Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Urogenit Tract Infect > Volume 20(2); 2025 > Article
- Review Article Beta-Lactamase-Mediated Antibiotic Resistance in Urinary Tract Infections: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies
-
Fanglin Shao1,*
 , Dengxiong Li2,*
, Dengxiong Li2,* , Jie Wang2
, Jie Wang2 , Zhouting Tuo3
, Zhouting Tuo3 , Zhipeng Wang4
, Zhipeng Wang4 , Wuran Wei2
, Wuran Wei2 , Ruicheng Wu2,5
, Ruicheng Wu2,5 , Dechao Feng1,5
, Dechao Feng1,5
-
Urogenital Tract Infection 2025;20(2):67-81.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550012006
Published online: August 31, 2025
1Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China
2Department of Urology, Institute of Urology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
3Department of Urological Surgery, Daping Hospital, Army Medical Center of PLA, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
4Department of Urology, Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
5Division of Surgery & Interventional Science, University College London, London, UK
-
Corresponding author: Dechao Feng Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China Email: fdcfenix@stu.scu.edu.cn ,dechao.feng@ucl.ac.uk -
Co-corresponding author: Ruicheng Wu Department of Urology, Institute of Urology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China. Division of Surgery & Interventional Science, University College London, London W1W 7TS, UK Email: ruicheng.wu@ucl.ac.uk - *These authors contributed equally to this study as co-first authors.
Copyright © Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 6,485 Views
- 73 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most prevalent bacterial infections globally, and are primarily caused by Escherichia and Klebsiella. The overprescription and inappropriate use of antibiotics have accelerated the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria. Beta-lactamases play a critical role in mediating antibiotic resistance in UTIs. These enzymes promote bacterial resistance through multiple mechanisms, including gene mutation, plasmid-mediated horizontal gene transfer, and the involvement of integrons. Comprehensive knowledge of the ways in which beta-lactamases contribute to resistance in UTIs is essential for improving treatment strategies. Advances in detection technologies, such as gene sequencing and mass spectrometry, have greatly enhanced the ability to monitor and predict bacterial resistance. Current therapeutic strategies include the application of beta-lactamase inhibitors, the development of novel antibiotics, and alternative treatments that have shown efficacy against beta-lactamase-mediated antibiotic resistance. This paper reviews the mechanisms of beta-lactamase-mediated resistance in UTIs and provides an in-depth overview of several detection methods and therapeutic approaches.
INTRODUCTION
CLASSIFICATION OF BETA-LACTAMASES
SYATUS AND MECHANISM OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE MEDIATED BY BETA-LACTAMASES
DETECTION TECHNIQUE OF BETA-LACTAMASES
THERAPEUTIC STRATEGIES OF BETA-LACTAMASE IN URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
PERSPECTIVE
CONCLUSIONS
-
Funding/Support
This study was supported by the regional innovation cooperation project of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 23QYCX0136).
-
Conflict of Interest
DF, a member of the Editorial Board of Urogenital Tract Infection, is a co-corresponding author of this article. However, he played no role whatsoever in the editorial evaluation of this article or the decision to publish it. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
-
Acknowledgments
We appreciated the Figdraw (www.figdraw.com) and Chengdu Basebiotech Co.,Ltd for their assistance in drawing and data process.
-
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: FS, DL, RW, DF. Data curation: FS, DL, JW, ZT, ZW, WW. Formal analysis: FS, DL, JW, ZT, ZW, WW. Methodology: FS, DL, JW, ZT, ZW, WW. Project administration: RW, DF. Visualization: FS, DL, JW, ZT, ZW, WW. Writing - original draft: FS, DL. Writing - review & editing: FS, DL, RW, DF.
NOTES

ESBL, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase; CFX, cefixime; AMC, amoxicillin/clavulanate; MEC, mecillinam; E. coli, Escherichia coli; MDR, multidrug resistant; P. aeruginosa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; K. pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae; C/T, ceftolozane/tazobactam; PIP/TAZ, piperacillin/tazobactam; CTX, cefotaxime; CAZ-AVI, ceftazidime-avibactam; IMP-REL, imipenem-relebactam; TOB, tobramycin; MER, meropenem; CPD, cefpodoxime proxetil; ATM-AVI, aztreonam-avibactam; GNB, Gram-negative bacteria; BLI, β-lactamase inhibitor; S. maltophilia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; CEP, cefepime; TAN, taniborbactam; LCs, linked complexes; MBL, metallo-β-lactamases; IMP, imipenem; VAB, vaborbactam; REL, relebactam; UTI, urinary tract infection.
- 1. Flores-Mireles AL, Walker JN, Caparon M, Hultgren SJ. Urinary tract infections: epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat Rev Microbiol 2015;13:269-84.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 2. Cai T. Recurrent uncomplicated urinary tract infections: definitions and risk factors. GMS Infect Dis 2021;9:Doc03.PubMedPMC
- 3. Kahlmeter G, Poulsen HO. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli from community-acquired urinary tract infections in Europe: the ECO•SENS study revisited. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2012;39:45-51.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Foxman B. Urinary tract infection syndromes: occurrence, recurrence, bacteriology, risk factors, and disease burden. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2014;28:1-13.PubMed
- 5. Chu CM, Lowder JL. Diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infections across age groups. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2018;219:40-51.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Zhu NJ, Weldegiorgis M, Carter E, Brown C, Holmes A, Aylin P. Economic burden of community-acquired antibiotic-resistant urinary tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis. JMIR Public Health Surveill 2024;10:e53828.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Sher EK, Džidić-Krivić A, Sesar A, Farhat EK, Čeliković A, Beća-Zećo M, et al. Current state and novel outlook on pre-vention and treatment of rising antibiotic resistance in urinary tract infections. Pharmacol Ther 2024;261:108688.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Geleta D, Abebe G, Alemu B, Workneh N, Beyene G. Mechanisms of bacterial drug resistance with special emphasis on phenotypic and molecular characterization of extended spectrum beta-lactamase. New Microbiol 2024;47:1-14.
- 9. Bayaba S, Founou RC, Tchouangueu FT, Dimani BD, Mafo LD, Nkengkana OA, et al. High prevalence of multidrug resistant and extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from urinary tract infections in the West region, Cameroon. BMC Infect Dis 2025;25:115.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 10. Paniagua-García M, Bravo-Ferrer JM; Pérez-Galera S, Kostyanev T, de Kraker ME, Feifel J, et al. Attributable mortality of infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales:results from a prospective, multinational case-control-control matched cohorts study (EURECA). Clin Microbiol Infect 2024;30:223-30.PubMed
- 11. Lawrence J, O'Hare D; van Batenburg-Sherwood J, Sutton M, Holmes A, Rawson TM. Innovative approaches in phenotypic beta-lactamase detection for personalised infection management. Nat Commun 2024;15:9070.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 12. Hidalgo-Tenorio C, Bou G, Oliver A, Rodríguez-Aguirregabiria M, Salavert M, Martínez-Martínez L. The challenge of treating infections caused by metallo-β-lactamase-producing gram-negative bacteria: a narrative review. Drugs 2024;84:1519-39.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 13. Ambler RP, Coulson AF, Frère JM, Ghuysen JM, Joris B, Forsman M, et al. A standard numbering scheme for the class A beta-lactamases. Biochem J 1991;276(Pt 1):269-70.PubMedPMC
- 14. Bush K. Recent developments in beta-lactamase research and their implications for the future. Rev Infect Dis 1988;10:681-90.PubMed
- 15. Lei H, Liao J, Lin Y, Liu T, Lei W, Gao W. Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in treatment guidance for deep neck space abscess. BMC Microbiol 2025;25:166.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Liang X, Han J, Cui Y, Shu X, Lei M, Wang B, et al. Whole-genome sequencing of flammulina filiformis and multi-omics analysis in response to low temperature. J Fungi (Basel) 2025;11:229.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Li H, Bao S, Farzad N, Qin X, Fung AA, Zhang D, et al. Spatially resolved genome-wide joint profiling of epigenome and transcriptome with spatial-ATAC-RNA-seq and spatial-CUT&Tag-RNA-seq. Nat Protoc 2025 Mar 21. doi: 10.1038/s41596-025-01145-9. [Epub].ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Aronin SI, Dunne MW, Yu KC, Watts JA, Gupta V. Increased rates of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase isolates in patients hospitalized with culture-positive urinary Enterobacterales in the United States: 2011 - 2020. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2022;103:115717.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Afsharikhah S, Ghanbarpour R, Mohseni P, Adib N, Bagheri M, Jajarmi M. High prevalence of β-lactam and fluoroquinolone resistance in various phylotypes of Escherichia coli isolates from urinary tract infections in Jiroft city, Iran. BMC Microbiol 2023;23:114.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. AbuSara A, Tayyeb N, Matalka L, Almomani B, Abaza H, Nazer L. Prevalence and predictors of multi-drug resistant organisms among ambulatory cancer patients with urinary tract infections. Infect Drug Resist 2023;16:747-53.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 21. Araújo MR; Sant'Anna LO, Santos N, Seabra LF, Santos LS. Monitoring fluoroquinolone resistance among ESBL-positive and ESBL-negative Escherichia coli strains isolated from urinary tract infections: an alert for empirical treatment. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 2023;56:e0513.PubMedPMC
- 22. Collingwood JD, Yarbrough AH, Boppana SB, Dangle PP. Increasing prevalence of pediatric community-acquired UTI by extended spectrum β-Lactamase-producing E. coli: Cause for Concern. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2023;42:106-9.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Gebremedhin MG, Weldu Y, Kahsay AG, Teame G, Adane K. Extended-spectrum β-Lactamase and carbapenemase-producing Gram-negative bacteria and associated factors among patients suspected of community and hospital-acquired urinary tract infections at ayder comprehensive specialized hospital, Tigrai, Ethiopia. Infect Drug Resist 2023;16:4025-37.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 24. Armah E, Osae-Nyarko L, Idun B, Ahiabu MK, Agyapong I, Kwarteng FB, et al. High prevalence of ESBL genes in commensal escherichia coli of the urinary tract: implications for antibiotic stewardship among residents of Ghanaian elderly nursing care homes. Genes (Basel) 2024;15:985.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Biset S, Moges F, Endalamaw D, Eshetie S. Multi-drug resistant and extended-spectrum β-lactamases producing bacterial uropathogens among pregnant women in Northwest Ethiopia. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2020;19:25.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 26. Bou Chebl R, Assaf M, Kattouf N, Abou Arbid S, Haidar S, Geha M, et al. The prevalence and predictors of extended spectrum B-lactamase urinary tract infections among emergency department patients: a retrospective chart review. Am J Emerg Med 2021;49:304-9.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Correction to: Clinical features and outcomes of infections caused by metallo-β-Lactamase-producing Enterobacterales: a 3-year prospective study from an endemic area. Clin Infect Dis 2024;79:580.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Niaz H, Skurnik M, Adnan F. Genomic and proteomic characterization of four novel Schitoviridae family phages targeting uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Virol J 2025;22:83.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 29. Chetri S. Escherichia coli: an arduous voyage from commensal to Antibiotic-resistance. Microb Pathog 2025;198:107173.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Harris M, Fasolino T, Ivankovic D, Davis NJ, Brownlee N. Genetic factors that contribute to antibiotic resistance through intrinsic and acquired bacterial genes in urinary tract infections. Microorganisms 2023;11:1407.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Edowik Y, Caspari T, Williams HM. The amino acid changes T55A, A273P and R277C in the beta-lactamase CTX-M-14 render E. coli resistant to the antibiotic nitrofurantoin, a first-line treatment of urinary tract infections. Microorganisms 2020;8:1983.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Xu T, Wu W, Huang L, Liu B, Zhang Q, Song J, et al. Novel plasmid-mediated CMY variant (CMY-192) conferring ceftazidime-avibactam resistance in multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2024;68:e0090624.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 33. Ghaly TM, Gillings MR, Penesyan A, Qi Q, Rajabal V, Tetu SG. The natural history of integrons. Microorganisms 2021;9:2212.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Abubaker KT, Anwar KA. Antimicrobial susceptibility and integrons detection among extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae isolates in patients with urinary tract infection. PeerJ 2023;11:e15429.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 35. Yang YM, Osawa K, Kitagawa K, Hosoya S, Onishi R, Ishii A, et al. Differential effects of chromosome and plasmid bla(CTX-M-15) genes on antibiotic susceptibilities in extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolates from patients with urinary tract infection. Int J Urol 2021;28:623-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 36. Al-Khlifeh EM, Alkhazi IS, Alrowaily MA, Alghamdi M, Alrashidi M, Tarawneh AS, et al. Extended spectrum beta-lactamase bacteria and multidrug resistance in jordan are predicted using a new machine-learning system. Infect Drug Resist 2024;17:3225-40.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 37. Dutta A, Mukherjee S, Haldar J, Maitra U. Augmenting antimicrobial resistance surveillance: rapid detection of β-Lactamase-expressing drug-resistant bacteria through sensitized luminescence on a paper-supported hydrogel. ACS Sens 2024;9:351-60.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 38. Suhandynata RT, Lund K, Caraballo-Rodríguez AM, Reed SL, Dorrestein PC, Fitzgerald RL, et al. Mass spectrometry-based detection of beta lactam hydrolysis enables rapid detection of beta Lactamase mediated antibiotic resistance. Lab Med 2022;53:128-37.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 39. Kaur H, Modgil V, Chaudhary N, Mohan B, Taneja N. Computational guided drug targets identification against extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing multi-drug resistant uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Biomedicines 2023;11:2028.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 40. Almomani BA, Khasawneh RA, Saqan R, Alnajjar MS, Al-Natour L. Predictive utility of prior positive urine culture of extended- spectrum β-lactamase producing strains. PLoS One 2020;15:e0243741.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Yan WX, Hunnewell P, Alfonse LE, Carte JM, Keston-Smith E, Sothiselvam S, et al. Functionally diverse type V CRISPR-Cas systems. Science 2019;363:88-91.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Chen JS, Ma E, Harrington LB, Da Costa M, Tian X, Palefsky JM, et al. CRISPR-Cas12a target binding unleashes indiscriminate single-stranded DNase activity. Science 2018;360:436-9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 43. Wang S, Wang S, Tang Y, Peng G, Hao T, Wu X, et al. Detection of Klebsiella pneumonia DNA and ESBL positive strains by PCR-based CRISPR-LbCas12a system. Front Microbiol 2023;14:1128261.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Olaru ID, Elamin W, Chisenga M, Malou N, Piton J, Yeung S, et al. Evaluation of the InTray and Compact Dry culture systems for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections in patients presenting to primary health clinics in Harare, Zimbabwe. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2021;40:2543-50.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 45. Rahman MK, Rodriguez-Mori H, Loneragan G, Awosile B. One health distribution of beta-lactamases in Enterobacterales in the United States: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2025;65:107422.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Kiemde D, Ribeiro I, Sanou S, Coulibaly B, Sie A, Ouedraogo AS, et al. Molecular characterization of beta-lactamase genes produced by community-acquired uropathogenic Escherichia coli in Nouna. J Infect Dev Ctries 2020;14:1274-80.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 47. Verma S, Kalyan RK, Gupta P, Khan MD, Venkatesh V. Molecular characterization of extended spectrum β-Lactamase producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates and their antibiotic resistance profile in health care-associated urinary tract infections in North India. J Lab Physicians 2023;15:194-201.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 48. Gray HA, Biggs PJ, Midwinter AC, Rogers LE, Fayaz A, Akhter RN, et al. Genomic epidemiology of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from humans and a river in Aotearoa New Zealand. Microb Genom 2025;11:001341.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Shen S, Huang X, Shi Q, Guo Y, Yang Y, Yin D, et al. Occurrence of NDM-1, VIM-1, and OXA-10 co-producing Providencia rettgeri clinical isolate in China. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021;11:789646.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 50. Piza-Buitrago A, Rincón V, Donato J, Saavedra SY, Duarte C, Morero J, et al. Genome-based characterization of two Colombian clinical Providencia rettgeri isolates co-harboring NDM-1, VIM-2, and other β-lactamases. BMC Microbiol 2020;20:345.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 51. Cave R, Ter-Stepanyan MM, Kotsinyan N, Mkrtchyan HV. An emerging lineage of uropathogenic extended spectrum β -Lactamase Escherichia coli ST127. Microbiol Spectr 2022;10:e0251122.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 52. Elshamy AA, Saleh SE, Aboshanab KM, Aboulwafa MM, Hassouna NA. Transferable IncX3 plasmid harboring bla(NDM-1), ble(MBL), and aph(3')-VI genes from Klebsiella pneumoniae conferring phenotypic carbapenem resistance in E. coli. Mol Biol Rep 2023;50:4945-53.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 53. Elshamy AA, Aboshanab KM, Yassien MA, Hassouna NA. Prevalence of plasmid-mediated resistance genes among multidrug-resistant uropathogens in Egypt. Afr Health Sci 2020;20:190-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 54. Dolatyar Dehkharghani A, Haghighat S, Rahnamaye Farzami M, Rahbar M, Douraghi M. Clonal relationship and resistance profiles among ESBL-producing Escherichia coli. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021;11:560622.PubMedPMC
- 55. Han H, Zhao Z, Lin Y, Lin B, Xu H, Zheng B. Co-production of NDM-1 and OXA-10 β-Lactamase in Citrobacter braakii strain causing urinary tract infection. Infect Drug Resist 2022;15:1127-33.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 56. Ramachandran G, Rajivgandhi GN, Chackaravarthi G, Kanisha CC, Siddiqi MZ, Alharbi NS, et al. Isolation and molecular identification of extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing bacteria from urinary tract infection. J Infect Public Health 2021;14:1911-6.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Urmi UL, Nahar S, Rana M, Sultana F, Jahan N, Hossain B, et al. Genotypic to phenotypic resistance discrepancies identified involving β-Lactamase genes, blaKPC, blaIMP, blaNDM-1, and blaVIM in uropathogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Drug Resist 2020;13:2863-75.PubMedPMC
- 58. Birgy A, Madhi F, Jung C, Levy C, Cointe A, Bidet P, et al. Clavulanate combinations with mecillinam, cefixime or cefpodoxime against ESBL-producing Enterobacterales frequently associated with blaOXA-1 in a paediatric population with febrile urinary tract infections. J Antimicrob Chemother 2021;76:2839-46.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 59. Thelen H, Dilworth TJ, Mercier RC. Examining the combination of cefixime and amoxicillin/clavulanate against extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli Isolates. Chemotherapy 2022;67:261-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 60. Gnanasekaran C, Alobaidi AS, Govindan R, Chelliah CK, Muhammad Zubair S, Alagarsamy S, et al. Piperacillin/tazobactum and cefotaxime decrease the effect of beta lactamase production in multi-drug resistant K. pneumoniae. J Infect Public Health 2021;14:1777-82.ArticlePubMed
- 61. Bassetti M, Vena A, Giacobbe DR. The safety of ceftolozane/tazobactam for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2023;22:533-40.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Sader HS, Mendes RE, Arends SJ, Carvalhaes CG, Shortridge D, Castanheira M. Comparative activity of newer β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from US medical centres (2020-2021). Int J Antimicrob Agents 2023;61:106744.ArticlePubMed
- 63. Miller AA, Shapiro AB, McLeod SM, Carter NM, Moussa SH, Tommasi R, et al. In vitro characterization of ETX1317, a broad-spectrum β-Lactamase inhibitor that restores and enhances β-Lactam activity against multi-drug-resistant Enterobacteriales, including carbapenem-resistant strains. ACS Infect Dis 2020;6:1389-97.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 64. Das CK, Nair NN. Elucidating the molecular basis of avibactam-mediated inhibition of class A β-Lactamases. Chemistry 2020;26:9639-51.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 65. Al Musawa M, Bleick CR, Herbin SR, Caniff KE, Van Helden SR, Rybak MJ. Aztreonam-avibactam: the dynamic duo against multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens. Pharmacotherapy 2024;44:927-38.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 66. Smith JR, Rybak JM, Claeys KC. Imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam: a novel β-Lactam-β-Lactamase inhibitor combination for the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections. Pharmacotherapy 2020;40:343-56.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 67. Lang PA, Parkova A, Leissing TM, Calvopiña K, Cain R, Krajnc A, et al. Bicyclic boronates as potent inhibitors of AmpC, the class C β-Lactamase from Escherichia coli. Biomolecules 2020;10:899.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Lence E, González-Bello C. Molecular basis of bicyclic boronate β-Lactamase inhibitors of ultrabroad efficacy - insights from molecular dynamics simulation studies. Front Microbiol 2021;12:721826.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 69. Lasko MJ, Nicolau DP, Asempa TE. Clinical exposure-response relationship of cefepime/taniborbactam against Gram-negative organisms in the murine complicated urinary tract infection model. J Antimicrob Chemother 2022;77:443-7.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 70. Wang X, Zhao C, Wang Q, Wang Z, Liang X, Zhang F, et al. Erratum to: in vitro activity of the novel β-lactamase inhibitor taniborbactam (VNRX-5133), in combination with cefepime or meropenem, against MDR Gram-negative bacterial isolates from China. J Antimicrob Chemother 2020;75:2019.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 71. Stewart AG, Harris PN, Henderson A, Schembri MA, Paterson DL. Erratum to: Oral cephalosporin and β-lactamase inhibitor combinations for ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae urinary tract infections. J Antimicrob Chemother 2021;76:281.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 72. Hafeez S, Zafar Paracha R, Adnan F. Designing of fragment based inhibitors with improved activity against E. coli AmpC β -lactamase compared to the conventional antibiotics. Saudi J Biol Sci 2024;31:103884.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 73. Proschak A, Martinelli G, Frank D, Rotter MJ, Brunst S, Weizel L, et al. Nitroxoline and its derivatives are potent inhibitors of metallo-β-lactamases. Eur J Med Chem 2022;228:113975.ArticlePubMed
- 74. Cotroneo N, Rubio A, Critchley IA, Pillar C, Pucci MJ. In Vitro and in vivo characterization of tebipenem, an oral carbapenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2020;64:e02240-19.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 75. Bersani M, Failla M, Vascon F, Gianquinto E, Bertarini L, Baroni M, et al. Structure-based optimization of 1,2,4-Triazole-3-Thione derivatives: improving inhibition of NDM-/VIM-type metallo-β-Lactamases and synergistic activity on resistant bacteria. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2023;16:1682.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 76. Chang CY, Lee YL, Huang YT, Ko WC, Ho MW, Hsueh PR. In vitro activity of imipenem/relebactam, meropenem/vaborbactam and comparators against Enterobacterales causing urinary tract infection in Taiwan: results from the Study for Monitoring Antimicrobial Resistance Trends (SMART), 2020. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2023;61:106815.ArticlePubMed
- 77. Kanwal A, Uzair B, Sajjad S, Samin G, Ali Khan B, Khan Leghari SA. et al. Synthesis and characterization of carbon dots coated CaCO(3) nanocarrier for levofloxacin against multidrug resistance extended-spectrum beta-lactamase Escherichia coli of urinary tract infection origin. Microb Drug Resist 2022;28:106-19.PubMed
- 78. Hayakawa K, Matsumura Y, Uemura K, Tsuzuki S, Sakurai A, Tanizaki R, et al. Effectiveness of cefmetazole versus meropenem for invasive urinary tract infections caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2023;67:e0051023.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 79. Delory T, Gravier S, Le Pluart D, Gaube G, Simeon S, Davido B, et al. Temocillin versus carbapenems for urinary tract infection due to ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae:a multicenter matched case-control study. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2021;58:106361.ArticlePubMed
- 80. Mohsenpour B, Ahmadi A, Azizzadeh H, Ghaderi E, Hajibagheri K, Afrasiabian S, et al. Comparison of three doses of amikacin on alternate days with a daily dose of meropenem during the same period for the treatment of urinary tract infection with E. coli: a double-blind clinical trial. BMC Res Notes 2024;17:38.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 81. Aththanayaka A, Weerasinghe G, Weerakkody NS, Samarasinghe S, Priyadharshana U. Effectiveness of selective antibiotics use in ESBL-related UTIs. BMC Microbiol 2024;24:360.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 82. Álvarez Otero J, Lamas Ferreiro JL, Sanjurjo Rivo A, Maroto Piñeiro F, González González L, Enríquez de Salamanca Holzinger I, et al. Treatment duration of complicated urinary tract infections by extended-spectrum beta-lactamases producing enterobacterales. PLoS One 2020;15:e0237365.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 83. Almohareb SN, Aldairem A, Alsuhebany N, Alshaya OA, Aljatli D, Alnemer H, et al. Effectiveness of oral antibiotics in managing extended-spectrum B-lactamase urinary tract infections: a retrospective analysis. SAGE Open Med 2024;12:20503121241259993.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 84. Hassuna NA, Rabie EM, Mahd WK, Refaie MM, Yousef RK, Abdelraheem WM. Antibacterial effect of vitamin C against uropathogenic E. coli in vitro and in vivo. BMC Microbiol 2023;23:112.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 85. Vazquez NM, Mariani F, Torres PS, Moreno S, Galván EM. Cell death and biomass reduction in biofilms of multidrug resistant extended spectrum β-lactamase-producing uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates by 1,8-cineole. PLoS One 2020;15:e0241978.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 86. Bier N, Hanson B, Jiang ZD, DuPont HL, Arias CA, Miller WR. A case of successful treatment of recurrent urinary tract infection by extended-spectrum β-Lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae using oral lyophilized fecal microbiota transplant. Microb Drug Resist 2023;29:34-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 87. Qiu Y, Gao Y, Bai Q, Zhao Y. Ion coupling and inhibitory mechanisms of the human presynaptic high-affinity choline transporter CHT1. Structure 2025;33:321-9.e325.ArticlePubMed
- 88. Feng DC, Zhu WZ, Wang J, Li DX, Shi X, Xiong Q, et al. The implications of single-cell RNA-seq analysis in prostate cancer: unraveling tumor heterogeneity, therapeutic implications and pathways towards personalized therapy. Mil Med Res 2024;11:21.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 89. Tuo Z, Zhang Y, Li D, Wang Y, Wu R, Wang J, et al. Relationship between clonal evolution and drug resistance in bladder cancer: a genomic research review. Pharmacol Res 2024;206:107302.ArticlePubMed
- 90. Weng T, Wang J, Yang M, Zhang W, Wu P, You C, et al. Nano materials for the delivery of bioactive factors to enhance angiogenesis of dermal substitutes during wound healing. Burns Trauma 2022;10:tkab049.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 91. Johnson RP, Ratnacaram CK, Kumar L, Jose J. Combinatorial approaches of nanotherapeutics for inflammatory pathway targeted therapy of prostate cancer. Drug Resist Updat 2022;64:100865.ArticlePubMed
- 92. Li J, Zhu L, Kwok HF. Nanotechnology-based approaches overcome lung cancer drug resistance through diagnosis and treatment. Drug Resist Updat 2023;66:100904.ArticlePubMed
- 93. Yao L, Bojic D, Liu M. Applications and safety of gold nanoparticles as therapeutic devices in clinical trials. J Pharm Anal 2023;13:960-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef
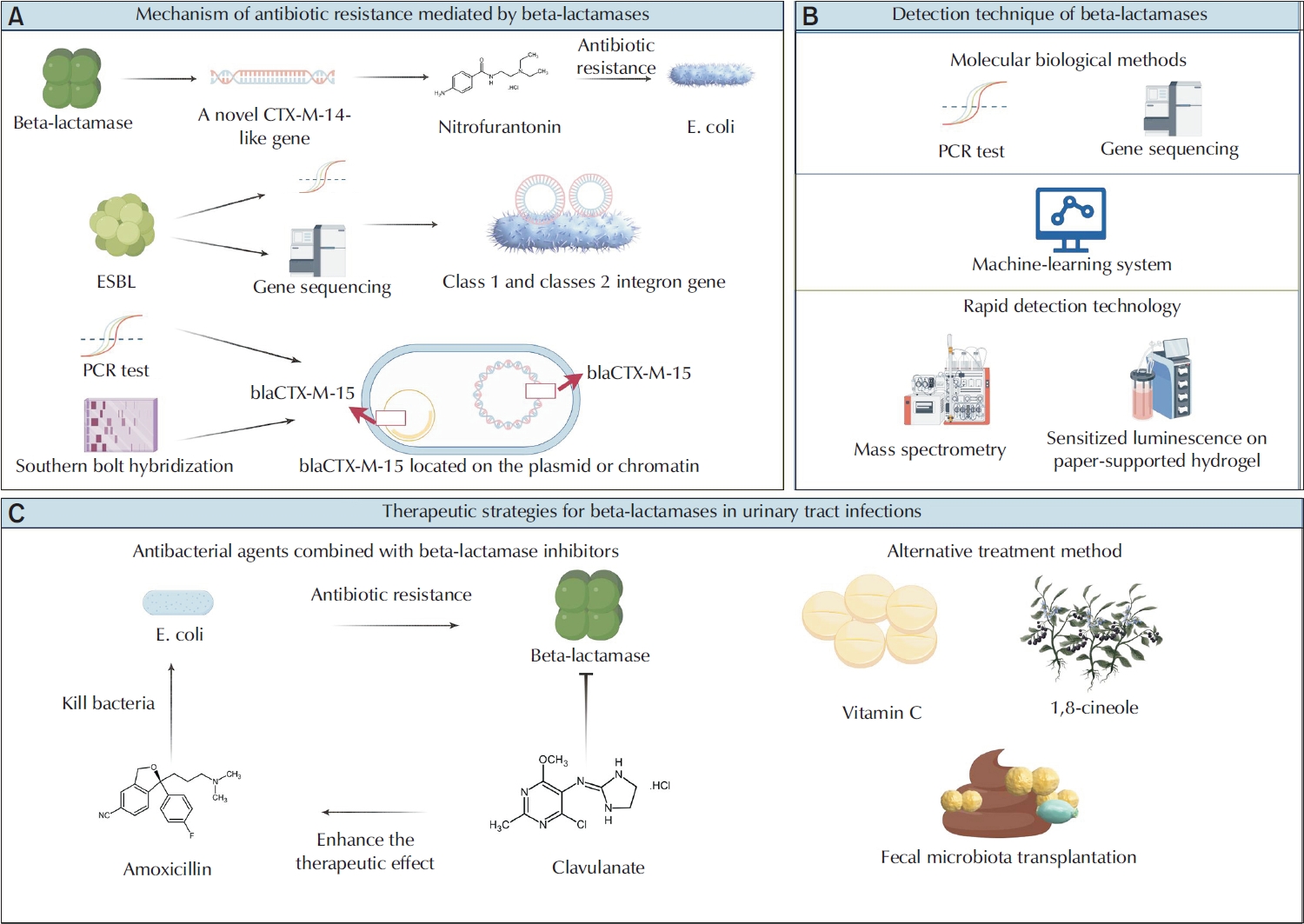
Fig. 1.
| Disease type | Organism | No. of patients | Antimicrobial agent(s) | Outcome | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Febrile urinary tract infections | ESBL-producing Enterobacterales | 54 | CFX + AMC; MEC + AMC | Effective treatment, no failures, no recurrent infections | 34453533 |
| Community-acquired urinary tract infection | E. coli | 46 | CFX + AMC | 85% susceptible; synergistic | 36417841 |
| Complicated urinary tract infections | MDR P. aeruginosa, ESBL-producing Enterobacterales | Review | C/T | Highly effective | 37394943 |
| Not applicable | K. pneumoniae | Not specified | PIP/TAZ, CTX | Data not provided | 34772638 |
| Not applicable | P. aeruginosa | 3184 | CAZ-AVI, C/T, IMP-REL, TOB, PIP/TAZ, MER | High susceptibility (96.4%-98%) | 36738849 |
| Not applicable | MDR Enterobacteriales | Not specified | ETX1317 + CPD | Strong broad inhibition | 32255609 |
| Complex IAIs, UTIs, and HAP | MDR GNB | See full text | ATM-AVI | Safe and effective | 39601336 |
| Complex UTIs and IAIs | MDR GNB | Not specified | IMI-REL | Well-tolerated | 32060929 |
| Not applicable | E. coli (AmpC) | Not applicable | Bicyclic boronates | Potent AmpC inhibition | 32545682 |
| Not applicable | P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, Enterobacteriaceae | Not applicable | Bicyclic boronates | Broad-spectrum efficacy | 34421880 |
| Neutropenic mice | Enterobacterales, P. aeruginosa, S. maltophilia | 18 | CEP alone; CEP/TAN | CEP alone ineffective; CEP/TAN kills | 34747449 |
| Not applicable | Enterobacteriaceae, P. aeruginosa | 500 | CEP/TAN, MER/TAN | Enhance CEP activity | 32335680 |
| UTIs caused by ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae | ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae | Not applicable | Oral cephalosporin/BLI combinations | Good in vitro activity | 33111952 |
| Not applicable | E. coli | Not applicable | LCs, CEF | Stable binding | 38125736 |
| Not applicable | MBL-producing GNB | Not applicable | Nitroxoline derivatives, IMP | Inhibits MBL | 34865870 |
| Complicated UTIs | MDR GNB | Full text | Tebipenem, MER | Equivalent to MER | 32423950 |
| Not applicable | MBL-producing GNB | Not applicable | MER, Triazole-thione derivatives | Low μM inhibitors | 38139809 |
| UTIs | Enterobacterales | 309 | IMP-REL, MER/VAB | Excellent efficacy (95%–99.3%) | 37059343 |
ESBL, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase; CFX, cefixime; AMC, amoxicillin/clavulanate; MEC, mecillinam;

 KAUTII
KAUTII
 Cite
Cite

