Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Effect of Residual Stone Fragments on Patient-Reported Quality of Life after Endoscopic Kidney Stone Surgery
- Sang Hee Lee, Jun-Koo Kang, Jae-Wook Chung, Yun-Sok Ha, Jun Nyung Lee, Seock Hwan Choi, Hyun Tae Kim, Tae-Hwan Kim, Eun Sang Yoo, Tae Gyun Kwon, Bum Soo Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):31-39. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
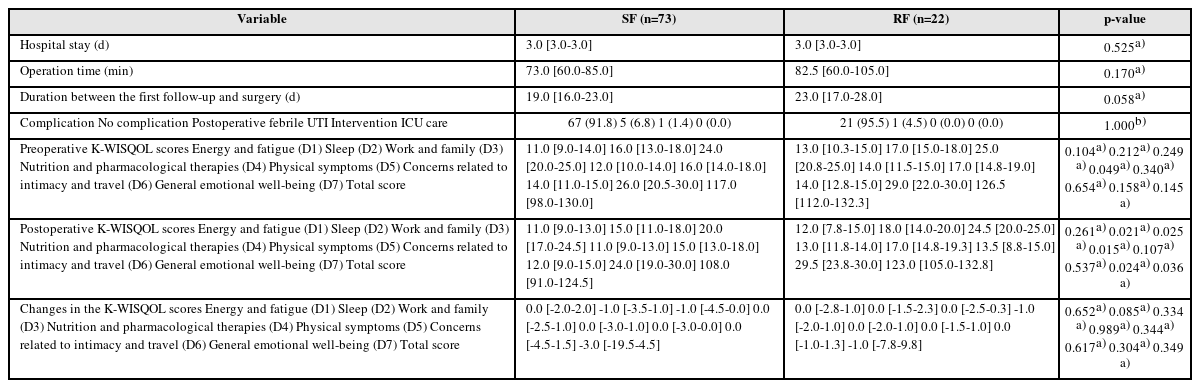
ePub - Purpose: This study examined the effects of residual fragments (RF) on the patient-reported quality of life (QOL) after kidney stone surgery, such as retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) and percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), using the Korean version of the Wisconsin Stone Quality of Life Questionnaire (K-WISQOL).
Materials and Methods: The medical records of 156 patients who underwent RIRS or PCNL and completed the preoperative and postoperative K-WISQOL from January 2021 to September 2023 were analyzed retrospectively. The patients were divided into RIRS and PCNL groups by the surgical method. The participants completed the K-WISQOL within four weeks before and after treatment. The patients’ baseline characteristics, surgical outcomes, and K-WISQOL scores were compared according to the presence of RF in each surgical group.
Results: Of the 156 patients, 95 underwent RIRS, and 61 underwent PCNL. In the RIRS group, the patients’ baseline characteristics and surgical outcomes were similar in the stone-free (SF) and RF subgroups. The changes in all K-WISQOL domain scores and total scores were similar in the two subgroups. In the PCNL group, the RF subgroup had a significantly higher proportion of staghorn stones, a significantly larger mean stone diameter and significantly longer operation time than those of the SF subgroup. But, the changes in all K-WISQOL domain scores and total scores were not significantly different between the two subgroups, as observed in the RIRS group.
Conclusions: This study showed that the presence of RFs after endoscopic kidney surgery did not affect the short-term patient-reported QOL regardless of the surgical methods.
- 3,565 View
- 39 Download

- Feasibility of Anesthesia-Free Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy in Elderly Patients with Urinary Tract Infections
- Duk Yoon Kim, Hyun Jin Jung, Eun Kyoung Yang, Won Yeol Cho
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(2):60-63. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.2.60
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: Patients with underlying diseases, particularly in the elderly, urinary tract obstruction with a ureter stone would progress to severe conditions. Some of them have poor general conditions to endure anesthesia. Therefore, this study validated the feasibility of ureteroscopic stone removal without anesthesia for elderly patients with ureter stones who were under impending septic conditions or severe urinary tract infections.
Materials and Methods: Thirty-four patients (16 males and 18 females) were included in this study. All of them had serious problems, making it difficult to endure anesthesia. Most of them were inserted pre-operative percutaneous nephrostomy catheter, and ureteroscopic lithotripsy was performed successfully after intravenous analgesic injection (pethidine 25 mg).
Results: The mean age was 71.8±10.84 years. The locations of the stones were upper ureter in 11, mid-ureter in 6, and lower ureter in 17 cases. Urine and blood cultures identified bacteria from 17/34 patients. Escherichia coli was the most common (10/17), followed in order by Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus epidermidis in 5 and 2 cases, respectively. Most patients had an abnormal white blood cell count (19,400±4,233.3/l) and elevated C-reactive protein levels (110.3±83.6 mg/L). No patient had to stop the operation because of intolerable pain. The mean of the visual analog pain scale was 3.2±0.86. The overall success rate was 100%.
Conclusions: The trial of ureteroscopic lithotripsy after administering analgesics could improve the condition of elderly patients whose general condition is too poor to endure anesthesia without serious complications.
- 1,938 View
- 10 Download

- Stone-Free Rates of mPCNL, PCNL, and RIRS: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- Dong Hyuk Kang, Kang Su Cho, Doo Yong Chung, Won Sik Jeong, Hae Do Jung, Do Kyung Kim, Joo Yong Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(1):14-25. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: Retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) and percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) are performed to treat renal stones, and miniature PCNL (mPCNL) is used as an alternative to conventional PCNL. We conducted a systematic review of published studies regarding RIRS, PCNL, and mPCNL and performed network meta-analysis on successful outcome (stone-free) rates.
Materials and Methods: The PubMed and EMBASE databases were searched up to December 2020. Data extraction formats were used to extract data on successful outcome rates, study designs, numbers of subjects and characteristics, and methods used to treat renal stones (i.e., RIRS, PCNL, or mPCNL).
Results: Data obtained by 25 studies were used to compare the stone-free rates of RIRS, PCNL, and mPCNL; six comparisons of PCNL and mPCNL, seven of mPCNL and RIRS, and 12 of RIRS and PCNL were analyzed. No difference was found between the stone-free rates of PCNL and mPCNL (odds ratio [OR]: 0.96; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.51-1.9) by network meta-analysis. However, the stone-free rate of RIRS was lower than that of mPCNL (OR: 0.41; 95% CI: 0.021-0.82) and PCNL (OR: 0.43; 95% CI: 0.22-0.82). Ranking analysis ranked mPCNL as No. 1 and PCNL as No. 2.
Conclusions: PCNL and mPCNL had better stone-free rates than RIRS for the treatment of renal stones, but the treatment outcomes of PCNL and mPCNL were no different. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extraplanar ultrasound-guided multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a retrospective comparative study in patients with complex nephrolithiasis
Geng-Geng Wei, Kristine J. S. Kwan, Yu Yang, Qing-Shan Yang, Zhen-Quan Lu, Lin Xiong, Xiang Xu
Frontiers in Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes of Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Results from a Multicenter Study by the Spanish Urology Association’s Renal Transplant Group
A. Sierra, H. Alfambra, J. M. López, A. Mercadé, L. L. Peri, R. Espílez, M. Álvarez–Maestro, R. Martínez–Corral, D. A. Pérez-Fentes, B. Etcheverry, S. Colom, F. Vigués, A. Alcaraz, M. P. Luque, C. Torrecilla, M. Musquera
World Journal of Urology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Supracostal ultrasound guided approach percutaneous nephrolithotomy (SUGA-PNL) versus retrograde intrarenal surgery for large volume isolated upper calyceal stones: a prospective randomized analysis
Ahmed Assem, Ahmed Abdalla, Mohamed Elzoheiry, Islam Nasser Abd Elaziz, Hesham Amr, Heba Bakr, Ahmed M Rammah
Urolithiasis.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Extraplanar ultrasound-guided multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a retrospective comparative study in patients with complex nephrolithiasis
- 5,293 View
- 66 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Is Preoperative Pyuria Associated with Postoperative Febrile Complication after Ureteroscopic Ureter or Renal Stone Removal?
- Seungsoo Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(1):1-5. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: The association between preoperative pyuria and postoperative febrile complications after ureteroscopic ureter or renal stone removal was examined.
Materials and Methods: From June 2014 to July 2016, 110 patients who underwent ureteroscopic ureter or renal stone removal by a single surgeon were evaluated. The patients were categorized as the “pyuria group” and “nonpyuria group.” The sex, age, stone laterality, stone location, stone size, preoperative urine culture results, and postoperative complications in each group were analyzed.
Results: The pyuria and nonpyuria groups were comprised of 55 patients each. The mean ages the pyuria and nonpyuria groups were 58.4±16.1 years and 54.4±13.2 years, respectively. There were respectively, 43 and 12 unilateral and bilateral stones in the pyuria group, and 53 and two in the nonpyuria group. The stone sizes of the pyuria and nonpyuria groups were 13.1±5.4 mm and 11.1±4.7 mm, respectively. The pyuria group contained more patients with bilateral stones and larger stones than the nonpyuria group. Five and two postoperative febrile complications were encountered in the pyuria group and the nonpyuria group, respectively. No significant difference in febrile complications was observed between the two groups. In logistic regression analysis, bilateral stones and larger stones were associated with pyuria.
Conclusions: In ureteroscopic stone removal surgery, preoperative pyuria was associated with bilateral and larger stones, but there were no associations with febrile complications.
- 1,533 View
- 3 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


