-
Risk Factors for Sepsis after Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery: Single Center Experience
-
Jinseok Kang, Koo Han Yoo, Taesoo Choi, Gyeong Eun Min, Dong-Gi Lee, Hyung-Lae Lee, Jeonghyouk Choi
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):93-100. Published online December 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.93
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose: To evaluate risk factors for sepsis after retrograde intrarenal surgery for treatment of renal stones.
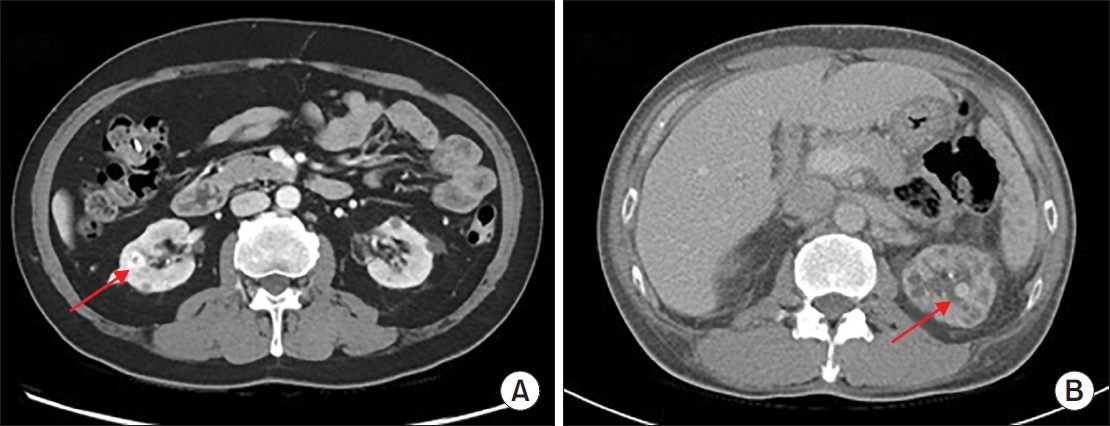
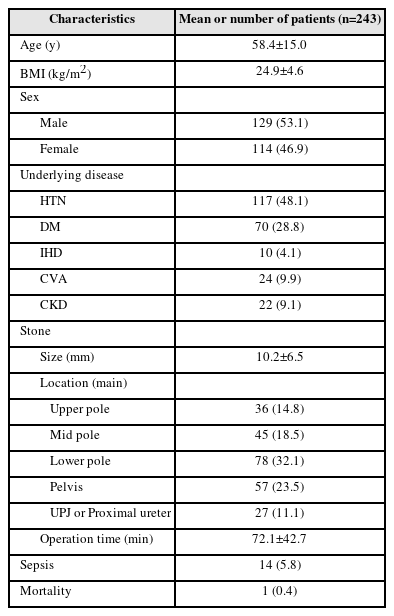
Materials and Methods: We analyzed the clinical data of 243 patients with kidney stones who visited our institution between April 2017 and April 2023. Age, sex, body mass index, underlying disease, location and size of stones, previous history of stones, previous history of urinary tract infections, duration of surgery, preoperative drainage, application of ureteral balloon dilation, and laboratory test results were included in the analysis.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 58.4 (±15.0) years; there were more men (53.1%) than women (46.9%). Of the 243 patients, the overall rate of sepsis was 5.8% (n=14) and the total mortality rate was 0.4% (n=1). In univariate analysis, history of urinary tract infection (p=0.019), positive preoperative urine culture test (p=0.009), operative duration of more than 90 min (p=0.004), and application of ureter balloon dilation (p=0.016) were statistically significant. In multivariate analysis, positive finding in the urine culture test performed before surgery (p=0.003), operation duration >90 min (p=0.005), and use of balloon dilation during surgery (p=0.011) were statistically significant.
Conclusions: There is a risk of progression to postoperative sepsis if bacteria are detected in the urine culture before surgery, if the operative time exceeds 90 min, or if balloon dilation is performed during surgery. Given that the probability of progression to sepsis is approximately 6%, close observation and active treatment are needed for patients with these risk factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Establishing an AI-based artifact correction system for intrarenal pressure monitoring using the LithoVue™ Elite ureteroscope: an EAU endourology and AUSET collaboration
Takahiro Yanase, Shuzo Hamamoto, Rei Unno, Steffi Kar Kei Yuen, Vineet Gauhar, Bhaskar K. Somani, Olivier Traxer, Yuya Sasaki, Ryosuke Chaya, Atsushi Okada, Kazumi Taguchi, Takahiro Yasui
World Journal of Urology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of postoperative infection factors of retrograde intrarenal surgery combined with negative pressure equipment for renal stones
Deheng Cui, Qinghong Ma, Qiuyan Zhang, Lian Zhang, Guoqiang Chen
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
-
5,113
View
-
90
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Is Double J Stenting or Percutaneous Nephrostomy More Suitable for Maximizing the Clinical Effects of Temporary Urinary Diversion for Acute Pyelonephritis with a Complicated Ureteral Stone?
-
Jeonghyouk Choi, Taesoo Choi, Dong-Gi Lee, Gyeong Eun Min, Hyung Lae Lee, Koo Han Yoo
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2019;14(3):87-92. Published online December 31, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2019.14.3.87
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose: This study compared the clinical benefits of double J (DJ) ureteral stenting with percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) for the management of acute pyelonephritis (APN) with complicated ureteral stones.
Materials and Methods: The records of 85 patients with complicated APN between December 2006 and July 2017 were reviewed retrospectively. Sixty one patients who underwent DJ or PCN for the management of acute urinary obstruction were enrolled in this study. Some of the participants were excluded for concurrent renal stones, multiple ureteral stones, ureteral stricture, malignancy, and anatomical anomalies. The patient and stone characteristics and peri-procedural laboratory test results of the groups were compared. The success rate, depending on the type of urinary diversion and the presence of immediate complications, were also analyzed.
Results: In this study, 19 patients underwent DJ stenting, and 42 patients underwent PCN as a transient urinary diversion. No failed procedures or immediate complications requiring subsequent intervention were encountered (Clavien–Dindo grade II-V). Urologists preferred PCN to DJ stenting in cases with an elevated serum creatinine level (p=0.001) and higher C-reactive protein (CRP) level (p<0.001). The indicative parameters for renal injury and septic conditions (white blood cell count, segment neutrophil, and creatinine levels) tended to show immediate improvement, whereas CRP did not; however, the differences in markers were not significant (p=0.701, 0.962, 0.288, and 0.360, respectively).
Conclusions: Both DJ stenting and PCN were safe and feasible methods for the management of complicated APN. With experienced urologists or radiologists, there may be little danger of prolonged renal failure or other procedure-related complications.
|