Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Original Articles
- Impact of Antibiotics on the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma
- Do Gyeong Lim, Ho Yeon Lee, Ho Seok Chung, Eu Chang Hwang, Seung Il Jung, Dong Deuk Kwon
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):75-81. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.75
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: Emerging evidence has suggested that prior or concurrent antibiotic (ATB) use may be associated with a poor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in patients with some solid tumors. This study examined the effects of ATB use on the oncological outcomes of patients receiving ICIs for mUC.
Materials and Methods: Patients receiving ICIs for mUC between 2018 and 2020 were assessed retrospectively. Those with over three cycles of atezolizumab or pembrolizumab were included. ATB use, defined as ≥ three days within 60 days before or three months after ICI administration, was compared between groups for oncological outcomes.
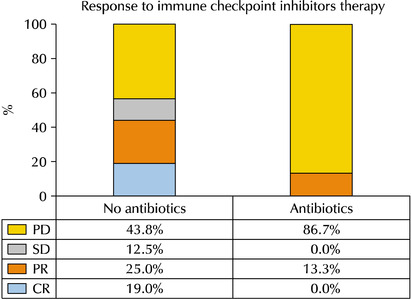
Results: Thirty-one patients were examined. The ATB-use and no-ATB-use groups consisted of 15 (48.4%) and 16 patients (51.6%), respectively. The ATB-use group showed a lower disease control rate (56.3% vs. 13.3%, p=0.023) than the no-ATB-use group. The objective response rate in the ATB-use group was lower than the no-ATB-use group, but the difference was statistically insignificant (43.7% vs. 13.3%, p=0.113). The ATB-use group had shorter progression-free survival (median three vs. six months, log-rank p=0.045) and shorter overall survival (median three vs. 14 months, log-rank p=0.023) than the no-ATB-use group. The most commonly used antibiotics were fluoroquinolones (46.7%), cephalosporins (40.0%), non-cephalosporin beta-lactams (6.7%), and nitrofurantoin (6.7%).
Conclusions: ATB may be associated with poorer oncological outcomes in patients with mUC who received ICI therapy. Hence, further research will be needed to understand the relationship between the modulation of ATB-related dysbiosis and gut microbiota composition with the oncological outcomes in patients with mUC.
- 3,035 View
- 11 Download

- Impact of Microbial Infection on Sperm Parameters of Seminal Bacteria in Asymptomatic Subfertile Males
- Sae Byuk Chang, Tae Jin Kim, Tae Heon Kim, Seung-Ryeol Lee, Young Kwon Hong, Dong Soo Park, Sun-Mi Cho, Dong Hyeon Lee, Young Dong Yu
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):82-92. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.82
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study examined the effects of asymptomatic bacteriospermia on the semen quality of subfertile males. The types of bacteria and their antibiotic susceptibility were also analyzed.
Materials and Methods: Semen was collected and analyzed from 510 subfertile males. One hundred and seventy-nine males showed bacteriospermia, while 331 males did not. The bacterial species, sperm parameters, hormone levels, underlying disease, and lifestyle patterns were compared between the two study groups.
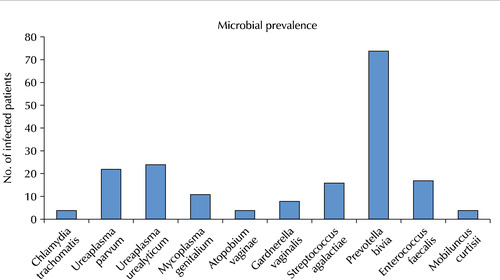
Results: The bacteriospermic males showed significantly higher rates of leukocytospermia (p=0.001) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragmentation than the non-bacteriospermic males. Sperm motility was significantly lower in the bacteriospermic males than in non-bacteriospermic males. The most common seminal bacterial species were Prevotella bivia (P. bivia, 41.3%) and Ureaplasma urealyticum (U. urealyticum, 13.4%). U. parvum showed the highest recurrence rates (31.8%) three months after the initial antibiotic treatment. Regarding the sperm parameters of bacteriospermic males, the sperm concentration, total motility, progressive motility, leukocytospermia, and DNA fragmentation were improved significantly after the initial antibiotics treatment. Multivariate logistic regression analyses revealed P. bivia, U. urealyticum, and U. parvum to be associated with the decreased motility and increased DNA fragmentation of spermatozoa. P. bivia was also associated with a decreased sperm concentration (p=0.002) and vitality (p=0.013).
Conclusions: Bacteriospermia decreased the sperm concentration, motility, normal morphology, and vitality. P. bivia is the most commonly observed bacteria in subfertile males. Appropriate antibiotic therapy of seminal bacteria species had a strong positive impact on improving the semen parameters.
- 8,470 View
- 41 Download

- Risk Factors for Sepsis after Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery: Single Center Experience
- Jinseok Kang, Koo Han Yoo, Taesoo Choi, Gyeong Eun Min, Dong-Gi Lee, Hyung-Lae Lee, Jeonghyouk Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):93-100. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.93
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: To evaluate risk factors for sepsis after retrograde intrarenal surgery for treatment of renal stones.
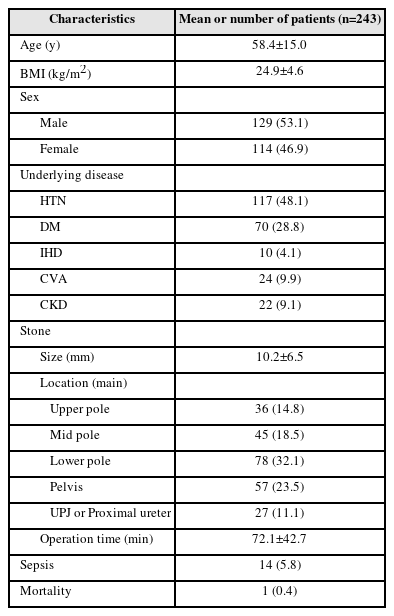
Materials and Methods: We analyzed the clinical data of 243 patients with kidney stones who visited our institution between April 2017 and April 2023. Age, sex, body mass index, underlying disease, location and size of stones, previous history of stones, previous history of urinary tract infections, duration of surgery, preoperative drainage, application of ureteral balloon dilation, and laboratory test results were included in the analysis.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 58.4 (±15.0) years; there were more men (53.1%) than women (46.9%). Of the 243 patients, the overall rate of sepsis was 5.8% (n=14) and the total mortality rate was 0.4% (n=1). In univariate analysis, history of urinary tract infection (p=0.019), positive preoperative urine culture test (p=0.009), operative duration of more than 90 min (p=0.004), and application of ureter balloon dilation (p=0.016) were statistically significant. In multivariate analysis, positive finding in the urine culture test performed before surgery (p=0.003), operation duration >90 min (p=0.005), and use of balloon dilation during surgery (p=0.011) were statistically significant.
Conclusions: There is a risk of progression to postoperative sepsis if bacteria are detected in the urine culture before surgery, if the operative time exceeds 90 min, or if balloon dilation is performed during surgery. Given that the probability of progression to sepsis is approximately 6%, close observation and active treatment are needed for patients with these risk factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Establishing an AI-based artifact correction system for intrarenal pressure monitoring using the LithoVue™ Elite ureteroscope: an EAU endourology and AUSET collaboration
Takahiro Yanase, Shuzo Hamamoto, Rei Unno, Steffi Kar Kei Yuen, Vineet Gauhar, Bhaskar K. Somani, Olivier Traxer, Yuya Sasaki, Ryosuke Chaya, Atsushi Okada, Kazumi Taguchi, Takahiro Yasui
World Journal of Urology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of postoperative infection factors of retrograde intrarenal surgery combined with negative pressure equipment for renal stones
Deheng Cui, Qinghong Ma, Qiuyan Zhang, Lian Zhang, Guoqiang Chen
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Establishing an AI-based artifact correction system for intrarenal pressure monitoring using the LithoVue™ Elite ureteroscope: an EAU endourology and AUSET collaboration
- 4,957 View
- 89 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Trends in Age-Specific Prevalence of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Young Hwan Kim, Se Hwa Hong, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Tae Hyoung Kim, Sae Chul Kim, Sang Baek Koh, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):101-106. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: To elucidate the longitudinal changes in the prevalence of lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) according to age over the past 10 years.
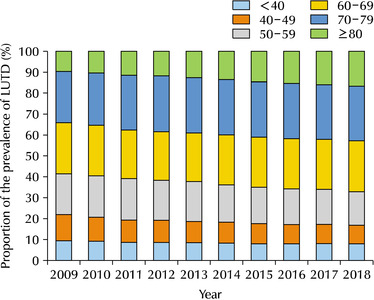
Materials and Methods: The changes in the proportion of prevalence for LUTD, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and urinary incontinence (UI) among South Koreans from 2009 to 2018, were analyzed using the National Health Information Database established by the Korean National Health Insurance Service. All conditions were defined according to the corresponding Korean Standard Classification of Diseases-8 for diagnosis and surgical procedures and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service codes for drugs.
Results: The 60-69, 70-79, and over 80 age groups accounted for more than 60% of the LUTD cases from 2009 to 2018, while significant increases in the crude prevalence of LUTD were observed over a 10-year period in all age groups (p for trend <0.05). In age groups over 60 years, LUTD was more prevalent in men than women, but there was no statistically significant difference in proportion (p>0.05). The changes in the prevalence and prevalence proportion exhibited similar trends in BPH, UI, and LUTD.
Conclusions: LUTD was more prevalent in the elderly aged over 60 years old than in younger adults. Therefore, this study suggests the development of nationwide healthcare policies to manage LUTD in the elderly population of South Korea, which is expected to become the world’s most aged population.
- 4,433 View
- 20 Download

Case Reports
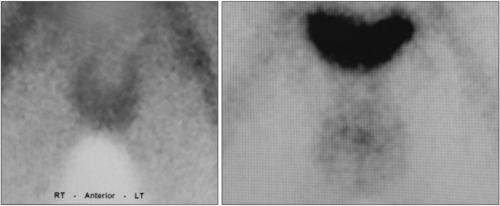
- A Case Report of Self-Inflicted Surgical Castration
- Koo Han Yoo, Sung-Goo Chang
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):107-109. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.107
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Religious beliefs are a very significant part of one’s life. We report the case of a strongly religious man who sought to remove his testicles. After enlisting in the military, the man had a surgical castration performed on him while on vacation from military service. The procedure aimed to rid the man of his libido, which he saw as a hindrance to his religious life. After the removal of the testes, his serum testosterone was 0.25 ng/ml. The luteinizing hormone, 22.1 (1.7-8.6 mIU/ml), and follicle stimulating hormone, 53.5 (1.5-12.4 mIU/ml) were elevated. Testicular scans showed an absence of both testes. This appears to be an unfortunate situation caused by false religious beliefs and the reckless use of internet resources.
- 7,384 View
- 24 Download

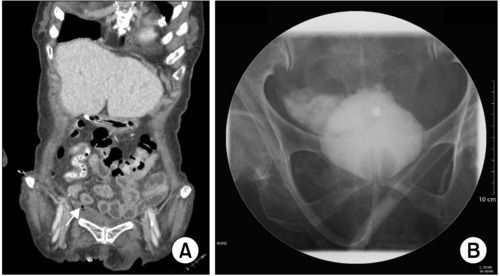
- Spontaneous Bladder Perforation in a Patient with a Long-Term Intraurethral Catheter
- Taegi Choi, Hyunkyung Lee, Junseok Kim, Sunghoon Lee, Younkyung Cho, Eunyoung Kang, Jinsun Kang, Sumin Lee, Eunju Na
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):110-113. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Urinary catheters are commonly used to address various urinary problems. However, the catheter itself can be a cause of several complications, including catheter-associated urinary tract infections, damage to the bladder and kidneys, and, in extremely rare cases, bladder perforation. We present a case of spontaneous bladder perforation in a patient who had a long-term indwelling intraurethral catheter. The patient with prior hypoxic brain damage suddenly developed tachypnea, tachycardia, and oxygen desaturation. Computed tomography and retrograde cystography revealed an extraperitoneal bladder perforation with an intra-pelvic abscess. Antibiotics were prescribed and a urinary catheter was inserted for drainage. After 11 weeks, the abscess resolved, and the catheter was removed to enable self-voiding. The perforation was attributed to chronic inflammation and distension of the bladder wall caused by the intraurethral catheter. Given the potential complications associated with long-term urinary catheterization, the timely removal of indwelling catheters should be considered.
- 4,550 View
- 18 Download

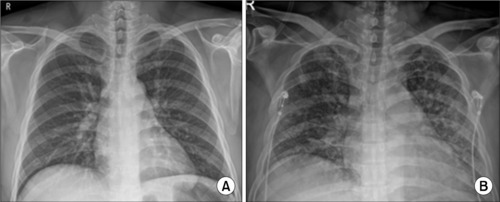
- Case of Life-Threatening Pneumonia during the Treatment of a Patient with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
- Kyung Kgi Park, Sung Dae Kim, Young-Joo Kim, Jung-Sik Huh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):114-118. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Acute bacterial prostatitis is an acute urinary tract infection associated with a bladder outlet obstruction or an immunosuppressed state. A 51-year-old man patient visited the hospital with fever, chills, and acute urinary retention that started the day before his visit after consuming a significant amount of alcohol. Conservative treatments, including catheterization for urinary drainage and antibiotics, were performed. On the third day of treatment for acute prostatitis, he complained of dyspnea. The level of oxygen differentiation was reduced significantly, and the tracheal insertion and ventilator were maintained after the radiological examination. The ventilator was discontinued, and the prostate abscess was operated on the eighth day of hospitalization. He was discharged without complications. This paper reports a case of life-threatening pneumonia and a prostate abscess during the treatment of a patient with acute bacterial prostatitis with a review of the relevant literature.
- 2,894 View
- 8 Download

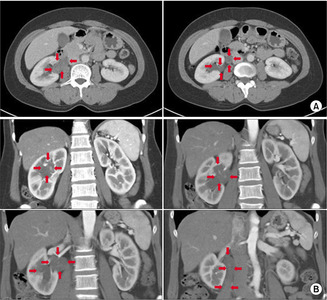
- Giant Fibroepithelial Polyp in the Renal Pelvis to the Upper Ureter
- Kyung Jin Chung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):119-122. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Benign ureteral tumors are rare owing to the predominance of malignancies in ureter tumors. Among them, fibroepithelial polyps are very rare, and giant fibroepithelial polyps are even rarer. This paper reports the author’s experience of giant fibroepithelial polyps detected incidentally. A 47-year-old woman was referred for severe right flank pain to the author’s center. A kidney computed tomogram revealed a long soft tissue lesion in the right kidney, upper polar calyx, pelvis, and whole proximal ureter with hydronephrosis. The radiologic reading was right renal pelvis urothelial cancer. Endoscopic removal was deemed impossible because the mass was filling the entire renal pelvis and upper ureter, so a nephroureterectomy was performed. After the nephroureterectomy, the pathology findings revealed a giant fibroepithelial polyp. This paper reports the treatment of giant fibroepithelial polyps of the ureter. Clinicians should consider the possibility of benign tumors and recommend a cautious approach to treatment if discovered.
- 2,683 View
- 17 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII



 First
First Prev
Prev


