Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
- Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):114-118. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
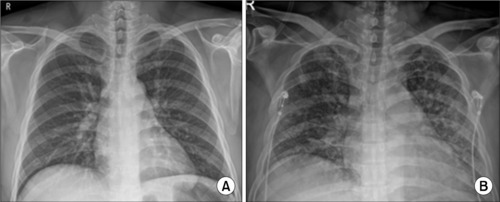
ePub - Acute bacterial prostatitis is an acute urinary tract infection associated with a bladder outlet obstruction or an immunosuppressed state. A 51-year-old man patient visited the hospital with fever, chills, and acute urinary retention that started the day before his visit after consuming a significant amount of alcohol. Conservative treatments, including catheterization for urinary drainage and antibiotics, were performed. On the third day of treatment for acute prostatitis, he complained of dyspnea. The level of oxygen differentiation was reduced significantly, and the tracheal insertion and ventilator were maintained after the radiological examination. The ventilator was discontinued, and the prostate abscess was operated on the eighth day of hospitalization. He was discharged without complications. This paper reports a case of life-threatening pneumonia and a prostate abscess during the treatment of a patient with acute bacterial prostatitis with a review of the relevant literature.
- 3,020 View
- 8 Download

- Antibiotic Sensitivity of Bacterial Strains from Prostate Abscess Pus Aspirated Using Ultrasound Guidance
- Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(1):26-30. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: A prostate abscess is a rare occurrence often caused by immune dysfunction. The diagnostic modality for a prostate abscess is computed tomography or transrectal ultrasound. Transrectal ultrasound-guided aspiration is one such method. If treatment is dependent on the abscess size. This study examined the bacterial strains drained under transrectal ultrasound and their antibiotic sensitivity.
Materials and Methods: The medical records of eight patients diagnosed with a prostatic abscess and treated by transrectal ultrasound-guided aspiration from March 2009 to December 2020 were reviewed retrospectively. The general characteristics, associated diseases, and bacterial strains and their antibiotic sensitivities were identified in blood, urine, and pus cultures.
Results: Eight patients were hospitalized. The average age was 59.5±6.05 years, and the average length of hospitalization was 16.88±5.49 days; 75% had diabetes. No patients had catheterization, spinal injury, or prostate biopsy prior to diagnosis. The mean prostate volume was 47.05±27.3 ml, and the mean prostate abscess size was 2.08±0.83 ml. Under transrectal ultrasonography, the prostate abscess size was 5.43±5.31 ml, and catheters were inserted for treatment in four cases (50%). In the abscess culture test, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus were found in four, three, and one case, respectively. E. coli and K. pneumoniae responded well to amikacin treatment, while seven cases responded well to Piperacillin/Tazobactam treatment.
Conclusions: Prostate abscesses occur mainly in diabetic patients. The most common cultures are E. coli and K. pneumoniae. Intravenous injection of amikacin or Piperacillin/Tazobactam may be helpful as a treatment prior to bacterial identification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
Urogenital Tract Infection.2023; 18(3): 114. CrossRef - Treatment Modality of Prostatic Abscess according to Size: A Retrospective Study
Gwon Kyeong Lee, Kyoung Ha Jang, Woo Seop Seong, Byeong Jin Kang, Kyung Hwan Kim, Hong Koo Ha
Urogenital Tract Infection.2022; 17(3): 96. CrossRef
- Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
- 3,113 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Case of Fournier’s Gangrene in a Patient with Long-Term Indwelling Catheterization due to Urinary Incontinence after Open Radical Prostatectomy
- Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(1):6-9. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.1.6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Fournier’s gangrene is a life-threatening disease that needs to be treated as soon as possible. An 82-year-old male, who exchanged a urethral catheter once a month for urinary incontinence management after open radical prostatectomy, presented with an acute onset of mental change and general weakness. After ten days’ hospitalization, the disease was diagnosed. The scrotal wall was opened, and the infectious tissue was exposed to the air and kept open with an aseptic dressing. After 45 days, his scrotal wound healed and returned to its typical appearance without scarring and wound disruption. He recovered fully from the infection. This paper reports a case of Fournier’s gangrene in a patient with long-term indwelling catheterization due to urinary incontinence after an open radical prostatectomy with a literature review.
- 1,790 View
- 1 Download

- Characteristics of Uropathogens in Patients with Bladder Stones
- Sum Kim, Sung Dae Kim, Kyung Kgi Park, Young-Joo Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2013;8(2):109-113. Published online October 31, 2013
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose: Bladder stones is not a rare disease, however, the number of patients with bladder stones has decreased due to improvement of nutrition, hygiene, and optimal antibiotics. Bladder stones are typically found in adults with urinary stasis, such as foreign body, benign prostate hyperplasia, spinal cord injury, and urinary tract infection, and in children with congenital genito-urinary abnormality. The aim of this study was to identify the clinical and microbiological characteristics of patients with bladder stones.
Materials and Methods: Patients who had bladder stones between March 2009 and December 2012 were retrospectively reviewed (Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea). We analyzed the presence of spinal cord injury, cancer, previous urinary tract calculi, and urinary tract infection associated with bladder stones and also investigated the largest diameter of bladder stone, and the number of bladder stones, as well as urine and blood culture.
Results: A total of 39 patients underwent cystolithotomy or cystolithotripsy. The most common presenting symptoms were voiding disturbance (n=15, 38.5%) and hematuria (n=10, 25.6%). Of these patients, 17 (43.3%) had positive growth of organisms. Of these organisms, Escherichia coli was found in five patients, Enterococcus fecalis in three patients, Pseudomonas aeruginosa in three patients, Klebsiella pneumoniae in two patients, Staphylococcus aureus in two patients, Proteus mirabilis in one patient, and Citrobacter in one patient.
Conclusions: We believe that urinary tract infection is a major risk factor in patients with bladder stones. Proper antibiotics would be required in order to reduce the risk of formation of bladder calculi. Further investigation will be needed.
- 383 View
- 1 Download

- Renal Papillary Necrosis with Calyceal Rupture: Caused by AcutePyelonephritis and Analgesic Abuse
- Jung-Sik Huh, Sung-Dea Kim, Kyung Kgi Park, Young-Joo Kim
- Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2013;8(2):121-124. Published online October 31, 2013
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Spontaneous renal rupture is a rare condition. Renal rupture most often occurs as a result of traumatic injury, a rare entity of obstructive uropathy with stones, and spontaneous causes such as malignancy. We report on a rare case of renal rupture caused by a ureter stone measuring 5 mm in size with acute pyelonephritis (APN) in a patient with renal papillary necrosis (RPN). The patient, who suffers from attacks of gouty arthritis, frequently used analgesic for pain relief. The patient was treated with temporary percutaneous drainage and antibiotics. This case demonstrates that RPN with APN can induce renal rupture even when ureter stones are small. Thus, consideration of all medical problems is important when deciding on treatment of patients with ureter stones.
- 503 View
- 0 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


