Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Trends in Age-Specific Prevalence of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Young Hwan Kim, Se Hwa Hong, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Tae Hyoung Kim, Sae Chul Kim, Sang Baek Koh, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):101-106. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: To elucidate the longitudinal changes in the prevalence of lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) according to age over the past 10 years.
Materials and Methods: The changes in the proportion of prevalence for LUTD, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and urinary incontinence (UI) among South Koreans from 2009 to 2018, were analyzed using the National Health Information Database established by the Korean National Health Insurance Service. All conditions were defined according to the corresponding Korean Standard Classification of Diseases-8 for diagnosis and surgical procedures and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service codes for drugs.
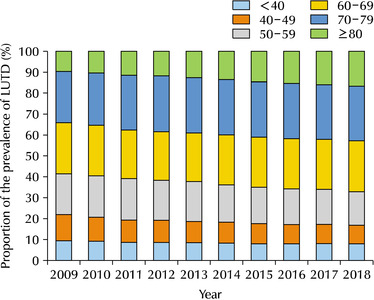
Results: The 60-69, 70-79, and over 80 age groups accounted for more than 60% of the LUTD cases from 2009 to 2018, while significant increases in the crude prevalence of LUTD were observed over a 10-year period in all age groups (p for trend <0.05). In age groups over 60 years, LUTD was more prevalent in men than women, but there was no statistically significant difference in proportion (p>0.05). The changes in the prevalence and prevalence proportion exhibited similar trends in BPH, UI, and LUTD.
Conclusions: LUTD was more prevalent in the elderly aged over 60 years old than in younger adults. Therefore, this study suggests the development of nationwide healthcare policies to manage LUTD in the elderly population of South Korea, which is expected to become the world’s most aged population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing strategies for managing urological disorders in aging populations: a comprehensive review
Hong Liu, Jie Wu
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Nursing strategies for managing urological disorders in aging populations: a comprehensive review
- 4,558 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Case of Fournier’s Gangrene in a Patient with Long-Term Indwelling Catheterization due to Urinary Incontinence after Open Radical Prostatectomy
- Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(1):6-9. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.1.6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Fournier’s gangrene is a life-threatening disease that needs to be treated as soon as possible. An 82-year-old male, who exchanged a urethral catheter once a month for urinary incontinence management after open radical prostatectomy, presented with an acute onset of mental change and general weakness. After ten days’ hospitalization, the disease was diagnosed. The scrotal wall was opened, and the infectious tissue was exposed to the air and kept open with an aseptic dressing. After 45 days, his scrotal wound healed and returned to its typical appearance without scarring and wound disruption. He recovered fully from the infection. This paper reports a case of Fournier’s gangrene in a patient with long-term indwelling catheterization due to urinary incontinence after an open radical prostatectomy with a literature review.
- 1,788 View
- 1 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


