Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
- Adult Syphilis: A Narrative Review of Clinical Insights and Public Health Implications in Urology
- Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):123-131. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550039017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
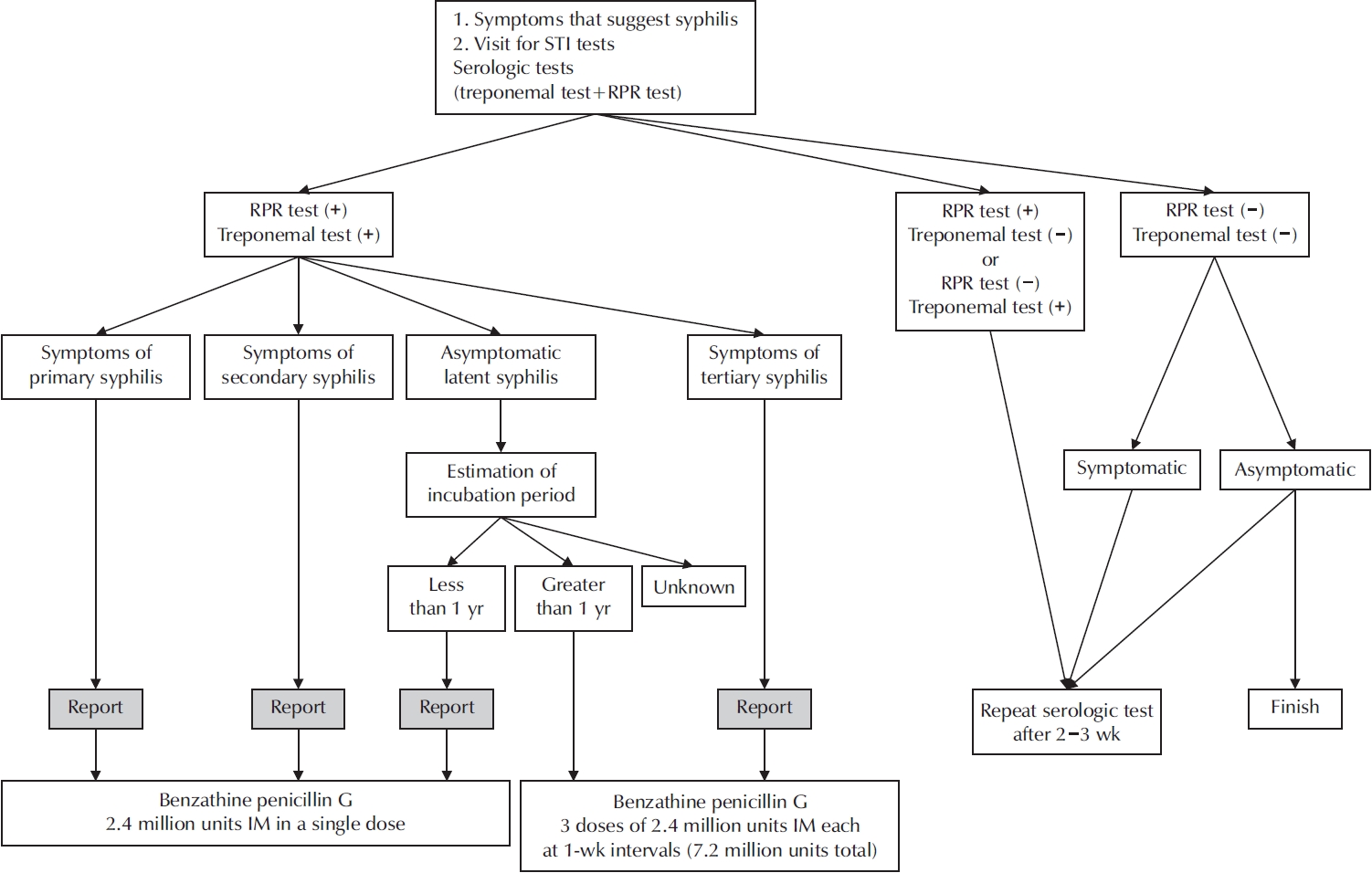
ePub - Syphilis continues to pose a major global public health concern, with more than 7 million cases reported worldwide in 2022, and its incidence continues to rise in numerous regions. In Korea, the shift from sentinel to universal notification in 2024 has revealed a markedly greater disease burden, particularly among men who have sex with men and among younger adults, underscoring changing epidemiological patterns and the urgent need for revised control strategies. In urological practice, syphilis presents with a wide range of often misleading symptoms, including painless genital ulcers, urethritis, and sexual dysfunction, that frequently resemble other genitourinary disorders and complicate diagnostic evaluation. Accurate identification relies on integrating a thorough clinical assessment with serologic testing while remaining alert to diagnostic challenges such as early latent infection, serofast states, and human immunodeficiency virus coinfection. Penicillin G remains the mainstay of therapy, with treatment regimens tailored to the stage of disease and to the presence or absence of central nervous system involvement. Effective partner notification, targeted screening, and consistent follow-up are essential to prevent reinfection and limit further transmission. At a public health level, a multifaceted strategy—strengthened surveillance systems, focused testing in high-risk populations, and embedding syphilis screening within broader sexually transmitted infection care frameworks—is critical to curbing its resurgence. In summary, prompt recognition, adherence to evidence-based management, and coordinated public health measures, together with ongoing advances in diagnostics and prevention, remain fundamental to reducing the continued spread of syphilis and mitigating its impact on both individual and population health.
- 581 View
- 9 Download

- A Narrative Review of Syphilis Notification Systems in Korea: Change to Mandatory Surveillance System
- Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):28-33. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550004002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
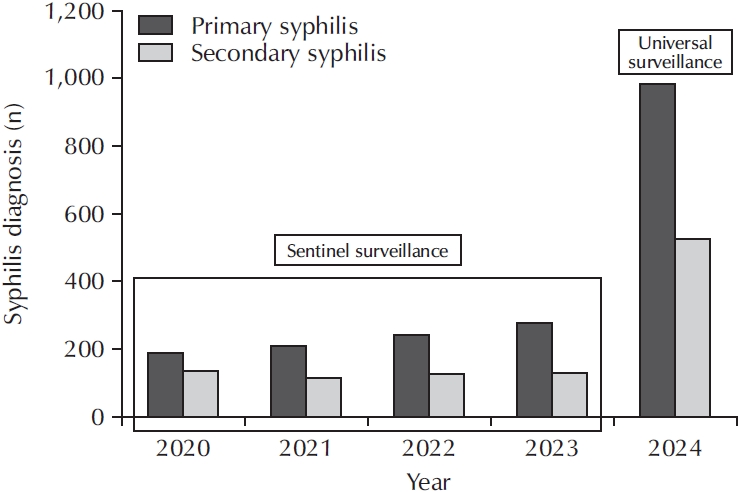
ePub - New cases of syphilis are clearly showing an increasing trend worldwide. However, in a sentinel surveillance system, the collection of information on disease outbreaks is limited, making it difficult to understand the overall outbreak situation and perform detailed analyses of patients' demographic characteristics and disease stages. In accordance with the revision of the Infectious Disease Prevention Act, syphilis was converted from a grade 4 infectious disease subject to sentinel surveillance to a grade 3 infectious disease subject to mandatory surveillance from January 1, 2024, with all medical institutions required to report syphilis diagnosis within 24 hours.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Adult Syphilis: A Narrative Review of Clinical Insights and Public Health Implications in Urology
Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(3): 123. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 5,280 View
- 38 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
- Syphilis Notification Systems in Korea over the Last 20 Years
- Yumi Seo, Gilho Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(1):16-23. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: The syphilis notification system has been revised three times in Korea during the last 20 years. Accordingly, we evaluated the performance of the three systems by analyzing data from the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA).
Materials and Methods: We analyzed trends of stage 1, 2, and congenital syphilis cases reported in the KDCA from 2001 to 2010 in the 1st sentinel (S1), from 2011 to 2019 in the 1st universal (U1), and 2020 in the 2nd sentinel (S2) notification system.
Results: A total of 21,820 syphilis cases were reported, 9,177 cases in S1, 12,321 in U1, and 322 in S2, respectively. The reported cases can be presented in the form of four expanding waves across the time period. Although the most commonly reported age group with infection was 20-29 years in all three reporting systems, the pattern of infections was different; the number of older patients was relatively high in the S1 group while the number of syphilis cases declined sharply in the older than 20-29 old age group in the U1 and S2 systems. Also, there was a sex-based difference in the three groups; the data from S1 were female-dominant but the data in U1 and S2 were male-dominant.
Conclusions: Our results showed that the universal notification system (U1) is superior in both the quantity and quality of data to the previous sentinel system (S1). The results from the new system, S2, are similar to those from U1. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert Consensus Study on the Redesign of the Sexually Transmitted Infection Surveillance System in Korea
Jin Bong Choi, Dong-Sook Kim, Chae Eun Shin, Su-Yeon Yu, Kyu Won Lee, Seung-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Narrative Review of Syphilis Notification Systems in Korea: Change to Mandatory Surveillance System
Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Recent Changes in Sexually Transmitted Infection in Korea: A Population-Based Analysis
Jae Yen Song, Kang Seob Kim, Chang Hee Han, Sangrak Bae
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(14): 5145. CrossRef - Rectal Syphilis Mimicking Malignancy: A Case Report
Sunjin Ryu, Bo-Kyeong Kang, Mimi Kim, Chul-Min Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2024; 85(3): 637. CrossRef - Temporal Trends in Syphilis Incidence among Men with HIV in Busan, Korea, 2005–2022: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Sun Hee Lee, Jeong Eun Lee, Soon Ok Lee, Shinwon Lee, Woo Seog Ko, Hyung-Hoi Kim, Kyung-Hwa Shin, Jin Suk Kang, Hyunjin Son
Viruses.2024; 16(2): 265. CrossRef
- Expert Consensus Study on the Redesign of the Sexually Transmitted Infection Surveillance System in Korea
- 2,755 View
- 10 Download
- 5 Crossref


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


