Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Reports
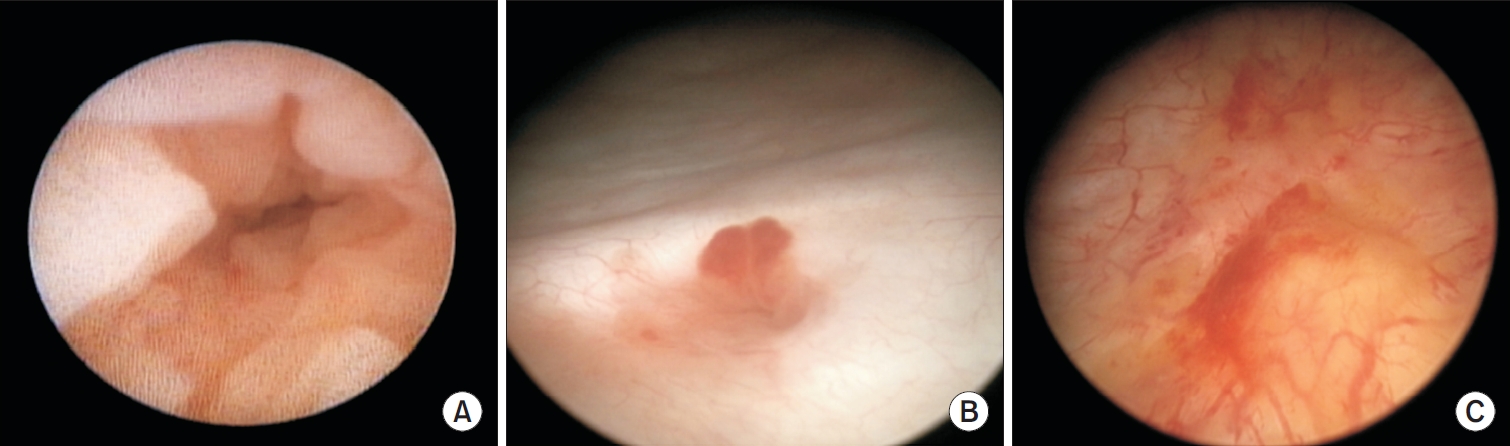
- Primary Bladder and Ureteral Amyloidosis Initially Diagnosed as Chronic Cystitis: A Case Report
- Seungsoo Lee, Dan Bee Lee, Hyun Jung Lee, Won Hoon Song, Sung-Woo Park, Jong Kil Nam
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):167-172. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550038019
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Primary localized amyloidosis confined to the urinary tract is uncommon and frequently misinterpreted due to clinical and radiologic overlap with more prevalent conditions. We describe a 69-year-old woman who experienced recurrent gross hematuria over 2 years and underwent initial transurethral resection based on a presumptive diagnosis of chronic cystitis. Subsequent evaluation revealed a left ureteral mass with hydronephrosis, raising concern for malignancy. Histopathologic examination of both bladder and ureteral specimens demonstrated amorphous eosinophilic deposits that stained positive with Congo red and showed apple-green birefringence under polarized microscopy. Immunofluorescence confirmed λ-light-chain predominance, establishing AL (amyloid light chain)-type amyloidosis without systemic involvement. The patient underwent complete endoscopic resection and remains asymptomatic during ongoing surveillance. This case highlights the diagnostic challenges posed by localized urinary amyloidosis and underscores the importance of histologic confirmation in atypical inflammatory lesions.
- 553 View
- 5 Download

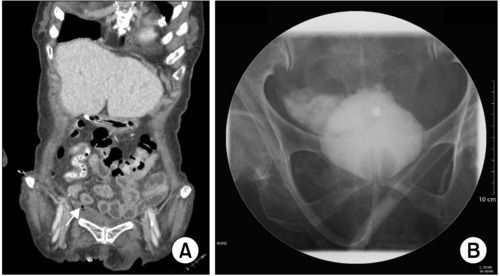
- Spontaneous Bladder Perforation in a Patient with a Long-Term Intraurethral Catheter
- Taegi Choi, Hyunkyung Lee, Junseok Kim, Sunghoon Lee, Younkyung Cho, Eunyoung Kang, Jinsun Kang, Sumin Lee, Eunju Na
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):110-113. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Urinary catheters are commonly used to address various urinary problems. However, the catheter itself can be a cause of several complications, including catheter-associated urinary tract infections, damage to the bladder and kidneys, and, in extremely rare cases, bladder perforation. We present a case of spontaneous bladder perforation in a patient who had a long-term indwelling intraurethral catheter. The patient with prior hypoxic brain damage suddenly developed tachypnea, tachycardia, and oxygen desaturation. Computed tomography and retrograde cystography revealed an extraperitoneal bladder perforation with an intra-pelvic abscess. Antibiotics were prescribed and a urinary catheter was inserted for drainage. After 11 weeks, the abscess resolved, and the catheter was removed to enable self-voiding. The perforation was attributed to chronic inflammation and distension of the bladder wall caused by the intraurethral catheter. Given the potential complications associated with long-term urinary catheterization, the timely removal of indwelling catheters should be considered.
- 4,736 View
- 18 Download

Original Articles
- Exploring National Trends in Bladder-Related Urological Procedures: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Hyosang Kwon, Wonjong Yang, Sangyong Park, Heesub Lee, Jong Keun Kim, Jun Hyun Han
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(2):50-59. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.2.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study examined the epidemiological trends of bladder-related urological procedures in South Korea from 2009 to 2021.
Materials and Methods: The data were obtained from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) database, encompassing various bladder-related urological procedures. The frequencies and trends were analyzed using statistical methods.
Results: Uroflowmetry, cystoscopy, prostate biopsy, and urethral dilation showed a positive trend, while prostate massage exhibited a negative trend. The 72-hour voiding function test, which started in 2017, also demonstrated a positive trend in frequency. A urodynamic study and mid-urethral sling operation exhibited an overall decreasing trend. Bladder-indwelling catheter, Nelaton catheterization, and cystostomy catheter change showed increasing trends, while suprapubic cystostomy showed a decreasing trend.
Conclusions: This 12-year analysis provided valuable insights into the epidemiological patterns and utilization of bladder-related urological procedures in South Korea. These trends highlight the evolving landscape of diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in bladder-related conditions and the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between urology and other medical departments. The results highlight the need for optimizing catheter-related care protocols, resource allocation, and continued monitoring of practices across healthcare settings.
- 2,566 View
- 9 Download

- Efficacy and Tolerability of Solifenacin Fumarate with Overactive Bladder Patients: A Multicenter Observational Study
- Jae Hun Shim, Se Young Choi, Joon Hee Gook, Yong-June Kim, Woo Heon Cha, Dae Hee Kim, Kyeong Hee Kim, Young Woong Park, Jin Mo Um, Il Sung Lim, Kyung Keun Seo, Kyu Seon Cho, Young Jae Lee, Mi-Kyung Lee, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(1):8-15. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.1.8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: Overactive bladder (OAB) is characterized by a series of highly prevalent symptoms among older adults. This study used the Overactive Bladder Symptom Score (OABSS) and Patient Perception of Bladder Condition (PPBC) tools to evaluate the efficacy and stability of solifenacin fumarate in the treatment of OAB.
Materials and Methods: This was a prospective, multicenter, single-arm, 12-week study that enrolled 163 OAB patients. The patients received 5 mg/day of solifenacin fumarate. The changes in the OABSS, symptoms, and PPBC scores were evaluated at 0, 4, and 12 weeks. Subgroup analysis of the OABSS and PPBC scores based on sex, diabetes mellitus (DM) status, and body mass index (BMI) were also evaluated.
Results: At the baseline (week 0), the mean OABSS for all patients was 8.45±2.38 (p=0.199). Subsequently, the mean OABSS declined to 5.41±2.69 (p=0.255) at four weeks and 4.21±2.61 (p=0.240) at 12 weeks. The OABSS subscore and PPBC score decreased significantly during the study (p<0.01). After cases were stratified according to sex, DM status, and BMI, the mean OABSS (mean and subscore) and PPBC score at four and 12 weeks were also improved significantly relative to the baseline scores (both p<0.05). The overall incidence of adverse events was 7.36% (12 cases), and three patients (1.82%) permanently discontinued solifenacin fumarate because of the adverse events.
Conclusions: Solifenacin fumarate is a safe and effective treatment alternative for relieving OAB symptoms, considering the balance between the efficacy, patientsʼ well-being, and tolerability.
- 4,502 View
- 20 Download

Case Report
- Von Brunn’s Nest in an Incidental Bladder Mass Found during Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate
- Seungsoo Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(1):13-15. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - A 62-year-old male with benign prostatic hyperplasia underwent holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. During surgery, a small nodular mass was found incidentally in the trigone of the bladder. The lesion was removed completely by a transurethral resection with a bipolar device. A pathology examination of the lesion indicated von Brunn’s nests.
- 3,808 View
- 23 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII
 First
First Prev
Prev


