Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Trends in Age-Specific Prevalence of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Young Hwan Kim, Se Hwa Hong, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Tae Hyoung Kim, Sae Chul Kim, Sang Baek Koh, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):101-106. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: To elucidate the longitudinal changes in the prevalence of lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) according to age over the past 10 years.
Materials and Methods: The changes in the proportion of prevalence for LUTD, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and urinary incontinence (UI) among South Koreans from 2009 to 2018, were analyzed using the National Health Information Database established by the Korean National Health Insurance Service. All conditions were defined according to the corresponding Korean Standard Classification of Diseases-8 for diagnosis and surgical procedures and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service codes for drugs.
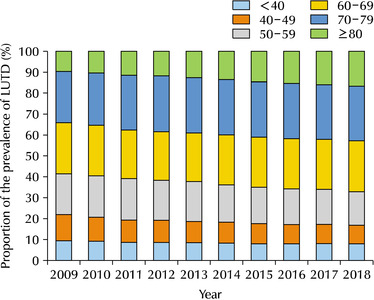
Results: The 60-69, 70-79, and over 80 age groups accounted for more than 60% of the LUTD cases from 2009 to 2018, while significant increases in the crude prevalence of LUTD were observed over a 10-year period in all age groups (p for trend <0.05). In age groups over 60 years, LUTD was more prevalent in men than women, but there was no statistically significant difference in proportion (p>0.05). The changes in the prevalence and prevalence proportion exhibited similar trends in BPH, UI, and LUTD.
Conclusions: LUTD was more prevalent in the elderly aged over 60 years old than in younger adults. Therefore, this study suggests the development of nationwide healthcare policies to manage LUTD in the elderly population of South Korea, which is expected to become the world’s most aged population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing strategies for managing urological disorders in aging populations: a comprehensive review
Hong Liu, Jie Wu
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Nursing strategies for managing urological disorders in aging populations: a comprehensive review
- 4,628 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review
- Comprehensive Review of COVID-19 on Benign Prostate Hyperplasia Patient Symptoms
- Joongwon Choi, Hong Jin Suh, Dong Hwan Lee, Tae-Kon Hwang, Jung Jun Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(2):31-35. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.2.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Since the outbreak of the global Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic in 2019, the number of confirmed cases has increased steadily worldwide. The most common symptom of COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) is respiratory symptoms. On the other hand, increased voiding frequency and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) have also been reported. Regarding the relationship between LUTS and COVID-19, only small size (n<100) retrospective studies have been reported, but the post-International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) increases compared to pre-IPSS after a COVID-19 infection in those older than 50 years. α-blockers and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors are relatively safe, but there are conflicting reports on 5α-reductase inhibitors; hence, further research is needed. Four major theories have been argued regarding the relationship between LUTS and COVID-19: renin-angiotensin system-related, androgen-related, inflammation-related, and metabolic derangement-related. In conclusion, elderly male patients often have benign prostate hyperplasia as a co-morbidity, and the severity of COVID-19 is high in this group. Therefore, voiding symptoms in these patient groups is of particular concern.
- 2,264 View
- 8 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


