Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Beyond the Number: Interpreting Prostate-Specific Antigen Elevation in the Context of Prostate Inflammation
- Byoungkyu Han, Ki-Hyuck Moon
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):132-143. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550032016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is indispensable but not cancer specific; inflammation, benign prostatic hyperplasia, urinary retention, ejaculation, and instrumentation can all elevate PSA and complicate cancer risk assessment. This review synthesizes current evidence and guidelines to support clinicians in interpreting PSA elevations when inflammation is present or suspected. Acute febrile urinary tract infection and acute bacterial prostatitis may produce very high PSA values, sometimes exceeding 100 ng/mL, and normalization can be slow; therefore, PSA testing during active infection is discouraged. When PSA is only mildly to moderately elevated, standardized repeat testing is essential because a meaningful proportion of results normalize on retesting. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-first pathway improves detection of clinically significant prostate cancer while reducing overdiagnosis and enables biopsy deferral after a negative MRI under structured monitoring. PSA density (PSAD) further refines triage alongside MRI, with practical working thresholds of roughly 0.10–0.20 ng/mL/cm3 calibrated to MRI quality and pretest risk. However, asymptomatic histologic prostatitis (National Institutes of Health category IV) is common and may raise PSA without reliably altering PSAD, which means that PSAD alone cannot confirm that an elevation is attributable solely to inflammation. Validated secondary biomarkers (e.g., Prostate Health Index, 4Kscore, IsoPSA [isoform PSA], Stockholm3, Proclarix, PCA3 [prostate cancer gene 3], SelectMDx [select molecular diagnostics], ExoDx [exosome diagnostics], MPS/MPS2 [MyProstateScore/MyProstateScore 2.0]) are best used selectively when MRI is negative or equivocal and clinical risk remains uncertain. A pragmatic sequence—confirm, image, and refine—helps minimize missed clinically significant cancer while reducing unnecessary antibiotics and biopsies when inflammation is the predominant driver of PSA elevation.
- 386 View
- 13 Download

Original Article
- Efficacy of Urovaxom for Improving Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Symptoms in Prostate Cancer Patients Who Underwent Radical Prostatectomy: A Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study
- Jun-Koo Kang, Yun-Sok Ha, Sungchan Park, Tae Gyun Kwon, Tae-Hwan Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):42-47. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550014007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) is a multifactorial condition that can significantly diminish quality of life. Although some patients have reported persistent pelvic pain after radical prostatectomy (RP), the prevalence and direct causal relationship between CPPS and RP remain unclear. This multicenter prospective study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of Urovaxom for improving CPPS symptoms. Materials and Methods: A total of 52 prostate cancer patients who underwent RP were enrolled and administered Urovaxom (60 mg/day) for 12 weeks. Changes in National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI), overactive bladder symptom score (OABSS), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), and inflammation markers (white blood cell [WBC], C-reactive protein [CRP]) were analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results
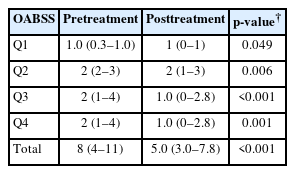
After 12 weeks of treatment, the NIH-CPSI total score significantly decreased from 19 (interquartile range [IQR], 16–23) to 12.5 (IQR, 8.0–16.8) (p<0.001). The OABSS total score decreased from 8 (IQR, 4–11) to 5 (IQR, 3.0–7.8), and the IPSS total score decreased from 13.5 (IQR, 10.0–22.8) to 10.5 (IQR, 5.0–17.0) (p<0.001). WBC levels showed a slight increase (p=0.028), but the clinical relevance of this change is uncertain and warrants further investigation. CRP changes were not statistically significant (p=0.274).
Conclusions
Urovaxom demonstrated significant efficacy in improving CPPS symptoms, particularly pain and reduced quality of life, in patients following RP. These findings suggest Urovaxom as a potential therapeutic option for CPPS after management using RP. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Addressing an Unmet Need in Postprostatectomy Care: Perspectives on Urovaxom
Byeong Jin Kang
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 118. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 4,760 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Crossref

Review Article
- Postoperative Microscopic Pyuria and Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern: A Literature Review
- Min-Kyu Kim, Ki Hong Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):73-79. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448026013
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - All patients who undergo transurethral prostate surgery exhibit pyuria and microscopic hematuria in postoperative urinalysis. Postoperative asymptomatic pyuria is associated with the inflammatory process and surface remodeling of the prostate, rather than infection. Various studies have investigated the incidence, duration, and risk factors for postoperative pyuria, noting that factors like age, surgery time, and prostate size can influence outcomes. Postoperative pyuria reflects tissue recovery and inflammation, and the use of antibiotics in asymptomatic patients may not be appropriate.
- 4,647 View
- 27 Download

Case Report
- Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
- Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):114-118. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
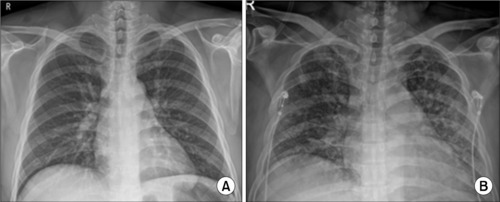
ePub - Acute bacterial prostatitis is an acute urinary tract infection associated with a bladder outlet obstruction or an immunosuppressed state. A 51-year-old man patient visited the hospital with fever, chills, and acute urinary retention that started the day before his visit after consuming a significant amount of alcohol. Conservative treatments, including catheterization for urinary drainage and antibiotics, were performed. On the third day of treatment for acute prostatitis, he complained of dyspnea. The level of oxygen differentiation was reduced significantly, and the tracheal insertion and ventilator were maintained after the radiological examination. The ventilator was discontinued, and the prostate abscess was operated on the eighth day of hospitalization. He was discharged without complications. This paper reports a case of life-threatening pneumonia and a prostate abscess during the treatment of a patient with acute bacterial prostatitis with a review of the relevant literature.
- 2,036 View
- 8 Download

Original Articles
- Treatment Modality of Prostatic Abscess according to Size: A Retrospective Study
- Gwon Kyeong Lee, Kyoung Ha Jang, Woo Seop Seong, Byeong Jin Kang, Kyung Hwan Kim, Hong Koo Ha
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(3):96-102. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.3.96
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study aimed to determine the treatment modality for prostatic abscesses according to size.
Materials and Methods: Twenty-five patients diagnosed with prostatic abscesses were retrospectively reviewed. All patients were treated with intravenous empirical and appropriate antibiotics according to culture results. They were grouped according to the size of the prostate abscess based on computed tomography results (group A, with prostate abscess ≤2 cm, n=10; group B, with prostate abscess size >2 cm, n=15), and their treatment modality and outcomes were compared.
Results: The prostatic abscess sizes were 1.31±0.37 and 3.49±1.06 cm for groups A and B, respectively. Prostate-specific antigen, prostatic volume, and comorbidity were not significantly different (p>0.05), whereas pelvic pain was significantly different (p=0.028). There was no difference in the microorganisms isolated from urine and blood culture, empirical antibiotics, and broad-spectrum antibiotics between the two groups (p>0.05). More patients in group B underwent transurethral abscess deroofing than those in group A (p=0.040). Patients in group B had a more extended hospitalization period and intravenous antibiotics duration than those in group A (p=0.024 and p=0.013, respectively). Group B had more cases of septic shock, intensive care unit admission, and mortality events than group A (p=0.024, p=0.001, and p=0.061, respectively). However, prostatic abscess recurrence and urological chronic complication did not significantly differ (p>0.05).
Conclusions: Appropriate use of antibiotics is crucial. This study shows that the treatment of patients with prostatic abscess >2 cm is more difficult, but transurethral abscess deroofing can lower mortality, prostatic abscess recurrence, and urological chronic complications.
- 4,563 View
- 26 Download

- Korean Multicenter Study of Infectious Complications after Transurethral Prostate Surgery in Patients with Preoperative Sterile Urine
- Seong Hyeon Yu, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Jae Duck Choi, Koo Han Yoo, Jeong Woo Lee, Dong Hoon Koh, Sangrak Bae, Seung Ok Yang, Joongwon Choi, Seung Ki Min, Hoon Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(3):81-88. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.3.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis and determine the risk factors of infectious complications after transurethral surgery of the prostate.
Materials and Methods: Seven hundred and seventy-two patients who underwent transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HOLEP) were reviewed. Of these, this study enrolled 643 patients without bacteriuria who had not received antibiotics for urinary tract infections for two weeks before surgery. The patients were divided into two groups according to the duration of the antibiotics (Group 1: less than one day, n=396 vs. Group 2: more than one day, n=247).
Results: The overall incidence of postoperative infectious complications in 643 patients was 5.0% (32/643). When postoperative infectious complications were compared according to the duration of the antibiotics (Group 1 vs. Group 2), the infectious complications rates were 5.6% (22/396) vs. 4.0% (10/247), respectively (p=0.393). When postoperative infectious complications were compared according to the duration of antibiotics (Group 1 vs. Group 2) in the TURP and HOLEP groups, the infectious complications rates were 6.3% (12/192) vs. 1.0% (1/103) (p=0.035) and 4.9% (10/203) vs. 6.0% (8/134) (p=0.677), respectively. The duration of Foley catheterization was independently associated with infectious complications (p=0.003).
Conclusions: The results showed that prolonged postoperative catheterization affects postoperative infectious complications associated with transurethral prostate surgery. Although antibiotics administered for less than one day are effective for antibiotic prophylaxis of transurethral prostate surgery, a longer antibiotic therapy is recommended for TURP.
- 3,468 View
- 24 Download

- The Feasibility of Radical Prostatectomy for Medication Refractory Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
- Seung Chan Jeong
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(3):76-80. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.3.76
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare the National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) scores of patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) given pharmacological treatment with those who additionally had prostate cancer and underwent surgical treatment.
Materials and Methods: From January 2000 to March 2021, a total of 7,650 patients were diagnosed with chronic prostatitis (N41.1) at our hospital, of which 234 patients were additionally diagnosed with prostate cancer. After excluding patients with severe benign prostatic hyperplasia (>100 g)-related lower urinary tract symptoms or neurological and psychiatric abnormalities, or advanced prostate cancer, 52 patients undergoing pharmacological treatment with a combination of drugs and 20 patients who underwent radical prostatectomy due to additional prostate cancer were included in the analysis. The NIH-CPSI scores of the two groups were compared at the first outpatient visit, 3 months, and 6 months after the first visit. The p-values were calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test, and the Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Results: Patients who underwent radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer showed significant reductions in the voiding and quality of life scores in the NIH-CPSI, but not the pain score at 3 months. After 6 months, there was a significant decrease in the overall NIH-CPSI. On the other hand, in the group on pharmacological therapy, the decrease was statistically significant only in the voiding score at 6 months. However, in the surgery group, 3 patients were found to be suffering from urinary incontinence, and 7 patients from erectile dysfunction.
Conclusions: Radical prostatectomy, therefore, appears to be a promising treatment that can be carefully considered for patients with refractory CP/CPPS who do not receive adequate treatment and thus have a poor quality of life.
- 2,829 View
- 9 Download

- Antibiotic Sensitivity of Bacterial Strains from Prostate Abscess Pus Aspirated Using Ultrasound Guidance
- Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(1):26-30. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: A prostate abscess is a rare occurrence often caused by immune dysfunction. The diagnostic modality for a prostate abscess is computed tomography or transrectal ultrasound. Transrectal ultrasound-guided aspiration is one such method. If treatment is dependent on the abscess size. This study examined the bacterial strains drained under transrectal ultrasound and their antibiotic sensitivity.
Materials and Methods: The medical records of eight patients diagnosed with a prostatic abscess and treated by transrectal ultrasound-guided aspiration from March 2009 to December 2020 were reviewed retrospectively. The general characteristics, associated diseases, and bacterial strains and their antibiotic sensitivities were identified in blood, urine, and pus cultures.
Results: Eight patients were hospitalized. The average age was 59.5±6.05 years, and the average length of hospitalization was 16.88±5.49 days; 75% had diabetes. No patients had catheterization, spinal injury, or prostate biopsy prior to diagnosis. The mean prostate volume was 47.05±27.3 ml, and the mean prostate abscess size was 2.08±0.83 ml. Under transrectal ultrasonography, the prostate abscess size was 5.43±5.31 ml, and catheters were inserted for treatment in four cases (50%). In the abscess culture test, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus were found in four, three, and one case, respectively. E. coli and K. pneumoniae responded well to amikacin treatment, while seven cases responded well to Piperacillin/Tazobactam treatment.
Conclusions: Prostate abscesses occur mainly in diabetic patients. The most common cultures are E. coli and K. pneumoniae. Intravenous injection of amikacin or Piperacillin/Tazobactam may be helpful as a treatment prior to bacterial identification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
Urogenital Tract Infection.2023; 18(3): 114. CrossRef - Treatment Modality of Prostatic Abscess according to Size: A Retrospective Study
Gwon Kyeong Lee, Kyoung Ha Jang, Woo Seop Seong, Byeong Jin Kang, Kyung Hwan Kim, Hong Koo Ha
Urogenital Tract Infection.2022; 17(3): 96. CrossRef
- Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
- 2,861 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Changes of Antimicrobial Resistance Causing Infections Following Transrectal Prostate Biopsy: Analysis of 10-Year Data
- Da Eun Han, Sun Tae Ahn, Jong Wook Kim, Du Geon Moon, Hong Seok Park, Mi Mi Oh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(3):55-60. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.3.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: The production of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) has emerged as one of the main causes of antimicrobial resistance. It is well known that infections of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae causes poor clinical outcomes. This study investigated the changes in the antimicrobial resistance patterns in infections following transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate (TR) biopsy over a 10 year period and analyzed whether the clinical course varies in infections caused by the ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae.
Materials and Methods: We retrospectively analyzed patients who had infections after a TR biopsy at the Korea University Guro Hospital from January 2010 to October 2019. Infection from a TR biopsy was defined as readmission due to a fever of 38 degrees or higher that occurred within one week after the biopsy.
Results: Among 1,855 patients who received a TR biopsy, 39 patients (2.10%) had infectious complications. Of 33 culture-positive patients, 29 patients (87.9%) showed quinolone resistance, 10 patients (30.3%) were ESBL-positive and 9 patients had concomitant quinolone resistance and were also ESBL-positive. 75% of ESBL-positive bacterial infections occurred after 2016 indicating increasing incidence in recent days. The only significant difference in the clinical course between the ESBL-negative and the positive group was the lower systolic blood pressure of the ESBL-positive group during hospitalization (p-value=0.018).
Conclusions: Infections due to the ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae showed a tendency to increase among TR biopsy patients since 2016. Although the clinical course of the ESBL-positive infection did not show significant differences to ESBL-negative infection, further analysis is needed because of the small number of patients.
- 1,813 View
- 6 Download

Case Reports
- Case of Fournier’s Gangrene in a Patient with Long-Term Indwelling Catheterization due to Urinary Incontinence after Open Radical Prostatectomy
- Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(1):6-9. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.1.6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Fournier’s gangrene is a life-threatening disease that needs to be treated as soon as possible. An 82-year-old male, who exchanged a urethral catheter once a month for urinary incontinence management after open radical prostatectomy, presented with an acute onset of mental change and general weakness. After ten days’ hospitalization, the disease was diagnosed. The scrotal wall was opened, and the infectious tissue was exposed to the air and kept open with an aseptic dressing. After 45 days, his scrotal wound healed and returned to its typical appearance without scarring and wound disruption. He recovered fully from the infection. This paper reports a case of Fournier’s gangrene in a patient with long-term indwelling catheterization due to urinary incontinence after an open radical prostatectomy with a literature review.
- 1,653 View
- 1 Download

- Von Brunn’s Nest in an Incidental Bladder Mass Found during Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate
- Seungsoo Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(1):13-15. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - A 62-year-old male with benign prostatic hyperplasia underwent holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. During surgery, a small nodular mass was found incidentally in the trigone of the bladder. The lesion was removed completely by a transurethral resection with a bipolar device. A pathology examination of the lesion indicated von Brunn’s nests.
- 3,345 View
- 23 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


