, comorbidities, Huang and Tseng classification, hydronephrosis, acute kidney injury, blood and urine tests, surgical interventions, percutaneous drainage, and conservative treatments, were compared between the survival and death groups. Risk factors for mortality due to EPN were analyzed using univariate and multivariate methods.
Results
The mean age of survivors and deceased patients was 67.8 and 69.0 years, respectively (p=0.136). The sex distribution (male/female) was 48/146 and 8/15, respectively (p=0.298). Of the 217 patients, 23 died, resulting in a mortality rate of 10.6%. In univariate analysis, the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.004), platelet count (p=0.005), and acute kidney injury (p=0.007) were significantly associated with mortality from EPN. In multivariate analysis, only the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.029) was identified as a risk factor. Mortality rates according to the Huang and Tseng classification were as follows: class I (5.88%), class II (7.50%), class IIIa (14.28%), class IIIb (25.00%), and class IV (23.07%).
Conclusions
EPN is associated with a high mortality rate. Among various clinical factors, the Huang and Tseng classification was the most significant indicator for predicting mortality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
-
3,370
View
-
60
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Characteristics and Treatment Trends for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A 10-Year Multicenter Retrospective Study
-
Seung-Kwon Choi, Koo Han Yoo, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(2):49-54. Published online August 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.2.49
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: This study examined the characteristics, current treatment trends, and outcomes of patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) in Korea.
Materials andMethods: Two hundred and seventeen patients diagnosed with EPN were evaluated using abdominal computed tomography in 2011-2021 at 15 institutes in Korea. The patients’ demographic and clinical characteristics, treatment modalities, and treatment outcomes were analyzed. The total study period was divided arbitrarily into groups A (2011-2014), B (2015-2017), and C (2018-2021) to analyze the trends in the EPN treatment.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 65.1 years; there were more female patients (74.2%) than male patients. The overall mortality rate was 10.6%. Ninety-five (43.8%), 98 (45.2%), and 24 (11.0%) patients were treated with medical, minimally invasive, and surgical management, respectively; the corresponding mortality rates were 13.7%, 6.1%, and 16.7%. There was no significant change in the proportion of patients treated with medical management over time (group A=46.5%, group B=47.0%, and group C=38.8%). The proportion of patients treated with minimally invasive management gradually increased over time (group A=35.2%; group B=43.9%; group C=55.0%), while those who underwent surgical management decreased gradually over time (group A=18.3%, group B=9.1%, and group C=6.3%). No differences in mortality rates were observed between the groups.
Conclusions: EPN with medical and minimally invasive management had a relatively high treatment success rate, which increased gradually, while surgical management decreased gradually over time in Korea. The mortality rate was relatively lower than that reported in studies published before the 2010s.
-
Bladder Dysfunction and Urinary Tract Infection
-
Ju-Hyun Shin, Yong-Gil Na
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2009;4(1):1-12. Published online April 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Urinary tract infection is responsible for major morbidity and mortality in the patients with the bladder dysfunction. Several factors appear to be responsible for an increased risk of infection in the bladder dysfunction. Significant residual urine, elevated intravesical pressure, frequent exposure to antibiotics and catheter use contribute to an increased risk of symptomatic urinary tract infection. The goals of lower urinary tract management in voiding dysfunction patients include achieving complete bladder emptying, maintenance of low intravesical pressures. Through these measures the aim is to prevent renal damage, while maximizing the patient's quality of life and independence.
|