-
Pelvic Pain in Men with Mycoplasma Genitalium
-
Yumi Seo
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(1):16-23. Published online April 30, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.1.16
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: There are debates about Mycoplasma genitalium (M. genitalium) causing prostate infection and inducing pelvic pains. Consequently, M. genitalium-associated pelvic pains were characterized and their manifestation in male pelvic pain syndrome (MPPS) was evaluated through a case-control study.
Materials and Methods: The presence of M. genitalium-associated pelvic pains was examined in 113 M. genitalium-infected men, and the typical presentations of mycoplasma-associated MPPS were characterized through a case-control study involving 80 mycoplasma-infected and 234 case-matched uninfected controls. Finally, changes in symptoms following antimicrobial treatments were compared between 27 cured and 14 persistently infected cases.
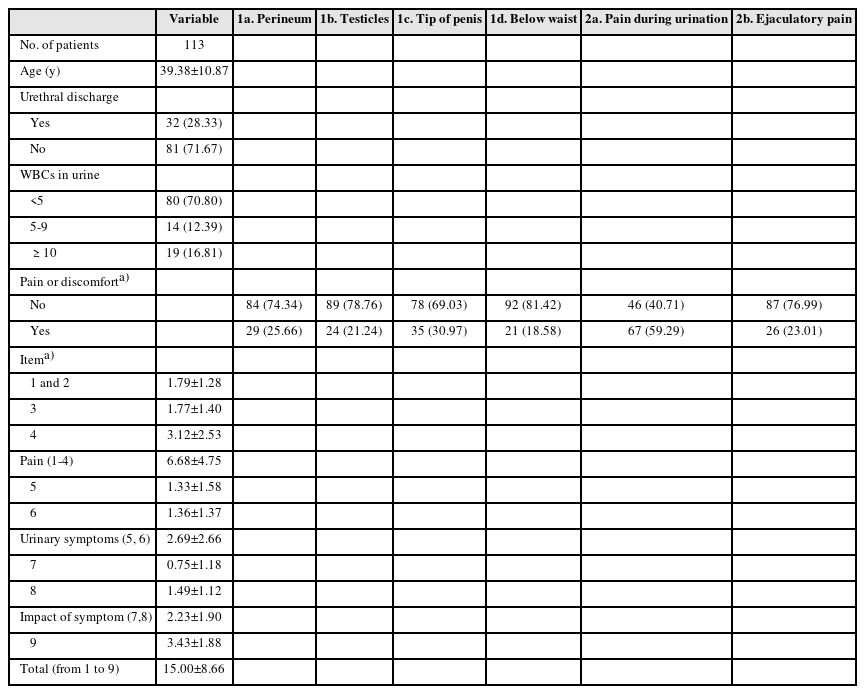
Results: Pain locations from 113 men were followed as items-1a for 25.7%, 1b for 21.2%, 1c for 31%, 1d for 18.6%, 2a for 59.3%, and 2b for 23% from the Korean National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) questionnaire. In addition, the sum scores from the pain domain, voiding domain and total score were 6.68±4.75, 2.69±2.66, and 15.00±8.66, respectively. Successful antibiotic therapy significantly reduced the total score from baseline (15.148±6.798 vs. 5.357±7.025, p=0.001). From the case-control study, mycoplasma-infected men had pains more frequently during urination (1c) and on the tip of the penis (2a) (all p=0.0001) than the controls.
Conclusions: It was found that M. genitalium infection is associated with clinically significant male pelvic pains, which improved with adequate antimicrobial therapies. Urethral irritation symptoms without pyuria may be the typical characteristics of mycoplasma-associated pelvic pains in MPPS.
-
Syphilis Notification Systems in Korea over the Last 20 Years
-
Yumi Seo, Gilho Lee
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2021;16(1):16-23. Published online April 30, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2021.16.1.16
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: The syphilis notification system has been revised three times in Korea during the last 20 years. Accordingly, we evaluated the performance of the three systems by analyzing data from the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA).
Materials and Methods: We analyzed trends of stage 1, 2, and congenital syphilis cases reported in the KDCA from 2001 to 2010 in the 1st sentinel (S1), from 2011 to 2019 in the 1st universal (U1), and 2020 in the 2nd sentinel (S2) notification system.
Results: A total of 21,820 syphilis cases were reported, 9,177 cases in S1, 12,321 in U1, and 322 in S2, respectively. The reported cases can be presented in the form of four expanding waves across the time period. Although the most commonly reported age group with infection was 20-29 years in all three reporting systems, the pattern of infections was different; the number of older patients was relatively high in the S1 group while the number of syphilis cases declined sharply in the older than 20-29 old age group in the U1 and S2 systems. Also, there was a sex-based difference in the three groups; the data from S1 were female-dominant but the data in U1 and S2 were male-dominant.
Conclusions: Our results showed that the universal notification system (U1) is superior in both the quantity and quality of data to the previous sentinel system (S1). The results from the new system, S2, are similar to those from U1.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Expert Consensus Study on the Redesign of the Sexually Transmitted Infection Surveillance System in Korea
Jin Bong Choi, Dong-Sook Kim, Chae Eun Shin, Su-Yeon Yu, Kyu Won Lee, Seung-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Narrative Review of Syphilis Notification Systems in Korea: Change to Mandatory Surveillance System
Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Recent Changes in Sexually Transmitted Infection in Korea: A Population-Based Analysis
Jae Yen Song, Kang Seob Kim, Chang Hee Han, Sangrak Bae
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(14): 5145. CrossRef - Rectal Syphilis Mimicking Malignancy: A Case Report
Sunjin Ryu, Bo-Kyeong Kang, Mimi Kim, Chul-Min Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2024; 85(3): 637. CrossRef - Temporal Trends in Syphilis Incidence among Men with HIV in Busan, Korea, 2005–2022: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Sun Hee Lee, Jeong Eun Lee, Soon Ok Lee, Shinwon Lee, Woo Seog Ko, Hyung-Hoi Kim, Kyung-Hwa Shin, Jin Suk Kang, Hyunjin Son
Viruses.2024; 16(2): 265. CrossRef
-
2,755
View
-
10
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Synchronous Verrucous Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Penis by Different Human Papillomavirus Infections
-
Yumi Seo, Gil Ho Lee
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2013;8(1):52-54. Published online April 30, 2013
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Synchronous verrucous carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the penis is a rare condition. We report on a case of penile carcinoma with a well demarcated and ulcerated endophytic squamous carcinoma lesion by human papillomavirus 16 and 61 types, and a whitish exophytic verrucous carcinoma lesion by an unknown lower risk human papillomavirus type.
|