-
Trends in Age-Specific Prevalence of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
-
Young Hwan Kim, Se Hwa Hong, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Tae Hyoung Kim, Sae Chul Kim, Sang Baek Koh, Jae Hung Jung
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):101-106. Published online December 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.101
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: To elucidate the longitudinal changes in the prevalence of lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) according to age over the past 10 years.
Materials and Methods: The changes in the proportion of prevalence for LUTD, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and urinary incontinence (UI) among South Koreans from 2009 to 2018, were analyzed using the National Health Information Database established by the Korean National Health Insurance Service. All conditions were defined according to the corresponding Korean Standard Classification of Diseases-8 for diagnosis and surgical procedures and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service codes for drugs.
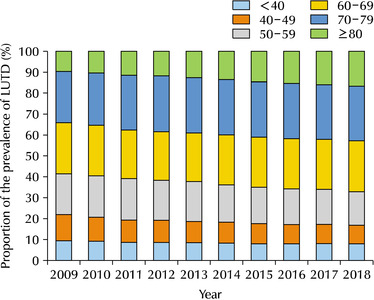
Results: The 60-69, 70-79, and over 80 age groups accounted for more than 60% of the LUTD cases from 2009 to 2018, while significant increases in the crude prevalence of LUTD were observed over a 10-year period in all age groups (p for trend <0.05). In age groups over 60 years, LUTD was more prevalent in men than women, but there was no statistically significant difference in proportion (p>0.05). The changes in the prevalence and prevalence proportion exhibited similar trends in BPH, UI, and LUTD.
Conclusions: LUTD was more prevalent in the elderly aged over 60 years old than in younger adults. Therefore, this study suggests the development of nationwide healthcare policies to manage LUTD in the elderly population of South Korea, which is expected to become the world’s most aged population.
-
Evaluationof Multiplex PCR for the Detection of Sexually Transmitted Pathogens using Clinical Specimens
-
Tae Hyoung Kim, Mi Kyung Lee
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2012;7(2):129-135. Published online October 31, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
Multiplex PCR can allow multiple pathogens to be detected in the same reaction tube, saving time and reagents. The aim of this study was to evaluate the multiplex PCR kit (Seegene, Korea) for detection of fastidious microorganisms such as six sexually transmitted pathogens.
Materials and Methods: Using clinical specimens, multiplex PCR and single PCR were used to test for Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma hominis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas vaginalis and Ureaplasma urealyticum.
Results: Multiplex PCR had an overall sensitivity of 97.2% and specificity of 100% compared to the single PCR. The limits of detection for the multiplex PCR and single PCR were from 3.03×10-6 to 7.06×10-7 μg/mL and from 3.03×10-6 to 3.03×10-31 μg/mL, respectively.
Conclusions: The multiplex PCR kit has considerable potential to use as a routine method in clinical laboratories. Before introducing the new multiplex PCR method in the laboratory, thorough evaluation and validation of multiplex PCR is essential. To achieve reliable results from multiplex PCR, feasible guidelines, standardization and quality control are of major importance. (Korean J UTII 2012;7:129-135)
-
Selection of Antibiotics According to the Costs and Efficacy of Empirical Antibiotics Therapy for Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Producing Uropathogens from Urine Culture Test in Patients with Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis
-
Se Jun Park, Jae Hyung Ryu, Sang Ho Park, Jung Won Choe, Sang Hyup Lee, Jung Hoon Kim, Kyung Do Kim, Tae Hyoung Kim, Mi-Kyung Lee
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2012;7(1):29-35. Published online April 30, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- "Purpose: The usage of antibiotics on urinary tract infection is high, thus, there is a high chance of acquiring resistance towards antibiotics. Followed by the usage of restricted antibiotics, the emergence of multiple drug resistant pathogens, such as ESBL producing pathogens, is frequently being reported, and the increase of resistant pathogens leads to the increase of medical treatment costs. An effective system of management and observation is needed for this. ESBL is an enzyme produced by gram-negative bacterium, which has beta-lactam rings, that restricts the effectiveness of penicillins and cephalosporins. Such antibiotics have been used as empirical antibiotics for acute cystitis. The effects of ESBL producing pathogens in patients on the curative effectiveness of empirical antibiotics are to be identified and appropriate antibiotics will be selected, according to the results with consideration to the cost. Materials and Methods: From the 4727 patients who have been diagnosed with cystitis between January 2000 and 2011 March, through urine culture test, 81 acute uncomplicated cystitis patients with ESBL producing pathogens were confirmed and their medical records were examined for this study. For 3~7 days empirical antibiotics, such as quinolone (ciprofloxacin / levofloxacin), cephalosporin (1st generation- cefroxadine / 2nd generation- cefprozil / 3rd generation- cefpodoxim, cefdinir), penicillin (amoxicillin-clavulanic acid), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, were used and the curative effects were confirmed through urine culture test, with the improvements on the initial symptoms. For each antibiotic, the average medical insurance cost of domestic market as of May 2011 was applied and calculation was done after averaging for 3 days. Results: In urinalysis of 81 patients (age 44.89±17.42, 17~64), pyuria was confirmed in the urine of 79 patients (97.5%) and microscopic hematuria was confirmed in the urine of 17 patients (21.0%). In urine culture test, Escherichia coli was cultured in the urine of 79 patients (97.5%) and Klebsillea pneumonia was cultured in the urine of 2 patients (2.5%). Thirty three patients (40.7%) complained of suprapubic pain, 55 patients (67.9%) of urodynia, 69 patients (85.2%) of frequent urination and 37 patients (45.7%) of urgent urination. After taking antibiotics, not including 6 patients who have not returned, there were improvements in urine culture test and symptoms in all patients. In the reexamination of urine culture test, no significant pathogens were found. According to the cost, the cost was the cheapest in the order of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (160/800mg, twice a day, 3 day therapy, 378 won), amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (250/125mg, three times a day, 3 day therapy, 3019.5 won), and ciprofloxacin (250mg, once a day, 3 day therapy, 3563.4 won). Conclusions: Even if ESBL producing pathogens were found in urine culture test of acute uncomplicated cystitis patient, curative effectiveness can be expected by just taking empirical antibiotic. In concerning the objective of this study as well as the efficacy and the cost, the most appropriate primary antibiotic is trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. The acute uncomplicated cystitis caused by ESBL producing pathogen has the same curative effects of antibiotics of the study, having no relations with the antibiotic sensitiveness. Therefore, the empirical antibiotic with no abnormal reactions, cheap cost and short duration of treatment should be selected for the therapy."
-
Clinical Outcome of Acute Bacterial Prostatitis; A Multicenter Study
-
Seong Ju Lee, Jin Mo Koo, Bong Suk Shim, Yong Hyun Cho, Chang Hee Han, Seung Ki Min, Sung Joo Lee, Hwan Cheol Son, Jun Mo Kim, Jong Bo Choi, Tae Hyoung Kim, Sang Kuk Yang, Kil Ho Lee, Yong Kil Na, Sung Ho Lee, Hee Jong Jung, Seung Il Jung, Chul Sung Kim, Jae Min Chung, Young Jin Seo, Won Yeol Cho, Kweon Sik Min, Sang Don Lee
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2011;6(2):165-170. Published online October 31, 2011
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- "Purpose: Proper guidelines concerning antibiotic administration for acute bacterial prostatitis (ABP) are unclear. We retrospectively analyzed treatment status and clinical outcomes to establish a proper treatment guideline. Materials and Methods: The clinical records of 669 patients from 21 hospitals diagnosed with ABP were reviewed. Prior manipulation, antibiotics administration, mean length of treatment, complication and procedure were analyzed. Results: The mean age of 538 patients (80.4%) without manipulation (group 1) and 131 patients (19.6%) with manipulation (group 2) was 58.3 years (range 19-88 years). Transrectal prostate biopsy was the most common cause of acute bacterial prostatitis (n=66; 50.4%). Of the clinical symptoms in the non-manipulation and manipulation groups, fever was most common (88.2% and 86.3%, respectively). Acute urinary retention (14.3% and 28.1%, respectively) was significantly increased in the manipulation group (p<0.05). Escherichia coli was the most frequently isolated bacterium from urine (72.0% and 66.7% of cases, respectively). Mean length of treatment was 6.5days and 7.9days, respectively; the difference was significant (p<0.05). Combination antibiotic therapy with third generation cephalosporin+aminoglycoside was used in 49.3% and 55.5% of cases, respectively. For single antibiotic therapy, second generation quinolones were used the most (35.5% and 34.3%, respectively). Sequale occurred in 29 group 1 patients (5.4%) and 20 group 2 patients (15.3%); the difference was significant (p<0.05). Conclusions: Prior manipulation was associated with 20% of ABP patients. Regardless of manipulation, clinical outcome was similar after treating with appropriate antibiotics."
|