Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Advances in the Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection: A Narrative Review
- Juan Victor Ariel Franco, Nicolás Meza
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):17-27. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550020010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
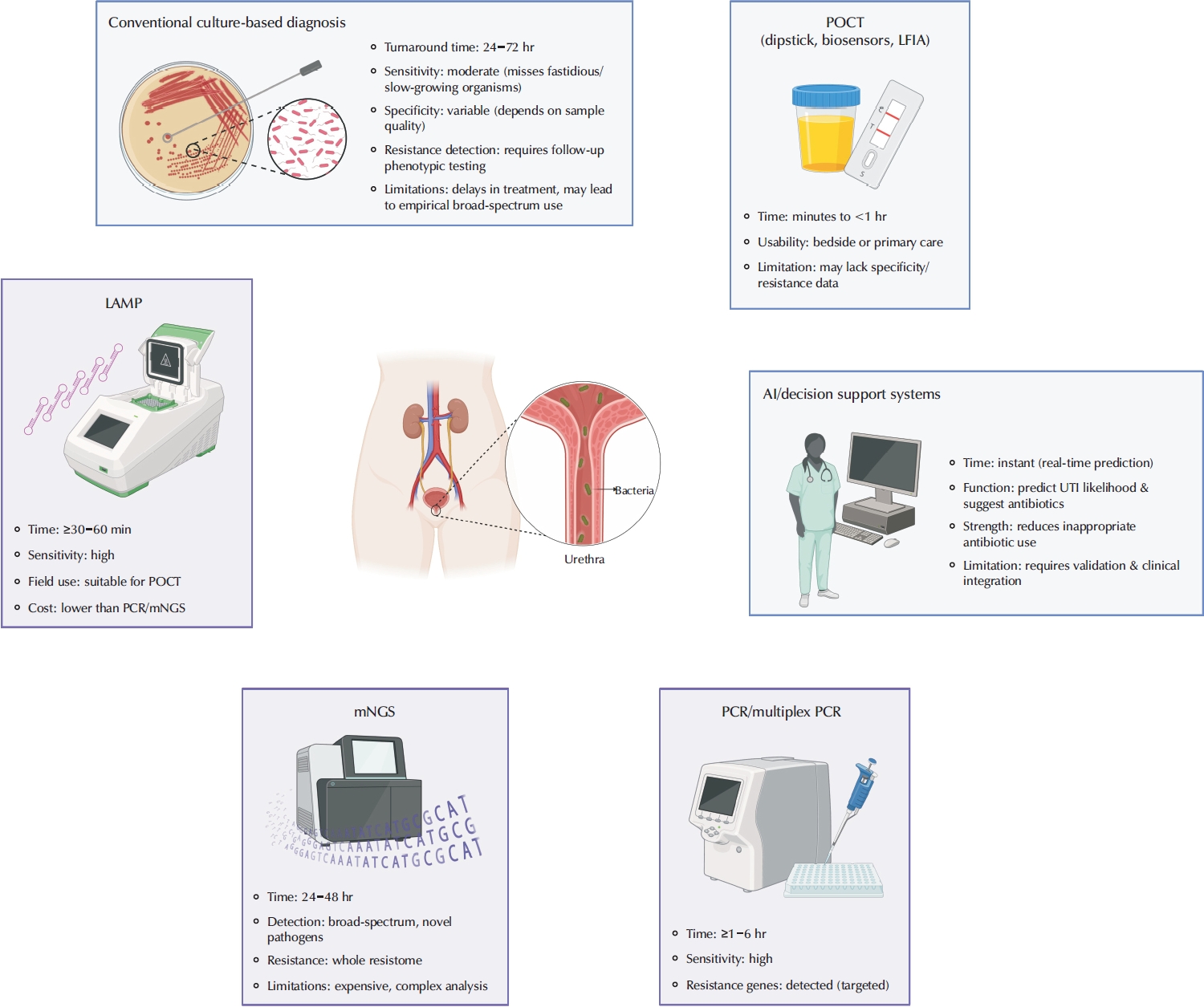
ePub - Urinary tract infections are among the most frequent bacterial infections, significantly impacting patient morbidity and healthcare resources. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial to ensure effective treatment, prevent complications such as pyelonephritis or sepsis, and reduce inappropriate antibiotic use, contributing to antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Despite consensus across international guidelines from organizations, challenges persist, particularly in distinguishing true infections from asymptomatic bacteriuria or nonspecific symptoms, especially in older adults. Recent advancements in diagnostic technology have emerged to address these limitations, including molecular diagnostics, point-of-care testing (POCT), and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven predictive models. Molecular techniques, notably polymerase chain reaction, loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and metagenomic next-generation sequencing, offer enhanced sensitivity and specificity, rapid detection times, and comprehensive identification of pathogens and resistance profiles. POCT innovations, such as lateral flow immunoassays, enzymatic-based rapid tests, and novel biosensors, facilitate prompt bedside diagnosis, although specificity challenges remain. Meanwhile, AI and machine learning models demonstrate significant potential for risk stratification, prediction of infection, and improving antibiotics prescription practices yet face barriers related to validation, practical integration, and clinical acceptability. Despite promising developments, significant gaps remain, including limited real-world implementation evidence, high costs, and insufficient data from diverse populations. Further rigorous clinical studies, economic evaluations, and practical implementation assessments are urgently required. Addressing these research gaps could substantially improve patient outcomes, optimize antibiotic stewardship, and reduce the global burden of AMR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis of urinary tract infections in the pediatric population – current practices, advances and progress
Maria Bitsori, Roza-Ioanna Poulaki, Emmanouil Galanakis
Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Diagnosis of urinary tract infections in the pediatric population – current practices, advances and progress
- 10,120 View
- 302 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


