-
Impact of the Timing of Percutaneous Nephrostomy on the Prognosis of Obstructive Urolithiasis With Sepsis: A Retrospective Cohort Study
-
Ji Eun Yu, Hyung Joon Kim, Hong Wook Kim, Young Seop Chang, Jin Bum Kim, Dong Hoon Koh
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):89-96. Published online December 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448018009
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic impact of time to percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) insertion on obstructive ureteral stones with sepsis.
Materials and Methods: Data were collected on patients who presented at our Emergency Department between 2017 and 2021 with obstructive uropathy due to urinary stones and underwent PCN insertion. Patients were stratified into 4 groups in accordance with the quick sepsis-related organ failure (qSOFA) score at presentation (<2 or ≥2) and time to PCN insertion (<4 hours or ≥4 hours) as follows: group 1, qSOFA < 2 and time to PCN insertion < 4 hours; group 2, qSOFA < 2 and time to PCN insertion ≥ 4 hours; group 3, qSOFA ≥ 2 and time to PCN insertion < 4 hours; group 4, qSOFA ≥ 2 and time to PCN insertion ≥ 4 hours. The prognostic impacts of the time to PCN insertion were compared between these groups
Results
The total cohort consisted of 96 patients, of whom 70 were classified as either group 1 or 2 (qSOFA < 2). Overall, 37 patients had a positive urine culture. The median time to PCN insertion was 218 minutes, and the median length of stay was 14 days. The hospitalization period was significantly shorter in group 3 than in group 4 (p=0.041).
Conclusions
A shorter length of stay was associated with more rapid PCN insertion in patients with obstructive uropathy and a high risk of sepsis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinical Characteristics, Microbiological Spectrum, Biomarkers, and Imaging Insights in Acute Pyelonephritis and Its Complicated Forms—A Systematic Review
Marius-Costin Chițu, Teodor Salmen, Paula-Roxana Răducanu, Carmen-Marina Pălimariu, Bianca-Margareta Salmen, Anca Pantea Stoian, Viorel Jinga, Dan Liviu Dorel Mischianu
Medicina.2026; 62(1): 222. CrossRef
-
4,609
View
-
39
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Does Music Have a Calming Effect on Pain and Anxiety in Patients Undergoing Cystoscopy?
-
Ye Chan Joo, Ji Eun Yu, Jae Hyun Baik, Young Seop Chang, Jin Bum Kim, Hyung Joon Kim, Dong Hoon Koh, Hong Wook Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(1):3-9. Published online April 30, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.1.3
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
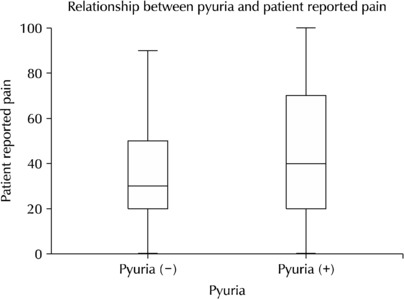
- Purpose: Cystoscopy is a diagnostic test performed frequently in urology outpatient clinics. Despite the large number of inspections, the associated pain, discomfort, or anxiety can markedly affect patient compliance and adherence to subsequent surveillance protocols. This study conducted a prospective, randomized study to investigate the potential efficacy of music and pyuria on pain or anxiety during outpatient cystoscopy.
Materials and Methods: In this single-institution, randomized study, the participants were assigned to a music-intervention or non-music control group. The music-intervention group underwent an identical procedure with the addition of Johann Sebastian Bach’s “Air on the G String” from Suite No. 3 in D major, BWV 1068. Urinalysis was performed to determine if pyuria affects pain during the procedure.
Results: The patient-reported outcomes, encompassing the changes in the STAI-X-1 (State-Trait Anxiety Inventory-X-1) scores, subjective levels of discomfort, embarrassment, satisfaction, and pain, were similar in the two groups. In contrast, the surgeons reported statistically significant differences in their evaluations of the same items as patient-reported outcomes of the two groups. The patient-reported pain showed no significant differences between the pyuria-negative group (0-2 and 3-5 WBC/HPF) and pyuria-positive group (>5 WBC/HPF).
Conclusions: The data from this study do not support the hypothesis that musical intervention during cystoscopy alleviates pain or anxiety to any significant extent. In addition, pyuria did not affect the patient’s reported pain. Nevertheless, a notable impact was observed in the surgeons’ assessments, suggesting that the musical accompaniment may alter the surgeons’ perception of patient pain and anxiety levels throughout the procedure.
-
Korean Multicenter Study of Infectious Complications after Transurethral Prostate Surgery in Patients with Preoperative Sterile Urine
-
Seong Hyeon Yu, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Jae Duck Choi, Koo Han Yoo, Jeong Woo Lee, Dong Hoon Koh, Sangrak Bae, Seung Ok Yang, Joongwon Choi, Seung Ki Min, Hoon Choi
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(3):81-88. Published online December 31, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.3.81
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis and determine the risk factors of infectious complications after transurethral surgery of the prostate.
Materials and Methods: Seven hundred and seventy-two patients who underwent transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HOLEP) were reviewed. Of these, this study enrolled 643 patients without bacteriuria who had not received antibiotics for urinary tract infections for two weeks before surgery. The patients were divided into two groups according to the duration of the antibiotics (Group 1: less than one day, n=396 vs. Group 2: more than one day, n=247).
Results: The overall incidence of postoperative infectious complications in 643 patients was 5.0% (32/643). When postoperative infectious complications were compared according to the duration of the antibiotics (Group 1 vs. Group 2), the infectious complications rates were 5.6% (22/396) vs. 4.0% (10/247), respectively (p=0.393). When postoperative infectious complications were compared according to the duration of antibiotics (Group 1 vs. Group 2) in the TURP and HOLEP groups, the infectious complications rates were 6.3% (12/192) vs. 1.0% (1/103) (p=0.035) and 4.9% (10/203) vs. 6.0% (8/134) (p=0.677), respectively. The duration of Foley catheterization was independently associated with infectious complications (p=0.003).
Conclusions: The results showed that prolonged postoperative catheterization affects postoperative infectious complications associated with transurethral prostate surgery. Although antibiotics administered for less than one day are effective for antibiotic prophylaxis of transurethral prostate surgery, a longer antibiotic therapy is recommended for TURP.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of Postoperative Urinary Tract Infection and Sepsis Rates After Adding Cystolitholapaxy to HoLEP:
A Retrospective Analysis
Federico Rovegno, Rajiv Pillai, Zafar Maan, Soumendra Datta, Omar Nasir, Gerald Rix
International Journal of Clinical Urology.2026; 10(1): 1. CrossRef
-
3,722
View
-
24
Download
-
1
Crossref
|