Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Original Articles
- Trend Analysis of Sexually Transmitted Infection Treatments in Korea
- Soeon Park, Byung Kyu Han, Sangrak Bae, Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):25-30. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: The revision of the 2023 Guidelines for the Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) has been released. Hence, it is necessary to analyze the current status of STI treatments in Korea.
Materials and Methods: A questionnaire was distributed to urologists and gynecologists from December 2022 to January 2023 through an online survey program. Three hundred and forty-one urologists and 302 gynecologists responded to the questionnaire.
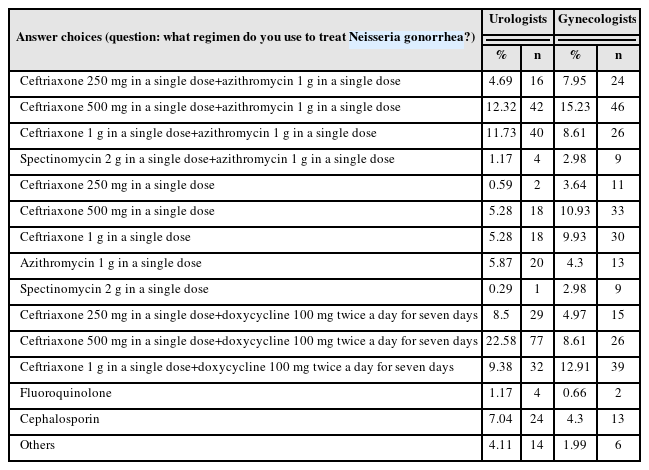
Results: For Neisseria gonorrhea treatment, ceftriaxone 500 mg and 100 mg of doxycycline twice daily for seven days were most preferred by urologists (22.58%). The treatment most preferred by gynecologists (15.23%) was 500 mg of ceftriaxone and 1 g of azithromycin in a single dose. Both urologists and gynecologists generally treat Chlamydia trachomatis according to the treatment guidelines. For treating Mycoplasma genitalium, 29.03% of urologists preferred administering azithro-mycin at 500 mg once daily, followed by 250 mg for four days. In contrast, 33.11% of gynecologists preferred doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for seven days.
Conclusions: Most urologists and gynecologists followed the treatments recommended in the 2nd edition of the STI treatment guidelines, revised in 2016. As many treatment regimens have changed because of the recent increase in antibiotic-resistant STIs, there is a need to encourage them to follow the new treatment guidelines. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Study of the Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Sexually Transmitted Infections Diagnosed by Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests
Jung Soo Son, Namhee Kim, Hong Sang Oh, Sang Won Park, Dong Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparative Study of the Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Sexually Transmitted Infections Diagnosed by Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests
- 6,763 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Residual Stone Fragments on Patient-Reported Quality of Life after Endoscopic Kidney Stone Surgery
- Sang Hee Lee, Jun-Koo Kang, Jae-Wook Chung, Yun-Sok Ha, Jun Nyung Lee, Seock Hwan Choi, Hyun Tae Kim, Tae-Hwan Kim, Eun Sang Yoo, Tae Gyun Kwon, Bum Soo Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):31-39. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study examined the effects of residual fragments (RF) on the patient-reported quality of life (QOL) after kidney stone surgery, such as retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) and percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), using the Korean version of the Wisconsin Stone Quality of Life Questionnaire (K-WISQOL).
Materials and Methods: The medical records of 156 patients who underwent RIRS or PCNL and completed the preoperative and postoperative K-WISQOL from January 2021 to September 2023 were analyzed retrospectively. The patients were divided into RIRS and PCNL groups by the surgical method. The participants completed the K-WISQOL within four weeks before and after treatment. The patients’ baseline characteristics, surgical outcomes, and K-WISQOL scores were compared according to the presence of RF in each surgical group.
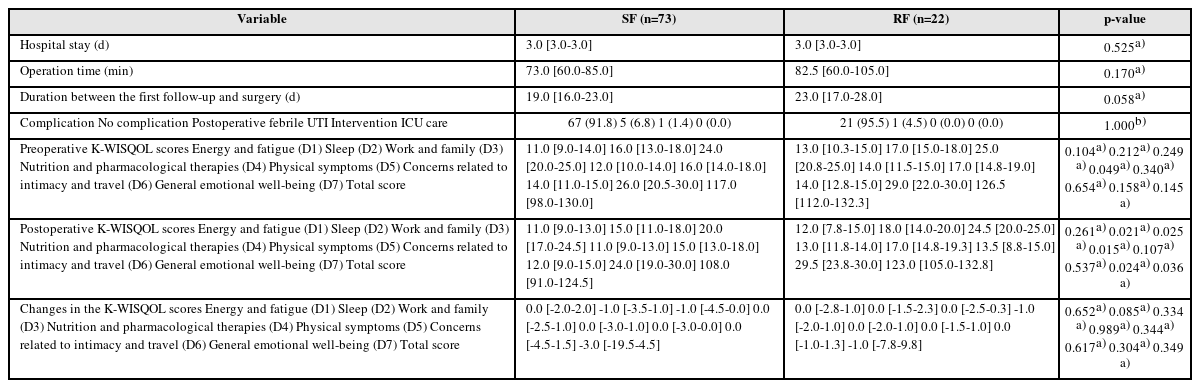
Results: Of the 156 patients, 95 underwent RIRS, and 61 underwent PCNL. In the RIRS group, the patients’ baseline characteristics and surgical outcomes were similar in the stone-free (SF) and RF subgroups. The changes in all K-WISQOL domain scores and total scores were similar in the two subgroups. In the PCNL group, the RF subgroup had a significantly higher proportion of staghorn stones, a significantly larger mean stone diameter and significantly longer operation time than those of the SF subgroup. But, the changes in all K-WISQOL domain scores and total scores were not significantly different between the two subgroups, as observed in the RIRS group.
Conclusions: This study showed that the presence of RFs after endoscopic kidney surgery did not affect the short-term patient-reported QOL regardless of the surgical methods.
- 3,565 View
- 39 Download

Case Reports
- Robotic Excision of a Huge Seminal Vesicle Cyst, Including Intracystic Papillary Adenoma, Saving Fertility
- Tae Hoon Oh, Ill Young Seo
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):40-43. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
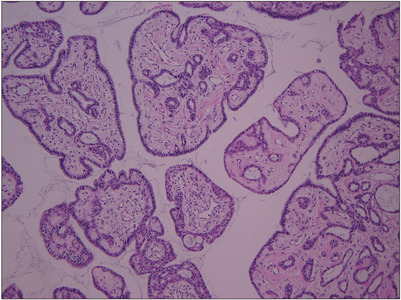
ePub - A seminal vesicle cyst is a rare disease, and an intracystic papillary adenoma within the seminal vesicle is extremely rare. The diagnosis and treatment of these diseases are challenging because of the limited data. This paper presents a robotic excision of a huge seminal vesicle cyst, including an intracystic papillary adenoma, preserving fertility in a 40-year-old man.
- 2,790 View
- 14 Download

- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: Case Report
- Kwang Jin Kim, Yoonsuk Lee, Yong Sung Cha, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Hong Chung, Hyun Kim, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):44-47. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) was conducted on two male patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome who were resistant to conventional medical therapies. Both patients underwent 20 sessions of 100% oxygen inhalation (2.0 atmosphere absolute for 90 min/day, five days/week for four weeks) in a hyperbaric chamber. The follow-up period was three months. Although the patients reported a slight improvement in the pain domain of the National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) after HBOT, no changes were noted in the other domains of NIH-CPSI and International Prostate Symptom Score. No adverse events were encountered during or after HBOT.
- 5,282 View
- 35 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII



 First
First Prev
Prev


