Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Report
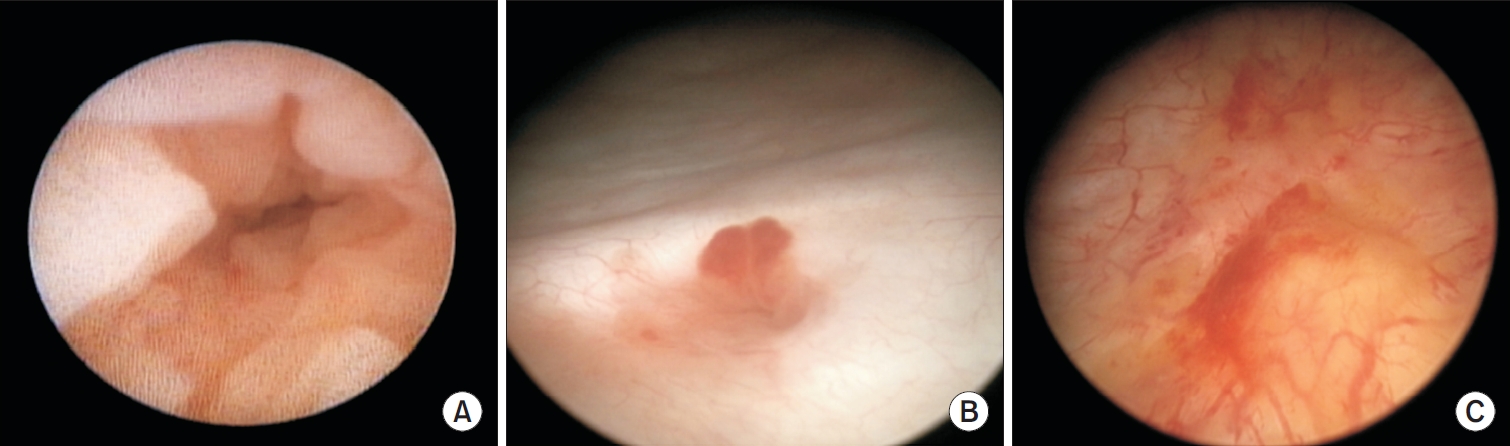
- Primary Bladder and Ureteral Amyloidosis Initially Diagnosed as Chronic Cystitis: A Case Report
- Seungsoo Lee, Dan Bee Lee, Hyun Jung Lee, Won Hoon Song, Sung-Woo Park, Jong Kil Nam
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):167-172. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550038019
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Primary localized amyloidosis confined to the urinary tract is uncommon and frequently misinterpreted due to clinical and radiologic overlap with more prevalent conditions. We describe a 69-year-old woman who experienced recurrent gross hematuria over 2 years and underwent initial transurethral resection based on a presumptive diagnosis of chronic cystitis. Subsequent evaluation revealed a left ureteral mass with hydronephrosis, raising concern for malignancy. Histopathologic examination of both bladder and ureteral specimens demonstrated amorphous eosinophilic deposits that stained positive with Congo red and showed apple-green birefringence under polarized microscopy. Immunofluorescence confirmed λ-light-chain predominance, establishing AL (amyloid light chain)-type amyloidosis without systemic involvement. The patient underwent complete endoscopic resection and remains asymptomatic during ongoing surveillance. This case highlights the diagnostic challenges posed by localized urinary amyloidosis and underscores the importance of histologic confirmation in atypical inflammatory lesions.
- 315 View
- 4 Download

Reviews
- Differences in Urine Microbiome of Acute Cystitis and Chronic Recurrent Cystitis in Women
- Woong Bin Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(1):1-7. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - The diagnosis of urinary tract infection (UTI) relies on urine culture tests to identify aerobic or anaerobic urinary tract pathogens. This method has limitations in identifying anaerobic bacteria, and there is uncertainty in identifying all bacteria. A new next-generation sequencing (NGS) method has gradually helped overcome these limitations, and the microorganisms present in the human urinary tract are gradually being revealed. This review introduces studies on the microbiome analyzed using NGS of urine from patients with acute cystitis and recurrent UTIs and discusses whether NGS may reveal the pathophysiology of the disease.
- 3,196 View
- 33 Download

- Importance to Promote Awareness in Patients with Recurrent Cystitis
- Sun-tae Ahn, Mi-mi Oh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(3):71-75. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.3.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - In spite of a high cure rate, cystitis is a common disease in women that often recurs within a year. The uncomfortable symptoms associated with recurrent cystitis affect the quality of life and overall daily life. However, the awareness pertaining to the treatment or prevention of recurrent cystitis has remained the same. Physicians and patients are unaware that recurrent cystitis can lead to several problems, such as socioeconomic burden and antibiotic abuse. Therefore, there is a requirement to enhance awareness of the socio-economic burden of recurrent cystitis, the effects on the quality of life of patients, and the importance of prevention and management after treatment.
- 2,559 View
- 12 Download

Original Article
- Pilot Study of Cystochon® (Cranberry Extract, Chondroitin Sulfate, and Hyaluronic Acid Complex) in Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
- Kwang Taek Kim, Jeong Woo Lee, Hyun-Sop Choe
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2022;17(2):36-41. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2022.17.2.36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study examined whether Cystochon® (cranberry extract, chondroitin sulfate, and hyaluronic acid complex) effectively improves the symptoms and problems of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) patients.
Materials and Methods: From December 2021 to May 2022, the medical records of IC/BPS patients who visited St. Vincent’s Hospital, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, or Gachon University Gil Medical Center were collected. For the treatment of IC/BPS, the patients were given pentosan polysulfate (PPS) for 12 weeks, with Cystochon® then added and maintained for an additional eight weeks. The OʼLeary–Sant symptom and problem index (Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index [ICSI], Interstitial Cystitis Problem Index [ICPI]) was used to measure the treatment response.
Results: After 12 weeks of PPS treatment, ICSI and ICPI improved in all patients. After adding Cystochon® for eight weeks, the ICSI and ICPI indicators improved further. In the ICSI category, significant improvement in symptoms was confirmed in the total ICSI score, particularly in the Q4 (pain-related) questionnaire after adding Cystochon®. In the ICPI category, significant problem improvement was confirmed in the total ICPI score, particularly in the Q1 (frequent urination) and Q4 (pain-related) questionnaires. Although not statistically significant, the remaining indicators generally tended to improve.
Conclusions: The orally administered combination of cranberry extract, chondroitin sulfate, and hyaluronic acid (Cystochon®) may have a clinically positive effect in patients with IC/BPS. Better clinical improvement can be expected when it is added to the PPS treatment, especially in the category of bladder pain. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anti-inflammatory effect of sea buckthorn in an HCl-induced cystitis rat model
Hyun Suk Yoon, Juyeon Yu, Shinhoon Kang, Hana Yoon
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2025; 66(1): 67. CrossRef - Pharmacological Properties of Shionone: Potential Anti-Inflammatory Phytochemical against Different Diseases
Varun Jaiswal, Hae-Jeung Lee
Molecules.2023; 29(1): 189. CrossRef
- Anti-inflammatory effect of sea buckthorn in an HCl-induced cystitis rat model
- 5,621 View
- 15 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Von Brunn’s Nest in an Incidental Bladder Mass Found during Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate
- Seungsoo Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2020;15(1):13-15. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2020.15.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - A 62-year-old male with benign prostatic hyperplasia underwent holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. During surgery, a small nodular mass was found incidentally in the trigone of the bladder. The lesion was removed completely by a transurethral resection with a bipolar device. A pathology examination of the lesion indicated von Brunn’s nests.
- 3,343 View
- 23 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev


