-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: Case Report
-
Kwang Jin Kim, Yoonsuk Lee, Yong Sung Cha, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Hong Chung, Hyun Kim, Jae Hung Jung
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):44-47. Published online August 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.44
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) was conducted on two male patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome who were resistant to conventional medical therapies. Both patients underwent 20 sessions of 100% oxygen inhalation (2.0 atmosphere absolute for 90 min/day, five days/week for four weeks) in a hyperbaric chamber. The follow-up period was three months. Although the patients reported a slight improvement in the pain domain of the National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) after HBOT, no changes were noted in the other domains of NIH-CPSI and International Prostate Symptom Score. No adverse events were encountered during or after HBOT.
-
Trends in Age-Specific Prevalence of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
-
Young Hwan Kim, Se Hwa Hong, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Tae Hyoung Kim, Sae Chul Kim, Sang Baek Koh, Jae Hung Jung
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):101-106. Published online December 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.101
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
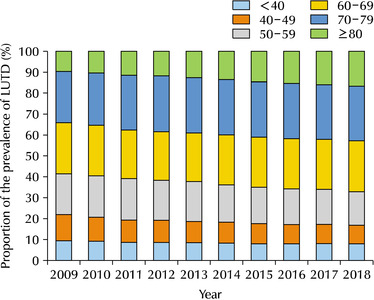
- Purpose: To elucidate the longitudinal changes in the prevalence of lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) according to age over the past 10 years.
Materials and Methods: The changes in the proportion of prevalence for LUTD, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and urinary incontinence (UI) among South Koreans from 2009 to 2018, were analyzed using the National Health Information Database established by the Korean National Health Insurance Service. All conditions were defined according to the corresponding Korean Standard Classification of Diseases-8 for diagnosis and surgical procedures and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service codes for drugs.
Results: The 60-69, 70-79, and over 80 age groups accounted for more than 60% of the LUTD cases from 2009 to 2018, while significant increases in the crude prevalence of LUTD were observed over a 10-year period in all age groups (p for trend <0.05). In age groups over 60 years, LUTD was more prevalent in men than women, but there was no statistically significant difference in proportion (p>0.05). The changes in the prevalence and prevalence proportion exhibited similar trends in BPH, UI, and LUTD.
Conclusions: LUTD was more prevalent in the elderly aged over 60 years old than in younger adults. Therefore, this study suggests the development of nationwide healthcare policies to manage LUTD in the elderly population of South Korea, which is expected to become the world’s most aged population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nursing strategies for managing urological disorders in aging populations: a comprehensive review
Hong Liu, Jie Wu
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
-
4,559
View
-
21
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Clinical Significance of National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index Pain Score in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
-
Chang Min Lee, Jae Mann Song, Kwang Jin Kim, Tae Wook Kang, Seung Hoon Ryang, Yun Byung Chae, Hyun Chul Chung, Jae Hung Jung
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2015;10(2):102-107. Published online October 31, 2015
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose: Many benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) patients were accompanied by pelvic pain apart from urinary symptoms. Therefore, we evaluate the treatment outcomes of alpha-blockers via a change of international prostate symptom score (IPSS) according to pain score of the National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI).
Materials and Methods: A total of 356 male patients with BPH from March 2011 to May 2014 were analyzed retrospectively. Prostate specific antigen, prostate volume, IPSS, NIH-CPSI, international index of erectile function (IIEF-5), and uroflowmetry were collected. Patients were categorized according to 2 groups based on the presence and severity of pain and baseline characteristics and treatment outcomes were analyzed.
Results: Two hundred twenty-nine patients (64.3%) reported pain/discomfort on NIH-CPSI. Mean IPSS, mean voiding symptoms, mean storage symptoms on IPSS, and mean IIEF-5 showed a significant difference in groups 1A and 1B. Logistic regression analysis showed that NIH-CPSI pain score was a significant predictive factor for severe IPSS (odds ratio, 2.830; 95% confidence interval, 1.307-6.129). After treatment for 3 months, improvement of IPSS, voiding symptoms, storage symptoms, and quality of life was observed in all groups (p=0.001, p<0.001, p=0.026, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001). Group 2B (pain score>5) showed greater improvement of symptoms and statistically significant difference compared with group 2A (pain score ≤5) (p=0.029, p=0.026).
Conclusions: We suggest that the presence and severity of pain score are helpful for therapeutic efficacy in patients with BPH.
-
Penile Mass Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
-
Seung Hoon Ryang, Minseob Eom, Tae Wook Kang, Chang Min Lee, Hyun Chul Chung, Jae Mann Song, Kwang Jin Kim, Jae Hung Jung
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2015;10(2):126-129. Published online October 31, 2015
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Tuberculosis of the penis is rare. The clinical features of penile tuberculosis are usually manifested as ulceration or scars. However, the authors encountered a case of penile tuberculosis that presented as a mass. A painless nodule at the base of the penis was noted in a 63-year-old male patient. Surgical excision was recommended, and pathologic finding revealed granulomatous inflammation in the mass. Acid fast bacilli stain and culture were negative, but a positive result was found in urine polymerase chain reaction for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. He was diagnosed with tuberculosis of the penis and underwent anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy.
|